* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Polycystic ovarian syndrome
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
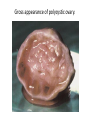
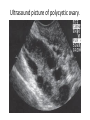
Polycystic ovarian syndrome Lec.4 Dr.Alyaa 2016/2017 Background Rotterdam criteria for diagnosing PCOS Requires the presence of two out of the following three variables and exclusion of other disorders: • Irregular or absent ovulations. • Clinical or biochemical signs of hyperandrogenism:( acne, hirsutism, alopecia.) • Polycystic ovaries on pelvic USS: ≥ 12 antral follicles on one ovary or ovarian volume >10mL. Aetiology: genetics Pathophysiology and labrotory finding: - Hyperandrogenism and anovulation in PCOS is caused by endocrine abnormality - High intraovarian androgen concentration inhibit follicular maturation. - E1 level is increased. - Elevated LH and LH:FSH ratio and elevated prolactin level in 25% of patients. - There is insulin resistance and compensatory hyperinsulinaemia as a result of PCOS and obesity. Insulin is a potent stimulus for secretion of androgen by the ovary also it suppress the synthesis of SHBG by the liver thus elevate the free androgen index. Patient are at increased risk of glucose intolerance or frank diabetes. Clinical features The clinical features of PCOS are as follows: • oligomenorrhoea/amenorrhoea in up to 75 percent • hirsutism; • subfertility in up to 75 per cent of women; • obesity in at least 40 per cent of patients; central type with higher waist to hip ratio • recurrent miscarriage in around 50–60 per cent of women; • acanthosis nigricans • may be asymptomatic. Investigations • Basal (day 2–5): LH, FSH, TFTs, prolactin, and testosterone. • If hyperandrogenisim: - dehydroepiandrosterone sulphate (DHEAS) - androstenedione - SHBG. • Exclude other causes of secondary amenorrhoea. • Pelvic USS. These investigation will show the following results: Ultrasound: increased stromal thickness and increased ovarian volume (>10 cm3)(specific for PCOS),and the presence of 12 or more follicles measured 2-9 mm in diameter. Serum endocrinology: Increase serum LH Increase serum LH : FSH ratio Increase serum androgen (testosterone and androstenedione) Decrease SHBG Increase estradiol and estrone Increase serum prolactin. Increase serum insulin level. Impaired glucose tolerance . Gross appearance of polycystic ovary. Ultrasound picture of polycystic ovary. Examination • BMI. • Signs of endocrinopathy, hirsutism, acne, alopecia, acanthosis nigricans. Long-term health consequences of PCOS • Ischaemic heart disease(7 fold increase in MI). • Type II diabetes is a known risk of obesity and insulin resistance, and pregnant women with PCOS are at increased risk of gestational diabetes, abortion & preeclampsia . • endometrial hyperplasia and, endometrial carcinoma. • There is also increased morbidity in obese PCOS who fails to reduce their weight. Management of PCOS: The options should focus on the main concern of the woman: - Lifestyle modification: - Menstrual irregularities: - Hyperandrogenism and hirsutism : - Treatment of infertility in PCOS: Lifestyle modification weight loss through exercise and diet has been proven effective in restoring ovulatory cycles and achieving pregnancy. Menstrual irregularities: • Weight loss. • COCP: low dose combined oral contraceptive preparation. Progesterone as medroxy progesterone acetate (provera) Or dydrogesterone (duphastone) for 12 days every 1-3 months to induce withdrawal bleeding. • Metformin. Hyperandrogenism and hirsutism : modified Ferriman and Gallway score may be used to evaluate the degree of hirsutism before and during treatment . 1. Physical treatment (Cosmetic) :depilatory cream, waxing & bleaching, electrolysis, shaving, plucking, Laser and photothermolysis . 2. Medical treatment: a. COCP: - First line is diane (ethinylestradiol 30 Mg with cyproterone acetate 2mg.CPA may cause liver damage, diane increase the risk of thromboembolism. - reduces serum androgen levels by increasing SHBG levels - providing a regular monthly withdrawal bleed and beneficial antiandrogenic effects. b. Antiandrogens such as eflornithine facial cream, finasteride, flutamide or spironolactone(is a weak diuretic with antiandrogenic properities can be used at a daily dose of 25-100 mg ). they: - can be used to help with acne and hirsutism - can take 6–9mths to improve hair growth - avoid pregnancy with usage of contraception (feminizes a male fetus). Hirsutism in PCOS patient After hormonal treatment Treatment of infertility in PCOS: 1. life style modification 2.Medical Induction of ovulation in PCOS patient by a. antioestrogen : - clomiphene citrate . Tamoxifene. b. gonadotrophin : c. GnRH analogues d. Metformin 3. Surgical method of ovulation induction 4. IVF 2.Medical Induction of ovulation in PCOS patient by a. antioestrogen : - clomiphene citrate . : is an orally active synthetic non steroidal compound with oestrogenic and non oestrogenic properties. It displace the oestrogen from it’s receptor at the hypo-thalamic pituitary axis reduce it’s negative feed back and encourage GnRH secretion. It’s administered at 50 mg daily dose on day 2-6 A course of 6-12 cycles can be used with monitoring by ultrasound for follicular response. Ovulation is expected in 80% and pregnancy in 40% . Adverse reaction to such treatment: -Antioestrogenic side effect including thickening of the cervical mucos and hot flushes in 10% of women. -abdominal pain ,nausea , vomiting . -headache and visual disturbance. -breast tenderness. -reversible hair loss. - ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome is rare in <1%. -Multiple pregnancy in 10%. -Ovarian cancer. Tamoxifen: has structure similar to clomiphene .the recommended dose is 2040 mg per day from day 3 for 5 days it have the same pregnancy rate as clomiphene with less potent antioestrogenic action on the cervical mucos. b. Medical induction by gonadotrophin used when the patient do not respond to clomifene or fails to conceive after 6-12 ovulatory cycles. - recombinant FSH or purified urinary hMG (FSH and LH). Gonadotrophin treatment result in cumulative Pregnancy rates of 40-50% and 1-2% rate of OHSS. c. GnRH analogues in ovulation induction : it’s used in conjunction with gonadotrophin to achieve pituitary down regulation to facilitate cycle control d. Metformin : this is an oral biguanide decrease the secretion of insulin and treat hyperinsulinaemia. decrease hyperandrogenism and abnormalities of gonadotrophin secretion and can restore menstrual cyclicity and fertility. The usual dose is 850 mg bid or 500 mg t.d.s. taken Before meal . Side effect of metformin: nausea ,vomiting , flatulance and diarrhoea . Metformin is not usually cause Lactic acidosis in non diabetic patient with PCOS with normal liver and renal Function. Regular checking of renal and liver function, metformin should discontinued for 3 days after iodine containing compound and should be discontinued during pregnancy. 3. Surgical method of ovulation induction Laparoscopic ovarian diathermy LOD: by diathermy or Laser, slim patient with high LH level. A unipolar coagulating current is used to deliver four punctures to a depth of 4 mm in each ovary . fewer multiple pregnancy rate with the cumulative pregnancy rate similar to those obtained with 3-6 cycle of gonadotrophin. LOD has replaces the wedge resection of the ovaries as it result into extensive peri-ovarian and peritubal adhesion. 4. IVF if ovulation cannot be achieved or does not succeed in pregnancy. - increased risk of (OHSS).