* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Light Bulbs
Survey
Document related concepts
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Heat transfer physics wikipedia , lookup
Thermophotovoltaic wikipedia , lookup
Ultrafast laser spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
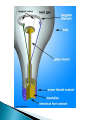
Mr. Fleming D. 5 Explain how electricity is used to produce heat and light in incandescent bulbs and heating elements. Light= Excitation of Electrons Ground State Excited State Ground State Light= Excitation of Electrons ◦ Light Bulbs in Microwave ◦ Atoms in Tungsten filament are excited by electricity Abnormally high melting point ◦ Measure of power in light bulb is Watt ◦ Most energy given off as heat Only 10% goes to light Contains argon and mercury instead of tungsten. Electricity excites gas molecules in light bulb Most energy is converted into visible light instead of heat. Mercury is highly toxic chemical • Ideal for replacement of incandescent lamps • Saves up to 75% on energy use • Lasts 7-10 times longer than an incandescent • Low thermal energy output ▪ Can use up to 50% less energy than a CFL. ▪ Widespread use over the next 20 years could reduce lighting energy demand by 33%. ▪ Currently more expensive to purchase compared to incandescent and CFLs. The NEED Project How LED works Present in many electronics Do not have filament Most energy efficient The NEED Project The NEED Project What is excited to produce light in a CFL? Argon & Mercury Vapor What is excited to produced light in an incandescent light bulb? Tungsten Filament What is the most energy efficient light bulb? LEDs Name one disadvantage with using this light bulb?