* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WWII - West Ada
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Nazi views on Catholicism wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II and American animation wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Invasion of Normandy wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
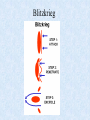
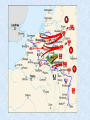
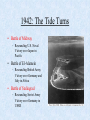
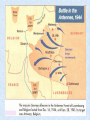
WWII Introduction: • Most devastating war in human history • 55 million dead • 1 trillion dollars • Began in 1939 as strictly a European Conflict • Widened to include most of the world Causes • Great Depression Rise of Fascist dictators • WWI and Treaty of Versailles Germany had to pay reparations and “war guilt” clause. Italy denied territories it wanted • Failure of League of Nations • Policy of Appeasement • World Domination-Extreme Nationalism • Japan victorious but wanted China • Germany wanted to created a “Third Reich” an empire to last 1,000 years Rise of Hitler • Nazi Party organized, 1920s • Nazi party largest in Germany, 1932 • Hitler voted as chancellor, 1933 • New parliament created • 450, 000 members • Larger than German army German Territorial Gains • Austria – March, 1938 • Munich Pact gives part of Czechoslovakia (Sudetenland) – Sept., 1938 • All of Czechoslovakia – March, 1939 • Poland – Sept., 1939 • By Summer of 1940, Germany Controlled Most of Europe • World shocked as France falls to Germans Significant Events of World War II Dates and Events that changed the world Major Leaders Axis Powers Adolf Hitler Nazi Germany Hideki Tojo Japan Benito Mussolini Italy Emperor Hirohito Japan 8 Major Leaders Allies Joseph Stalin Soviet Leader Winston Churchill British Prime Minister Franklin Delano Roosevelt US President 10 Major Leaders 11 Harry S. Truman US President September 1, 1939 • Germany invades Poland using the Blitzkrieg (“lightning war”) • England and France, declare war on Germany • United States again chooses isolationism and neutrality Blitzkrieg Fall of France 1940 May 10, 1940 • Fall of France • France surrenders June 25 • Total Victory for Germany except for: • “Miracle at Dunkirk” – Germany does not attack with army – Allows most of the British forces to escape and fight again another day July 1940 • The Battle of Britain • 3 month air war between Luftwaffe and RAF • Germany suffers a major defeat Reason’s for British victory: •RADAR •Over home soil •More gas/time to fight •Easier to save pilots •Germans change tactics •Attack English cities •Stop attacks on English air force December 7, 1941 “… a date which will live in infamy.” • Japan sneak attacks Pearl Harbor on Sunday morning • 18 ships sunk or badly damaged • 188 planes destroyed and 159 damaged • 2403 U.S. Military killed (1102 Arizona) & 1178 wounded • America enters war with Allies Damages Pearl Harbor Dec. 7, 1941 USS Arizona Allies United: U.S.S.R, The U.S., and England. 1942: The Tide Turns • Battle of Midway – Resounding U.S. Naval Victory over Japan in Pacific • Battle of El-Alamein – Resounding British Army Victory over Germany and Italy in Africa • Battle of Stalingrad – Resounding Soviet Army Victory over Germany in USSR September 1943 • Italy signs armistice with Allies (1st Axis country to leave war) • Germans disarm their allies and take over military defenses • Germany continues to fight in Italy until 1945 June 6, 1944 • D-Day of Operation Overlord • Led by Supreme Allied Commander Dwight D. Eisenhower • Nearly 250,000 men and boys participated in the invasion of Normandy region of France • The battle for the beachhead lasted nearly 2 months • This was the beginning of the end for Hitler and Germany Normandy Invasion, D-Day D-Day Landing on Normandy Beach December 1944 – January 1945 • Germany last desperate attack to win the war • The Battle of the Bulge • Hitler’s army had broken through the allied line creating a bulge. • U.S. and allied troops had pushed back the bulge by mid January. Spring 1945 • April 12 FDR dies in office • April 30th – Hitler commits suicide • May 7th – Germany formally surrenders • Gen. Eisenhower: “The mission of this allied force was fulfilled at 0241 local time, May 7th 1945.” • May 8th – V-E (Victory in Europe) Day declared August 1945 • America’s secret development of the A-Bomb = “Manhattan Project” • President Harry S. Truman and U.S. drop 1st atomic bomb on Hiroshima killing 80,000 people (“Little Boy”) August 1945 • August 9th U.S. drops 2nd atomic bomb of Nagasaki killing 70,000 people (“Fat Man”) August 1945 August 15th Japan surrenders on battleship U.S.S. Missouri V-J Day (Victory over Japan) Declared Results of World War II • America gets out of the Great Depression • Introduction of weapons of mass destruction (nuclear weapons) • Start of Cold War • United Nations formed (new and improved League of Nations) • Israel established as country for all Jews Related Websites • World War II Timeline http://history.acusd.edu/gen/ww2Timeline/s tart.html • National World War II Memorial http://www.wwiimemorial.com/ • National D-Day Museum http://www.ddaymuseum.org/ Hitler Gets Busy • • • • • Gestapo Created -- April, 1933 Jewish Boycott – April, 1933 Jewish Books Banned & Burned – May, 1933 27,000 People in Camps – July, 1933 Kristallnacht (“Night of the Broken Glass”) – November 1938 • Illegal to Leave Germany – October, 1941 • French and Britain unsure • U.S. isolationist February, March, & April 1942 • February 19th – Executive Order 9066 Internment of 110,000 Japanese Americans in 48 states (California) • April 18th – Doolittle Raid 16 B-25 bombers from the USS Hornet fly 666 miles to bomb Tokyo. • April – Bataan Death March 5000-10,000 Filipinos & 500-600 U.S. Dead 5000 U.S. died in Camps. Japan never ratified 1929 Geneva Agreement