* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Hot Spots of the Cold War
Cuban Missile Crisis wikipedia , lookup
Cuba–Soviet Union relations wikipedia , lookup
1960 U-2 incident wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Berlin Blockade wikipedia , lookup
Containment wikipedia , lookup
Allied-occupied Germany wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Operation Anadyr wikipedia , lookup
Eastern Bloc media and propaganda wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Culture during the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1962–1979) wikipedia , lookup
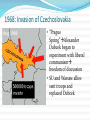
A Jewish State is Created British Balfour Declaration – Arthur Balfour, British Foreign Secretary declares that he favors the establishment of a Jewish state in Palestine Arabs, consider the Jews invaders and violent conflict emerges The United Nations Resolution – 1947 –the United Nations partitioned the Palestine area into two (one Arab and one Jewish) May 14, 1948 – independence of a Jewish state, Israel is declared with the support of U.S. President Harry Truman first prime minister was David Ben-Gurion Arab nations; Lebanon, Syria, Jordan, Egypt, and Iraq immediately invade Israel but are defeated in 1949, as Israel expands its borders Cold War implications – United States and Israel become firm allies, while the Soviet Union supports the Arabs The Six Day War (1967) Israel was invaded by Egypt, Jordan, and Syria. Israel defeated the Arab nations and took claim to the West Bank (Jordan), the Golan Heights (Syria), and the Gaza Strip and the Sinai Peninsula (Egypt) Religious and cultural differences still the root of conflict in the area. Many experts believe if a World War III would occur it would happen here. The U.S. still backs Israel while Arab countries like Iran feel Jews are intruding on Muslim Holy Land Map 29–4 ISRAEL AND ITS NEIGHBORS IN 1949 The territories gained by Israel in 1949 did not secure peace in the region. In fact, the disposition of those lands and the Arab refugees who live there has constituted the core of the region’s unresolved problems to the present day. Germany: The Partition Was important because it ensured no rebellious uprisings would occur. It made the people of Germany understand the seriousness of their defeat Gave the Allied powers more time to figure out the best plan for a nonthreatening Germany Soviets’ Advantage Sector proximity to the SU b/c it acted as a buffer zone against western invasion Allowed for Soviet expansion Allowed an attempt to make all of Berlin the communist capital of East Germany The Division of Germany SU took technology from Germany as reparations. Factories were torn out of Berlin and the Russian zone and taken back to Russia German Communist Party took control of the gov’t of Soviet zone under Walter Ulbricht Berlin, the capital France, Britain, and U.S. were planning on unifying their zones into a democratic West Germany SU set up a blockade around Berlin to try to squeeze out the Allies so the SU could take full control of Berlin Western powers did not want a military confrontationWWIII? The Berlin Airlift 13,000 tons of supplies were flown to Berlin daily SU did not want to chance war so they did not interfere and the blockade was lifted 1949 Germany will be split into West and East Germany Nikita Khrushchev (1953-1964) Replaced Stalin after his mysterious death in 1953 In “The Secret Speech,” Khrushchev condemned the vicious rule of Stalin Started “de-Stalinization”—reducing the power of the secret speech Allowed more intellectual freedom BUT, Hungarian uprising of 1956 was crushed by the Red Army Retreated from Stalin, but not from Communism or authoritarian gov’t Timeline: Tensions increase 1956 the US and SU began to talk about “peaceful coexistence” 1957SU launches Sputnik, first satellite to orbit the earthSIGNIFICANCE? 1958Negotiations began to limit nuclear testing 1959U.S. leaders visited Moscow and Khrushchev toured the U.S. Paris Summit Conference A meeting was scheduled for the leaders of several countries to meet in Paris Just before the SU shot down an American U-2 spy plane Khrushchev demanded an apology from Pres. EisenhowerHe refused Khrushchev was in Paris but did not attend the conferenceBack where we started NO TRUST! The Berlin Wall In 1961 a large number of Germans were leaving East Germany and entering West Berlin Aug. 1961 a concrete wall was built to separate West and East Berlin Effects of the Cuban Missile Crisis The Soviet Union removes missiles from Cuba The United States removes missiles from Turkey The United States and Soviet Union avoid nuclear war Kennedy and Khrushchev establish a “hot line” telephone system to keep communications openMoscow to Washington D.C. In 1963, the U.S., Great Britain, and the Soviet Union signed the Nuclear Test Ban which ended aboveground nuclear tests Khrushchev lost prestige in the SU and will be removed from power in 1964 The Brezhnev Era On Oct. 16, 1964 Khrushchev was forced to resigntoo much, too fast and CMC fiasco Leonid Brezhnev emerged as the dominant figure in SU Communist Party 1968: Invasion of Czechoslovakia “Prague Spring”Alexander Dubcek began to experiment with liberal communism freedom of discussion SU and Warsaw allies sent troops and replaced Dubcek In the summer of 1968, Soviet tanks rolled into Czechoslovakia, ending that country’s experiment in liberalized communism. This picture shows defiant flag-waving Czechs on a truck rolling past a Soviet tank in the immediate aftermath of the invasion. Hulton Archive Photos/Getty Images, Inc. Brezhnev Doctrine declared the right of the SU to interfere in communist countries to sustain communist gov’ts of Eastern Europe Détente with the United States Nixon’s “détente” or cooling off relations with the Soviets during the late 60s and early 70s Nixon and Brezhnev conclude agreements on trade and reduction of nuclear arms President Gerald Ford, SU and other European nations sign Helsinki Accordthe Soviet sphere is Eastern Europe as long as human rights are protected 1979:Invasion of Afghanistan Brezhnev gov’t invaded to ensure SU influence in central Asia U.S. embargoed grain shipments to SU, boycotted 1980 Olympics in Moscow, sent aid to Afghan rebels CIA directed rebel forces of whom were radical Muslims Conflict will last for 10 years resulting in about 20,000 SU deaths Reagan Ends Détente Ronald Reagan elected in 1980 and 1984 and begins presidency by calling the Soviets the “Evil Empire” Reagan begins a massive military buildup and pushes for “Star Wars” The Soviets unable to keep pace will begin to feel the financial crippling of their country REVOLUTION IS COMING!!! Mikhail Gorbachev Becomes Soviet leader in 1985 Introduces “glasnost” (openness) and “perestroika” (restructuring) with the SU Will be the leader when the Revolutions of 1989 engulf Eastern Europe and the Berlin Wall is torn down Reagan Ends Détente P. 1133 Read last section on Reagan and answer the following question. How did Ronald Reagan change the path of the Cold War ending détente and pushing the SU towards its financial downfall?