* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download LiquidHub Business Strategy
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Customer relationship management wikipedia , lookup
Customer experience wikipedia , lookup
Business model wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Internal communications wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
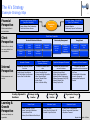
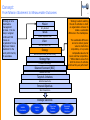
What is Strategy? Definition and questions to provoke our strategic thinking 1 Definition of Strategy In essence, "Strategy is the direction and scope of our organization over the long-term: which achieves advantage for the organization through our configuration of resources within a challenging environment, to meet the needs of markets and to fulfill stakeholder expectations." Questions to Provoke Our Strategic Thinking: How can our business be different from what our competitors do? What is our unique, key idea(s)? What can we do that others can’t do at all or as well? How can we increase the distance and difference between us and our competitors? Why, where and how can we provide something that customers like better than anything else available and yet also earn significant margins? How can we create extra value? How can we control more, yet own less? Who are the best people for us to collaborate with, and how can we make it attractive for them to collaborate with us rather than someone else? What success have we had that was unplanned and unexpected? How can we multiply this success? Strategic Analytical Tool: Balanced Scorecard (BSC) Framework The Strategy Financial Perspective “If we succeed, how will we look to our Shareholders?” Client Perspective “To achieve our vision, how must we look to our client?” Internal Perspective “To satisfy our customers, which processes much we excel at?” Learning & Growth Perspective “To achieve our vision, how must our organization learn & improve?” 2 Strategy: How we expect to create value; the art is to identify and excel at the critical few processes that are the most important to client value proposition. The Balanced Scorecard not only is used to improve the measurement of an organization’s intangible assets, but also is a framework for describing and measuring strategies for creating value. It consists of the following elements: Financial Performance: is a lag indicator, providing the ultimate definition of an organization’s success. Strategy describes how an organization intends to create sustainable growth in shareholder value. Client Success: with targeted customers provides a principal component for improved financial performance. In addition to measuring the lagging outcome indicators of client/customer success, such as satisfaction, retention and growth, the client perspective defines the value proposition for targeted client segments. Choosing the client value proposition is the central element of strategy. Internal Processes: create and deliver the value proposition for clients. The performance of internal processes is a leading indicator of subsequent improvements in client and financial outcomes Learning & Growth: objectives describe how the people, technology & organization climate combine to support the strategy. Improvements in learning and growth measures are lead indicators for internal process, client and financial performance. Intangible assets are a key source of sustainable value creation. Objectives in the 4 perspectives link together in a chain of cause-&effect relationships. Enhancing & aligning intangible assets leads to improved internal processes, which in turn, drives success for clients and shareholders. Adapted from: Kaplan & Norton So How to We Meets the Needs of Our Shareholders? Balanced Scorecard Strategy Map: A Framework for Creating Strategy Financial Results Create Shareholder Value: ROCE, EVA, EBIDTA Revenue Growth Strategy Our ultimate goal is to deliver value-based metric(s) to our shareholders through financial growth & operational productivity Close Revenue at New Clients [Prospects] Productivity Strategy Increase Revenues at Existing Clients Optimize Cost Structure Optimize Utilization Client Value Proposition Clarifies the conditions that will create value for our clients: defines the specific strategy to compete for new clients & retain existing ones. Value Creating Processes Defines the business processes that we must master to support our client value proposition. Alignment & Readiness Defines the intangible & tangible assets that must be aligned, integrated & mobilized to create value 3 product leadership customer intimacy operational excellence “Client Value Proposition” Service/Solution Attributes Price [Innovation Quality Processes] Time “Build the Franchise” Functionality “Increase Customer Value” [Innovation Strategic Job Processes]Families Image Relationship Service Relationships “Achieve Operational Excellence” [Customer Management Strategic IT Processes] Portfolio Brand “Be a Good Corporate Citizen” [OperationalOrganization Change[Regulatory & Processes] Agenda Environmental Processes] “Enable a Motivated, Prepared & Aligned Workforce” “Build & Align Core & Strategic Competencies” “Build & Align Information Technology Infrastructure” “Create a Climate for Action & Continuous Improvement” [Human Capital] [Information Capital] [Organizational Capital] Adapted from: Kaplan & Norton Strategic Analytical Tool: 4 Generic Strategies-Customer Objectives for Different Value Propositions Best Total Cost Lowest-Cost Supplier Examples: Southwest Airlines, Dell, Wal-Mart, McDonald’s Product Leader “offer products & services that are consistent, timely and low-cost” 1 2 Appropriate Selection Speedy