* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Spring Framework
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
Wishing for Spring
Presented by Robert Kaul
The Spring Framework
•Where did it come from?
•Why use it?
•What is it?
•Who uses it?
•How does it work?
History of Spring
It all started with some meteorologists…
History of Spring
First milestone release 1.0 in March 2004
by Rod Johnson J2EE developer
2.0 October 2006
2.5 November 2007
3.0 December 2009
Why use Spring?
Designed for
Consistency
Maintainability
Simplicity
Jolt Productivity Award in 2006
For “Jolting” the industry
JAX Innovation Award in 2006
Java Specific innovation
J2EE without Spring
Brought standardization to core middle-tier concepts.
Transaction management (aka talking to a database)
Over-complex
Distributed applications hard to develop, debug, deploy and
maintain.
Take excess effort to develop
Disappointing performance
J2EE without Spring
Excessive amounts of “Plumbing” code
Code reviews showing large amounts of code that doesn’t
do anything
Try/catch blocks to acquire and release JDBC(Java database
connection) resources
Writing and maintaining plumbing code drains resources
Attempts at design patters resulted in workarounds for
application programing interfaces(APIs) I.E. (JDBC)
Spring into Easier Consistency
Helps Structure whole applications
Takes care of “plumbing” code
Dependency injection
Aspect oriented programming
Managing transactions
Security
Social networking
Who would want to use Spring
How does it?
Wire beans
Inject dependencies
Declare beans
AOP
Database transactions
Web applications
Security
Spring’s Container
Inversion of control container
Keeps track of all application resources
Allows serialization of objects
Using dependency injection
Spring’s Container
Wired beans interact with each other and are kept track of
by the container
Dependency injection
Good dependency injection should leave code decoupled
Easy to maintain
Easy to test
Should be able to inject with the injected knowing it.
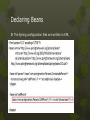
Declaring Beans
Assume a ContactablePerson that implements a Person
Public class ContactablePerson implements Person {
private Phone phone;
public ContactablePerson(Phone phone){
this.phone = phone;//phone is injected
}
public void AnswerPhone( throwDialException){
phone.answer();
}
}
Declaring Beans
The Spring configuration files are written in XML
Declaring Beans
Why configuration files?
For the sake of consistency
Everything in spring has some form of configuration file.
This is a simple fast way of easing a developer into
something they will have to use on something much
more complex.
Aspect-Oriented Spring
Point cut with advice before an action or after an action.
Primarily for keeping track of data access; whens,
wheres and how-manys
To improve performance or get rid of something unused.
Easy to update a current program using AOP
Used for other things as well
Spring uses this for it’s security features
Aspect-Oriented Spring
This is part of a MovieWatchers class
AOP Spring Config
Database access with Spring
J2EE does it so does Spring
Cuts down the need for “Plumbing” code
Using the Templating design pattern.
Allows for different types of databases.
Achieves communication through eight different
Templates
Template classes
JDBC’s Exceptions v. Spring’s
Database access with Spring
Why Template database access?
Always going to have the same 7 steps throughout the
interaction
Establish a connection
Start transaction
Execute query
Return data
Commit/rollback the transaction
Close connection
Handle exceptions
Developers only really want to execute the query.
Database access with Spring
Spring allows the developer to change their query while
handling the other 6 steps
This leads to
Higher quality queries
Higher productivity
Database access with Spring
Spring’s Model-view-controller
The Spring way of allowing a user to view data on the
web
Has different view capabilities
The Most common is a Java Server Page or JSP
For all practical purposes is just smart HTML page linked to
an data-access-object’s methods.
For example home.jsp would be linked to
HomeController.java
Spring’s Model-view-controller
Allows for web pages to have a Tile Layout
Tile: piece of web page defined separately
For example, sidebar.jsp
Also allows for a type of inheritance sidebarCalendar.jsp
Makes maintenance easier
Moving pieces easier than rewriting a whole HTML page
Mygreatlakes.org
Different View Resolvers
Here they are...
InternalResourceViewResolver // used for the example
ContentNegotiatingViewResolver
BeanNameViewResolver
FreeMarkerViewResolver
JasperReportsViewResolver
ResourceBundleViewResolver
TilesViewResolver
VelocityViewResolver
XmlViewResolver
XsltViewResolver
Life cycle of a request
Spring Model-view-Controller
Generally Start with a home page a work out through
the navigation
Craig Wall’s Spring in Action 3.0 Spitters example
Spitters is a twitter-like web application
HomeController used to welcome users to Spitters by
displaying recent spits.
Spitters HomeController
Spitters HomeController
@Controller marker indicates that this is a controller
class allows spring to register it as a bean and keep
track of it
@inject updates the context file automatically with the
ref tag injecting the SpitterService upon creation
@RequestMapping this marks the method to handle
requests from “/” or from “/home” it also gets the Map
of Strings to Object and stores it in a model map to be
displayed later by the view
The return “home” is the name of the view on which the
map should be rendered
Rendering Spring Views
Rendering Spring Views
<%@taglib prefix= these imports allow you to
accomplish smart HTML
things like iterate through a map
${variableName} is a variable reference from the
homeController bean
<s:url value= Spring’s way of creating context that is
relative to a particular Spitter
Also used for referencing static content like images
This example doesn’t show everything
input & file upload.
Spring Security
Features…
Easy Configuration using Spring Dependency Injection
Non-Intrusive Setup
Don’t have to deploy libraries to your Server
Non-Invasive
Keeps security out of objects
Pluggable Architecture
Easy to replace, customize or extend parts
Password encoding
Caching
LDAP Support
Supports HTTP Digest authentication
Never sends password over a wire
Spring Security
Any web application using personal identification data
must have:
Authentication
Authorization
Web request level and method level
Accomplished using
Dependency injection
Aspects
Conclusion
Features…
Dependency Injection
Declaring beans
Aspect-Oriented ability
Point cuts
Database access
Templating and Templates
Spring Model-view-controller
Tile Layouts
Rendering views
Views
Things I didn’t talk about…
Web flow capabilities REST
Transaction management
Wiring a bean using spEL regular expression language…
References
Walls, Craig, Mr. Spring in Action. Illus. Marija Tudor. Ed. Sebastian Stirling. 3rd ed. Shelter
Island: Manning, 2011. Print.
"SpringSource." SpringSource. VMware, 2011. Web. 7 Nov. 2011.
<http://www.Springsource.org/
features/modern-web>
Jose, Benoy. "The Spring Framework." Rev. of Spring Framework. http://javaboutique.
internet.com,
2011. Web. 13 Oct. 2011.
<http://javaboutique.internet.com/tutorials/Spring_frame/>.
Johnson, Rod. "Introduction to the Spring Framework." theserverside. TechTarget, 1 May
2005. Web. 2
Nov. 2011. <http://www.theserverside.com/news/1364527/
Introduction-to-the-Spring-Framework>.
Javabeat, Niraimathi. "Extending ViewResolver and Chaining ViewResolvers in Spring MVC."
javabeat. N.p., 2011. Web. 13 Nov. 2011. <http://www.javabeat.net/articles/
247-extending-viewresolver-and-chaining-viewresolvers-in-sp-1.html>.
Questions