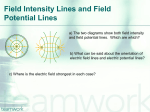
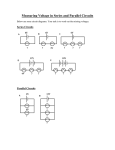
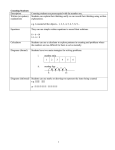
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1 Electronics Introduction
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Automatic test equipment wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Nanogenerator wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Electrical engineering wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunications engineering wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Night vision device wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Music technology (electronic and digital) wikipedia , lookup
S3 INNOVATION ELECTRONICS STARTER – IN YOUR GROUPS… With the person sitting closest to the door writing down your suggestions on the sheet of paper, the other members of the group should each - • Give an example of electronic devices that you own • Give a brief description of what it does • Explain how they would do the same things without this device LESSON TITLE: ELECTRONICS Learning Intention: To identify similarities in electronic devices To understand the steps involved in every electronic device. Activity: Building block diagrams Success Criteria: All – Remember the three stages involved in every electronic device. Most – Follow block diagrams for electronic devices Some – Will be able to design a block diagram for an electronic device Electronic Devices These are examples of electronic systems/devices. Radio Computer Stopwatch Calculator Fire Alarm Electronic Systems All electronic systems have 3 parts: input process (or processor) output input process output Input Detects some type of energy (eg. light, heat, sound) and changes it to electrical energy. This is then passed to the process. What energy is detected in the following Inputs? a) Microphone b) Switch c) Light Dependent Resistor d) Thermistor Can you think of other examples of INPUTS? Process Changes the electrical energy from the input so that the system can do its job. This is then passed on to the output subsystem. Output Converts the electrical energy from the process subsystem into another type of energy which can be used. For example: heat, light, movement What energy do the following outputs produce? a) Loudspeaker b) Light Bulb c) LED d) Motor Can you think of more examples of outputs? Block Diagrams The easiest way to represent an electronic system is through a block diagram. Eg. The diagram below is for a calculator Input Process Output Keypad Calculating Circuits Display Activity Can you make a block diagram for a Public Address System Input microphone m Process aamplifier Output lloudspeaker Smoke Detector IInput Smoke Sensor P Process O Output Logic Circuits b buzzer Plenary 1. What are the three stages of any electronic device? 2. For tomorrow, draw a block diagram for one of the following: • • • CD player Radio Stopwatch