* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Honors Geometry Section 8.3 Similarity Postulates and Theorems
Dessin d'enfant wikipedia , lookup
Penrose tiling wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Brouwer fixed-point theorem wikipedia , lookup
Apollonian network wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
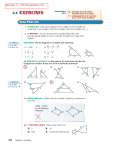
Geometry Sections 8.4 & 8.5 Similarity Postulates and Theorems To say that two polygons are similar by the definition of similarity, we would need to know that all corresponding sides are proportional and all ______________ corresponding angles are congruent ___________. The following postulate and theorems give us easier methods for determining if two triangles are similar. Angle-Angle Similarity Postulate (AA Similarity) If TWO ANGLES OF ONE TRIANGLE ARE CONGRUENT TO TWO ANGLES OF A SECOND TRIANGLE, then the triangles are similar. Side-Angle-Side Similarity Theorem (SAS Similarity) If TWO SIDES of one triangle are PROPORTIONAL to TWO SIDES of a second triangle and the INCLUDED ANGLES are CONGRUENT, then the triangles are similar. An included angle of two sides is the angle FORMED BY THOSE TWO SIDES. Side-Side-Side Similarity Theorem (SSS Similarity) If the THREE SIDES of one triangle are PROPORTIONAL to the THREE SIDES of a second triangle, then the triangles are similar. Examples: Determine if the triangles are similar. If so, write a similarity statement and identify the postulate or theorem used. A B C D E AA ACE ~ DCB NONE 31.25 20 ? 25 16 ? 18.75 12 1.5625 1.5625 1.5625 SSS ABC ~ FDE AA ABC ~ EDC