* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 4 PowerPoints - The Jeffersonian Experience
Constitutional amendment wikipedia , lookup
Fourth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Eighth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Second Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Fifth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
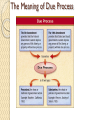
Unit 4 Civil Liberties and Civil Rights Chs. 19-21 I. Bill of Rights (1-10) A. 1st Amendment: 1. FREEDOM OF RELIGION JEFFERSON- “Wall of Separation” The Lemon Test (Lemon v. Kurtzman, 1971) The purpose must be nonreligious. Can neither advance nor inhibit religion. Must not excessively entangle the government with religion. 2. FREEDOM OF SPEECH • Freedom is NOT absolute (Schenck v. United States) • Obscenity (Miller v. California) “community standards” • Symbolic speech (Texas v. Johnson) • Citizens United v. Federal Election Commission 3. FREEDOM OF THE PRESS 4. RIGHT TO ASSEMBLE 5. RIGHT TO PETITION THE GOVERNMENT I. Bill of Rights (1-10) [con’t.] B. 2nd Amendment: a well regulated militia, being necessary to the security of a free state, the right of the people to keep and bear arms, shall not be infringed. 1. militia - a body of citizen soldiers as distinguished from professional soldiers. 2. Powers v. Rights RIGHT – District of Columbia v. Heller C. 3rd Amendment: protections against housing troops in private homes I. Bill of Rights (1-10) [con’t.] D. 4th Amendment: protections against unwarranted searches and seizures Probable cause – there is a reasonable basis for believing that a crime may have been committed (for arrest) and that evidence of the crime is present in the place to be searched (for search). Exclusionary Rule – evidence gained illegally cannot be used in court. The 5th Amendment provides that “no person … shall be deprived of life, liberty, or property without due process of law…”. I. Bill of Rights (1-10) [con’t.] E. 5th Amendment: 1. DUE PROCESS (proper legal procedures) a. Substantive due process – the law itself b. Procedural due process – how law is enforced c. 14th Amendment - extends due process to State and local governments. • Process of Incorporation – most of the Bill of Rights now apply to the States. The Meaning of Due Process I. Bill of Rights (1-10) [con’t.] E. 5th Amendment: [con’t.] 2. DOUBLE JEOPARDY – can’t be tried twice for same crime 3. SELF-INCRIMINATION – right to remain silent 4. EMINENT DOMAIN – just compensation KELO V. NEW LONDON, CT I. Bill of Rights (1-10) [con’t.] F. 6th Amendment: right to council and jury in criminal trials G. 7th Amendment: right to jury in civil trials H. 8th Amendment: protections against cruel and unusual punishment I. 9th Amendment: rights are not restricted to those listed in Amendments 1-8. a. RIGHT TO PRIVACY Established in Griswold v. Connecticut, 1965, outlawing birth-control was unconstitutional. Uses IX, I, III, V & XIV amendments b. ABORTION • provoked controversy when Roe v. Wade, 1973, applied the right to privacy to a woman’s right to an abortion. I. Bill of Rights (1-10) [con’t.] J. 10th Amendment: those powers not stated are reserved to the states and the people II. Original Constitutional Rights 1. Writ of Habeas Corpus— A court order which prevents unjust arrests and imprisonment 2. Bills of Attainder— laws passed by Congress that inflict punishment without a court trial 3. Ex Post Facto Laws— new laws cannot apply reprimands to individuals for actions that happened in the past III. Slavery A. Slavery and Involuntary Servitude 1. The 13th Amendment, ratified in 1865, ended slavery in this country. It also protects against involuntary servitude, or forced labor. – Neither the draft nor imprisonment can be classified as involuntary servitude. 2. Unlike any other part of the Constitution, the 13th Amendment covers the actions of private individuals as well as the government. IV. Affirmative Action the encouragement of increased representation of women and minority-group members, esp. in employment. A. Cases and Measures 1. Regents of the University of California v. Bakke, 1978 Allan Bakke sued the University of California for reverse discrimination and won. This case shows that the Constitution does not allow race to be used as the only factor in the making of affirmative action decisions. 2. Adarand Constructors v. Pena, 1995 The Supreme Court’s decision in this case holds that racial classifications imposed by the national government must be analyzed under a standard of “strict scrutiny” and that preferential treatment based on race is “almost certainly unconstitutional,” even if it is intended to benefit minority groups suffering from past injustices. V. Citizenship citizen – a member of a state who owes allegiance to it by birth or naturalization and is entitled to full civil rights. A. by BIRTH 1. Jus Soli 2. Jus Sanguinis the law of the blood, law of the soil, or or to whom one is born. where one is born. A child who is born The 14th abroad to at least one Amendment citizen, and who has at confers citizenship some time lived within to any person born the United States, can within the United petition for citizenship. States. IV. Citizenship (con’t.) B. by NATURALIZATION Naturalization – the legal process by which a citizen of one country become a citizen of another.