* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Supply and Demand
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Planned obsolescence wikipedia , lookup
Grey market wikipedia , lookup
Pricing science wikipedia , lookup
Yield management wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Revenue management wikipedia , lookup
Gasoline and diesel usage and pricing wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
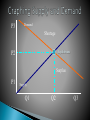
Marketing Co-Op Supply: the amount of goods producers (sellers) are willing and able to sell Demand: the amount of goods customers (buyers) are willing and able to buy As price increases the amount producers are willing and able to produce increases P3 The arrows move in the same direction!! P2 P1 Q1 Q2 Q3 Cost of production Number of producers (competition) Disasters and other big events Labor union demands Technology and inventions Prices of other products As price increases the amount the customer is willing and able to pay decreases P3 The arrows move in different directions!! P2 P1 Q1 Q2 Q3 Tastes and preferences Number of consumers Consumer (market) expectations Substitute goods Promotion (sales, commercials, customer awareness) The degree to which demand for a product is affected by price Elastic Inelastic A change in price creates a change is demand A change is price has very little effect on demand The point at which consumers will only buy so much of a given product, regardless of how low the price is Equilibrium: when supply and demand are equal Shortage: when demand exceeds supply Surplus: when supply exceeds demand P3 Demand Shortage Equilibrium P2 Surplus P1 Supply Q1 Q2 Q3 Pennies and Paperclips A rivalry between two or more businesses to attract scarce customer dollars Price: using prices to attract customers Non-price: using anything other than the sale price of a product ◦ Ex: higher quality, new features, larger assortment Monopoly: there is only one supplier of a product (there is no competition) Lower prices Better quality products New, improved products Choice of where to buy Wider product selection More and better customer service