* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 8- Business Organization
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
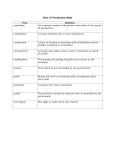
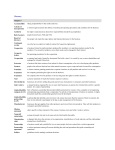
Business Organizations Starting a Business Entrepreneurs: people who decide to start a business and are willing to take risks Entrepreneurs should collect information about the business, the factors of production for the products, and learn about taxes and laws relating to the business. Help from Government Federal and state governments offer help to small businesses. The Federal government’s Small Business Administration often helps finance startups, or new small businesses. A small business incubator might also add businesses n your area. Small Business Incubator: private or government funded agency that assists new businesses by providing advice or low-rent buildings and supplies The Internet has a great deal of information to help entrepreneurs. Expenses New equipment, wages, insurance, taxes, electricity, telephone service, rent, supplies, inventory, etc. At the beginning you may only buy parts as you need them but over time you will expand your business and have inventory available. Inventory: extra supply of the items used in a business, such as raw materials or goods for sale Expenses Wages are the expense paid in order to compensate employees. Business owners should pay themselves what they would make elsewhere because opportunity cost is important in determining what career one chooses. Profit In order to track profit, a business should add wages and other expenses including taxes. The expenses should be subtracted from the business’s receipts, or income received from the sale of goods and services. Advertising Advertising: information about a company and the service / product it is selling Advertising can be purchased on radio, television, print media, billboards, etc. Record Keeping Businesses must track all expenses and income. Internet programs and software will track revenues and expenses on the computer. Business purchases can be deducted from the amount of taxes an owner owes. Risk A business owner must balance the risk against the advantages of being self-employed. An owner might have to spend part of his/her savings in order to start a business or keep a business running. An owner has to be able to afford expenses and advertising in order to be successful. Sole Proprietorships and Partnerships The most basic type of business in the sole proprietorship. Sole Proprietorship: business owned and operated by one person The biggest advantage is that the owner receives all the profits and has full control of the business. The biggest disadvantage is that the owner has unlimited liability. Unlimited Liability: requirement that an owner is personally and fully responsible for all losses and debts of a business Personal assets may be seized to pay off business debts. Assets: all items to which a business or household holds legal claim Partnership: business that two or more individuals own and operate Partners sign a legally binding agreement describing the duties of each partner, division of profits and distribution of assets at end of partnership. The biggest advantage is that partners share control and profits. The biggest disadvantage is the partners have unlimited liability. Limited Partnerships Limited Partnership: special form of partnership in which one or more partners have limited liability but no voice in management One partner is called the general partner. The general partner assumes all of the management duties and has full responsibility for debts of the partnership. Other partners are limited. They only contribute money and property and have no voice in the partnership’s management. Limited partners have no liability for the losses beyond what they initially invest. Joint Ventures Joint Venture: partnership set up for a specific purpose for a short period of time. The joint venture is dissolved after it has accomplished its goal. Joint ventures are sometimes are sometimes sold later for profit. The Corporate World and Franchises Corporation: type of business organization owned by many people but treated by law as through it were a person; it can own property, pay taxes, make contracts, and so on The need for financial capital Wanting financial backers who will lend funds without having a hand in the business. Corporations have a distinct existence from stockholders. A major advantage is stockholders have limited liability, meaning they are not personally responsible, only the business loses money and assets. A major disadvantage is corporations pay more taxes than other forms of business organizations. Stock: share of ownership in a corporation that entitles the buyer to a certain part of the future profits and assets of the corporation Limited Liability: requirement in which an owner’s responsibility for a company's debts is limited to the size of the owner’s investment in the firm Registering the Corporation Register the corporation in the state where it will be headquartered. File the articles of incorporation which includes: Name, address, and purpose of corporation Names and addresses of the initial board of directors (the new board will be elected at the first stockholder’s meeting) Number of shares of stock to be issued Amount of money capital to be raised through issuing stock. Selling stock Raise capital by selling stocks or bonds. Common stock gives stockholders right to vote and a percentage of future profits. Preferred stock doesn’t give voting rights, but guarantees a dividend and these stockholders have first claim on assets left over if corporation goes out of business. Naming a Board of Directors Stockholders elect a board of directors who will supervise and control the corporation by hiring people to run the day-to-day operations of the business. Franchise: contract in which one business (the franchiser) sells to another business (the franchisee) the right to use the franchiser's name and sell its products The franchisee pays a fee that could include a percentage of all money taken in. Franchises often have training programs to teach the franchise and to set the standards of business operations.