* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Adjusting Entries Review
Financialization wikipedia , lookup
Securitization wikipedia , lookup
Merchant account wikipedia , lookup
Life settlement wikipedia , lookup
History of insurance wikipedia , lookup
Continuous-repayment mortgage wikipedia , lookup
Interest rate wikipedia , lookup
Present value wikipedia , lookup
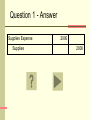
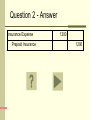
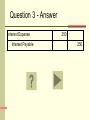
Microcomputer Accounting Applications – QuickBooks Adjusting Entries Review Accounting Cycle QuickBooks supports all the transactions included in the Accounting Cycle Journalize and post transactions - journal entries are created from transactions entered in on-screen forms and are maintained in accounts defined in the Chart of Accounts Prepare adjusting entries - adjusting entries must be manually entered using the Make Journal Entries window Prepare trial balance – run unadjusted and adjusted trial balances from the Reports menu Create financial statements – prepare income statement, balance sheet, statement of cash flows from the Reports menu Close the temporary accounts - QuickBooks closes Revenue 2 and Expense accounts when the Closing Date is set Adjusting Entries This review focuses on adjusting entries. Following are several transactions relating to adjusting entries for ABC Company. ABC Company’s fiscal year ends on December 31 and all adjusting entries are to be recorded as of that date. How to Use this Review For each transaction you are given, write your answer on a piece of paper. Once you have answered the problem, click the slide to reveal the answer. Click if you want more information on how the problem was solved. Click to proceed to the next question. Question 1 ABC Company shows a balance of $3,000 in the Supplies (asset) account. A physical count indicates $1,000 of supplies on hand at the end of the fiscal period. Journalize the required adjustment for supplies. Question 1 - Answer Supplies Expense Supplies 2000 2000 Question 1 - Explanation Supplies Expense Supplies 2000 2000 This adjustment is for the supplies that have been used during the fiscal period but not yet recorded. Any time an asset is used, an expense account will be debited and an asset account will be credited. In this case, the expense is Supplies Expense and the asset is Supplies. The amount of the adjustment is calculated as the difference between the beginning supplies balance and the ending supplies balance. Beginning Balance $3,000 Ending Balance 1,000 Supplies Used (Expense) 2,000 Question 2 ABC Company paid $2,400 for a two-year insurance policy on January 1 of the current year. Prepare the required adjustment for the expired insurance at the end of the current year. Question 2 - Answer Insurance Expense Prepaid Insurance 1200 1200 Question 2 - Explanation Insurance Expense 1200 Prepaid Insurance 1200 This adjustment involves a prepaid item, specifically, prepaid insurance. Prepaid items are assets. As prepaid items get used up, the asset is converted into an expense. An adjusting entry is required to recognize the expense (debit Insurance Expense) and reduce the used asset (credit Prepaid Insurance). The amount for this entry is calculated by dividing the total payment ($2400) by the period covered (24 months), then multiplying the monthly amount ($100) by the months in this period (12). $2400/24 = $100 per month (insurance expires at $100/month) 12 months in the current year X $100 = $1200 insurance expense Question 3 ABC Company has a $10,000 note payable due March 15 of next year. The note originated on July 1 of the current year and bears interest at the rate of 5%. Prepare the required journal entry to recognize interest expense. Question 3 - Answer Interest Expense Interest Payable 250 250 Question 3 - Explanation Interest Expense 250 Interest Payable 250 This is an example of an adjustment requiring an accrual. While interest has been accruing (building up) on this note, it has not been recorded. The expense must be recognized (debit Interest Expense) and the amount of interest to be paid upon maturity is accrued in a liability account (credit Interest Payable). Interest is calculated as Principal X Rate X Time. Principal $10,000 Interest Rate .05 Anuual Interest 500 Time Period covered 6/12 months (July 1 – Dec 31) Interest Expense $250 Question 4 ABC Company received $36,000 on January 1 of the current year for a project to be completed over the next two years. Journalize the adjustment to recognize the income earned on this project at the end of the current year. Question 4 - Answer Unearned Fees Fees Earned 18000 18000 Question 4 - Explanation Unearned Fees Fees Earned 18000 18000 This is an example of an adjustment for unearned revenue now earned. When the cash for this project was received, the Cash account was debited and the Unearned Fees account (a liability) was credited. As work is completed on the project the liability decreases (debit Unearned Fees) and the revenue increases (credit Fees Earned). The amount of fees earned at year-end is calculated as follows: Amount Received $36,000 Divided by Period Covered 24 months Earnings per Month $1,500 Months of Work in this Period 12 Fees Earned $18,000 Question 5 ABC Company has performed $12,000 of services that have not been billed as of fiscal year-end. Prepare the adjusting entry to record the fees earned. Question 5 - Answer Accounts Receivable Fees Earned 12000 12000 Question 5 - Explanation Accounts Receivable Fees Earned 12000 12000 This is an example of accrued earnings. In this situation fees have been earned but not yet billed and therefore not recorded. Since the fees will be paid at a later date, debit Accounts Receivable for the amount to be received and credit the appropriate revenue account (in this case, Fees Earned) for the amount earned ($12,000 in this case). Question 6 ABC Company purchased an automobile for $35,000 on January 1 of the current year. The automobile is expected to have a useful life of 5 years and a salvage value of $5,000. Using the straight-line method of calculating depreciation, prepare the adjusting entry necessary at the end of the current year to record annual depreciation on the automobile. Question 6 - Answer Depreciation Expense - Automobile Accumulated Depreciation-Automobile 6000 6000 Question 6 - Explanation Depreciation Expense - Automobile Accumulated Depreciation-Automobile 6000 6000 Depreciation is the systematic write-off of the cost of an asset to expense over the period benefited (useful life). Straight-line depreciation is calculated as follows: Asset Cost $35,000 Less Salvage Value If depreciation is being calculated for a partial year, take the annual depreciation, and divide by 12 to get depreciation per month. Then multiply by the months covered in the period being reported. Equals Base Divided by Useful Life Equals Annual Depreciation -5,000 $30,000 5 $6,000 End of Review See your Principles of Accounting or Intermediate Accounting text for more information.