Purchase “products & services that expand existing performance boundaries into the highly desirable” High-Performance Products Examples: Sony, Mercedes, Intel Penetrate New Markets First to Market “provide the best total solution to our customers” 3 Complete Customer Solutions Consistently High Quality Quality of Solutions Provided Number of Products/Services per Customer Quality of Client Relationship Customization of Solution Examples: IBM, Goldman Sachs System Lock-In Examples: Proprietary Operating system, eBay, Yellow Pages 4 “high switching costs to end-use customers” Offer Broad Selection & Convenient Access Provide a Widely Used Standard Provide Innovation on a Stable Platform “add value to complementors” Offer Easy-to-Use Platform & Standard Provide Large Customer Base 4 The 4i’s Strategy Example Strategy Map Financial Perspective What we must deliver to our shareholders Revenue Growth Strategy [$250M] [Long-Term Dimension] Internal Perspective What processes we must excel at How we must develop our organization Optimize Utilization Continuously Improve Cost Structure Client Value Proposition Services & Solutions Attributes Guaranteed Results Superior Quality Leading-Edge Functionality Industry Experts EA/SOA Focused Certified Technologists Relationship Management Customizable Solutions Responsive, 24/7 Client Service Trusted , Consistent & Personal Relationship Image/Brand Community Activist Progressive Firm Award-Winning Organization Innovation Processes Customer Management & Marketing Processes Operations Management Processes Regulatory & Social Processes Processes that create new products & services Processes that enhance client value Processes that produce & deliver services & solutions Processes that improve communities and the environment Optimize Demand/Supply Deliver Quality Engagements Optimize Solution Infrastructure Manage Engagement Risk [PMO] Manage Financial Risk Manage Pipeline Risk Be Green Promote Health of Associates Invest in Community Leverage Best Employment Practices Rapidly Develop New Solutions Run Each Solution Like a Business Acquire Firms That Add Value Creating Alignment & Readiness: Learning & Growth Perspective Productivity Strategy [20% EBITDA] [Short-Term Dimension] Shareholder Value Deepen Existing Client Relationships Create New Revenue Sources Client Perspective What we offer our clients; how we are distinct from our competitors 5 Design Compelling Brand Communicate Value Proposition Select Targeted Clients Acquire Targeted Clients Retain Clients Focus on Solution Selling Strategic Job Families Human Capital Attain Consulting 101 Skills Attain Technology Certifications Create Solution Skills Attract, Grow & Retain the Best People Strategic IT Portfolio Information Capital Establish Intranet Create Time Entry Reports / BI Establish Project Work Area Organization Change Agenda Organization Capital Create Culture of Improvement Clearly Communicate Expectations Emphasize Teamwork Adapted from: Kaplan & Norton Concept: From Mission Statement to Measureable Outcomes Strategy is not a stand-alone management process. It is one step in a logical continuum that moves an organization from a high-level mission statement to the work performed by its associates. 6 Strategy is about selecting the set of activities in which an organization will excel to create a sustainable difference in the marketplace. Mission Why We Exist Values What’s Important to Us Vision What We Want to Be Strategy How We Create Value [Our Game Plan] Strategy Map Translate the Strategy Balanced Scorecard [BSC] The sustainable difference can be to deliver greater value to clients than competitors, or to provide comparable value but at lower cost than competitors. “Differentiation arises from both the choice of activities and how they are performed.” Measure and Focus Targets & Initiatives What We Need to Do Personal Objectives What I Need to Do Strategic Outcomes Satisfied Shareholders Delighted Clients Efficient and Effective Processes Motivated & Prepared Workforce Concept: The Brand & the Brand Spectrum brand spectrum: attribute hierarchy EMOTIONAL ATTRIBUTES One of the foundations for developing a strong & distinctive brand is to understand how clients feel. It is especially helpful to understand not only what motivates choice and behavior by also where a brand resides in the Brand Spectrum. Understanding what motives consumers to choose one brand over another helps identify which functional & emotional benefits are the “cost of entry” and which can make a brand distinctive in the market. WILL DIFFERENTIATE Emotional attributes such as: trust, interesting, respect, indispensable MAY DIFFERENTIATE Specialty areas, trends MUST-HAVEs TO BE CONSIDERED Value/price attributes, customer service, variety, strength in basic products FUNCTIONAL ATTRIBUTES 7 In today’s highly competitive markets, the attributes which differentiate a brand are emotional rather than functional. In fact, many of the functional attributes are the cost of entry. In contrast, the true differentiators are emotionally based. As a result, the success of genuine brands depends on the emotional link they can make with consumers. Identification of the attribute hierarchy is very helpful in the development of a promise by identifying which attributes are needed for differentiation. A second key step in developing a distinct & differentiated promise is to understand what type of relationship clients have with your brand and with key competitors. Is it more functionally driven, resulting in little to no differentiation & customer loyalty? The stronger the emotional ties with your brand, the stronger the customer loyalty. Conversely, if few emotional links exist with your brand, clients