* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Economics 308 - CSUNEcon.com
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
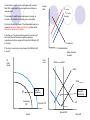
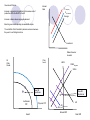
Economics 161 Principles of Economics Quiz #1 Spring 2012 Rules of Engagement The quiz is worth 10 points to be added onto the next exam after the curve is computed. The quiz is open book, open note, and students may freely collaborate in small groups. Current Events The current recession was started by the collapse in the housing markets. It was exacerbated by the financial crises which affected credit markets. Timeline of Government revenues versus government outlays (or spending) as a percentage of GDP- Reagan Tax Cuts Reagan Obama The president’s response was a huge increase in government spending, an attempt to raise taxes, and an increase in government regulation of businesses. Question Suppose the economy started out in long run equilibrium before the current recession. Depict the short run effects of the housing crisis. Indicate on your graph what happens to Real GDP, the price level, interest rates and investment. How does the Permanent Income hypothesis impact your answer? Show how your answer to 1(a) will change if the general public perceives the drop in housing prices to be permanent. Suppose the government did nothing in response to the housing crisis. How would the economy adjust in the long run? Depict on your graph and explain. In response to the crisis, President Obama increased government spending and argued for an increase in income tax rates. Depict the effect of these policies on the economy in the short run. Suppose the president’s response included an increase in government regulation of businesses which increased their costs. Depict the effect of increased regulation on the economy in the short run. Factors That Change Aggregate Demand The collapse of the housing market causes a negative wealth shock, i.e. a decrease in people’s wealth. The decrease in wealth causes a decrease in consumption and a drop in AD The first step in the analysis is to identify what has changed in the world, whether it affects AD or AS, and which way to shift the curves. The decrease in wealth causes a decrease in AD, a drop in Real GDP, a decrease in the price level and an increase in unemployment. Interest Rate S2-Temporary S2-Permanent The decrease in wealth causes a decrease in savings, an increase in the interest rate and decrease in investment. Savings Permanent Income Hypothesis. If the drop in housing prices is viewed as permanent, the drop in AD will be greater and the decrease in savings will be smaller. In the long run, if housing market recovers, the economy will self correct back to the original equilibrium because unemployment will rise, wages will fall, and the SRAS will shift to the right. Investment If the drop in housing prices is permanent the LRAS will shift to the left. Dollars Saved or Invested Price Level All Other Goods LRASPerrmanentLRAS SRAS SRASTemporary New SR Equilibrium Institutional PPF New SR Equilibrium AD Physical PPF AD2-Permanent Natural GDP Good X Real GDP Permanent Income Hypothesis If the decrease in wealth is permanent: Decrease in AD will be greater. Change in savings will be smaller. If the decrease in wealth is temporary: Decrease in AD will be smaller. Change in savings will be greater. Because with a permanent change in wealth, people will downgrade their lifestyle. With a temporary change in wealth, people will try to maintain their lifestyle. Cher is selling her Malibu mansion for a staggering $45 million. The ‘Believe’ singer built the three-storey property, which overlooks the Pacific Ocean, in 1992. The 14,000 sq ft house boasts six bedrooms, seven bathrooms, a theatre, gym, tennis court, swimming pool and guest house. Property tax is $675,000 ($56,250 per month) plus insurance $450,000 (37,500). Running the house (electricity, gardening, cleaning, repairs, etc,) is approxiamtely $10,000 per month. Monthly Nut: $56,250+$37,500+$10,000= $103,750 Government Policies. Interest Rate Increase in government regulation that increases cost of production shifts the SRAS to the left. S2-Temporary S2-Permanent Savings Increase in taxes reduces aggregate demand. Boost in government spending increases AD- maybe. The net effect of the President’s policies is unknown because they work in conflicting directions. Investment Dollars Saved or Invested Price Level All Other Goods LRAS SRASRegulation SRAS New SR Equilibrium New SR Equilibrium AD4-Government Spending Institutional PPF AD Physical PPF AD AD3-Taxes2-Permanent Natural GDP Good X Real GDP