* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Economic Indicators
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
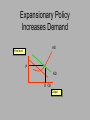
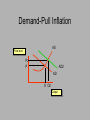
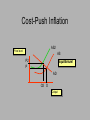
Warm-up: Get a yellow text 1. 2. 3. 4. What does GDP stand for? How do we calculate GDP? What do we use to measure inflation? How do we measure unemployment? Begin Unit 3 Macroeconomics SSEMA1 b. Define Gross Domestic Product (GDP), economic growth, unemployment, Consumer Price Index (CPI), inflation, stagflation, and aggregate supply and aggregate demand. c. Explain how economic growth, inflation, and unemployment are calculated. N.B. #25- Economic Indicators • Add the new vocab words to your list • Read and take 2-column notes on Lesson 9 (pp.72-77) of the EOCT Coach • Be sure to answer the following questions in your notes: 1.How are GDP, the CPI, and the unemployment rate calculated? 2.What are the characteristics of the four types of unemployment? Economic Indicators Quiz Time!!!!!!!! Question 1 What type of unemployment? • Construction workers are laid off for the winter, but plan to return to work when the weather is better. Question 2 What type of unemployment? • Workers are laid off at a Pog factory. A downturn in the economy has lowered demand for luxury items. Question 3 What type of unemployment? • The United States has lost manufacturing jobs as a result of a change to a service-oriented economy. Question 4 What type of unemployment? • A fast-food worker graduates from college and quits his job to look for a better career. Question 5 True or False? Unemployment in the U. S. has recently been higher than 8 percent. Quiz!! 1. In your own words, describe what GDP attempts to measure. 2. Explain the formula for calculating GDP. Naked Econ Read from the bottom of p. 177-the top of p. 181 1. Why do dollars have value? 2. What is the best way to think about inflation? 3. What does it mean if I receive 5% interest in an investment while the inflation rate is 3%? MACROECONOMIC GOALS LOW UNEMPLOYMENT LOW INFLATION STABILITY GROWTH ECONOMIC GROWTH Defined by sustained increases in GDP adjusted for inflation The Business Cycle • The ups and downs of the economic activity • The good times and bad times • P. 310 The Business Cycle 4 phases 1. Expansion- increasing GDP and growth 2. Peak- the top of the expansionary periodlowest unemployment 3. Contraction- decreasing GDP-increasing unemployment 4. Trough- “the bottom” of the contraction The Business Cycle Peak contraction Expansion Trough The Business Cycle Recession Decline in real GDP for 6+ months The Business Cycle Recession • Worst in 1929-1933 (33% decline in GDP) • 10 in US since 1945 The story of Peorgia • Work with a partner who has the same numbered handout as you do. • Calculate all the economic indicators for Peorgia • We will work with this more soon! The story of Peorgia • Work with your group to determine which phase of the business cycle Peorgia is in • Create a skit involving all group members that shows what life might be like during this phase of the bussiness cycle. Overview • Aggregate Supply and Demand • Supply and Demand at the MACRO level Aggregate Supply The amount of GDP an economy will produce at each and every price level Aggregate Supply Price level AS Output Aggregate Demand Amount of GDP that will be demanded at different price levels Aggregate Demand Price level P AD O Output Aggregate Supply and Demand AS Price level Equilibrium! P AD O Output Key learning: When aggregate demand is equal to aggregate supply at a level that just employs all available productive resources with no change in price level, the economy is at full-employment, noninflationary equilibrium Aggregate Supply Determinants 1. Cost of inputs (ex.the cost of oil falls!) 2. Productivity (ex. we get better computers!) 3. Government regulations (ex. We have to spend money to clean up pollution!) Aggregate Supply Shifters: Change in cost of inputs (domestic or imported) Change in productivity Government regulations Price level AS1 Output AS2 Aggregate Demand Determinants 1.Consumer Spending 2.Investment Spending 3.Government Spending Aggregate Demand Shifters: Change in Consumer Spending Change in Investment Spending Change in Government Spending Price level P AD1 O Output AD2 Aggregate Supply and Demand and the Business Cycle • Complete the chart on your paper • For AD and AS, predict if there will be an increase, a decrease, or no change. • Also, state if the curve will shift to the right or to the left. Aggregate Supply and Demand and the Business Cycle We can try to stimulate the economy by manipulating the AD and AS curves. When AD is below full-employment production falls and unemployment results AS Price level P AD O Output Aggregate Supply and Demand AS Price level P AD O Output Unemployment!! Aggregate Supply and Demand AS Price level Equilibrium! P AD O Output Aggregate Supply and Demand and the Business Cycle We want to move the curves back to the fullemployment noninflationary equilibrium! How Can We Shift the Curves and Help (Hopefully) the Economy? Two Tools: 1. Fiscal Policy 2. Monetary Policy Expansionary Policy Increases Demand AS Price level P AD O O2 Output Warning!!! • Demand-Pull Inflation: Rise in the price level when agg. Demand exceeds agg. Supply. Demand-Pull Inflation AS Price level P2 P AD2 AD O O2 Output Warning!!! • Cost-Push Inflation: Rise in the price level due to increase in costs of production (shifts agg.supply curve left). Cost-Push Inflation AS2 Price level AS P2 P Equilibrium! AD O2 O Output Aggregate Supply and Demand AS Price level Equilibrium! P AD O Output The Business Cycle 1. Be sure to label all points on the B. C. graph 2. During which phase is production increasing? 3. During which period is unemployment likely to be lowest? Why? The Business Cycle As an economy moves from recession to expansion, what is likely to happen to Wages? Peak Investments? Employment? Profits? Trough