are more functionally driven and can more easily be persuaded to choose another brand. Competitors that operate at the functional level have to constantly reinforce their relationship with clients, usually through pricing adjustments and promotions. Strategic Analytical Tool: Balanced Scorecard Strategy Map – Explanation of Terms FINANCIAL PERSPECTIVE: CLIENT PERSPECTIVE: INTERNAL PERSPECTIVE: INTERNAL PERSPECTIVE: The BSC retains the financial perspective as the ultimate objective for profit-maximizing firms. Financial performance measures indicate whether the company’s strategy, including its implementation and execution, are contributing to bottom line improvement. Financial objectives typically relate to profitability – measured by EBITDA. Basically, financial strategies are simple; firms make more money by [1] selling more, and [2] spending less. Thus, the firm’s financial performance improves through 2 basic ways – revenue growth and productivity. Revenue growth occurs by deepening relationships with existing customers, selling entirely new products, selling to clients in new segments. Productivity improvements can occur in 2 ways [1] reduce costs, and [2] utilize assets more efficiently. The revenue growth strategy requires a specific value proposition, in the customer perspective, that describes how the organization will create differentiated, sustainable value to targeted segments. Managers identify targeted customer segments in which the business unit competes. Successful outcomes from a well-formulated & implemented strategy are: client satisfaction, retention, acquisition, profitability, market share and account share. A strategy should identify specific customer segments The client value proposition defines the company’s strategy by describing the unique mix of product, price, service, relationship and image that a firm offers its targeted clients. The client value proposition should communicate what the firm expects to do for its customers better or differently than its competitors. Internal processes accomplish 2 vital components of strategy: [1] produce & deliver the value proposition for clients; [2] improve processes & reduce costs for the productivity component Operating processes produce & deliver the service/solution to clients Client management processes expand & deepen relationships with targeted customers. Customer Selection Process: defines a set of customer characteristics that describes an attractive client Customer Acquisition Processes: relates to generating leads, communicating to new potential clients, pricing and closing. Customer Retention is a result of excellent service & responsiveness to customer requests. Growing a client’s business involves managing the relationship effectively, becoming known as a trusted advisor. Innovation processes develop new products, processes and services, often enabling the firm to penetrate new markets & customer segments. Managing innovation includes 4 sets of processes: [1] identify opportunities for new products and services; [2] manage the research and development portfolio; [3] design & develop new products & services; [4] bring the new products and services to market. Once ideas for new products & services have been generated, managers must decide which project to fund and which will be developed entirely with internal resources, which done collaboratively in a joint venture and which will be licensed. Regulatory & Social Processes: help organizations continually earn the right to operate in communities in which they product & sell. Regulations impose standards on firms’ practices. LEARNING & GROWTH PERSPECTIVE: Learning & growth describes the organization’s intangible assets and their role in strategy. Human Capital: the availability of skills, talent and know-how required to support the strategy. Information Capital: the availability of information systems, networks and infrastructure required to execute the strategy. Organization Capital: the ability of the organization to mobilize and sustain the process of change required to execute the strategy. Whereas all organizations attempt to develop their people, technology & culture, most do not align these intangible assets with their strategies. The key to creating this alignment is granularity – that is, to move beyond generalities and focus on specific capabilities and attributes required by the critical internal processes of strategy 8 Strategy Map, Balanced Scorecard and Action Plan The Strategy Map describes the logic of the strategy, showing clearly the objectives for the critical internal processes that create value and the intangible assets required to support them. The Balanced Scorecard translates the strategy map objectives into measure & targets. But objectives and targets will not be achieved simply because they have been identified; the organization must launch a set of action programs that will enable the targets for all the measures to be achieved. The organization must supply scarce resources – people, funding and capacity – for each action program. These action programs are referred to as Strategic Initiatives. For each measure on the Balanced Scorecard, managers must identify the strategic initiatives needed to achieve the target. These initiatives achieve results. Hence, the execution of strategy is managed through the execution of initiatives. The action plans that define & provide resources for the strategic initiatives must be aligned around the strategic themes, and must be viewed as an integrated bundle of investments instead of as a group of stand-alone projects. Each strategic theme should have a self-contained business case. Strategic Analytical Tool: The process for defining strategy 9