* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Growth and Development
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
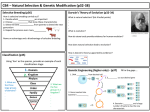
New Genes For Old Part 1 Learning Objectives • To learn how plants and animals can be changed by selective breeding. • To learn about the advantages and disadvantages of selective breeding. • To learn about the problems with small gene pools. Success Criteria • I can state why selective breeding is important. • I can describe the stages involved in selective breeding. • I can state 2 major problems with involved with inbreeding in selective breeding. Starter Why are the following organisms important to humans? • • • • • Milk Butter Meat Fertiliser Manure used for energy • Works on farms • • • • • • • Good pet Loyal Brave Working dog Security Police use Drug sniffing Starter What is the link between these animals? All of the breeds of dog are descende d from WOLVES! SELECTIVE BREEDING Selective Breeding • None of the following organisms would be around today without the help of humans. • Farmers choose animals and plants with the best characteristics. • They then breed them to produce offspring that have those characteristics too. Selective Breeding Todays cows have huge udders because farmers have selected and bred cows that produce lots of milk. In fact, modern cows would be in pain or even die if not milked. Dogs are only around because humans domesticated wolves thousands of years ago. Over time, breeding for particular characteristics has led to all the breeds we see today. Selective Breeding: Cows Jersey cows produce milk that is rich in cream, but there isn’t much of it. Friesian cows produce lots of milk, but it isn’t very creamy. What could be done in order to produce lots of creamy milk? Cross-breed a Jersey cow with a Friesian bull Cross-breed a Friesian cow with a Jersey bull Choose the best the offspring that produce high-quantity, creamy milk. Repeat this for many generations. Questions 1. Why would farmers want to plant wheat crops that grow quickly? 2. Why do farmers want pigs that produce lots of baby piglets? 3. Name one characteristic of strawberry plants that would be useful to gardeners. 4. Describe how a farmer could produce a plant with large, sweet strawberries, if she starts with a plant that has small, sweet berries and one with large, non-sweet berries. Answers 1. To produce a higher yield and therefore make more money. 2. To make a greater profit off each female pig (sow), as piglets can be sold. Would also mean more meat production, hence greater profit. 3. Disease-resistance. Sweet-tasting. Fast-growing. 4. Breed the two plants together. Choose the plants that produce the largest, sweetest berries and then keep breeding for many generations. Selective Breeding: Dogs • There are over 300 breeds of dogs in the world. Strong dogs Clever dogs Stupid dogs • All are the same species and only exist because of selective breeding by humans. • Their characteristics have been selected for over hundreds of generations. • COMPLETE WORKSHEET 1: “DOG BREEDING” Answers in folder: Collins B3g1 lesson file. Problems with Selective Breeding • As you’ve probably noticed, selective breeding involves mating animals that are closely related. • This is called inbreeding. • It can lead to lots of health problems within a species. Bulldogs have been bred with large folds of skin on their faces. This is a recessive characteristic that affects their sight. Suggest reasons why bulldogs would not survive in the wild… HIGHER Inbreeding • The inbreeding involved in selective breeding causes a reduction in the gene pool. • This means there are fewer types of alleles. With fewer alleles, animals and crops are more likely to die of disease. The sheep on the right has deformities due to generations of inbreeding, causes vital genes to be lost from the population. PLENARY Plenary • Produce a comic strip depicting the stages involved in the selective breeding of large sheep with a lot of wool. • Start with: - Large male sheep (not much wool) - Average sized female (lots of wool) Learning Objectives • To learn how plants and animals can be changed by selective breeding. • To learn about the advantages and disadvantages of selective breeding. • To learn about the problems with small gene pools. Success Criteria • I can state why selective breeding is important. • I can describe the stages involved in selective breeding. • I can state 2 major problems with involved with inbreeding in selective breeding.