* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download m5zn_4836f241122847a
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
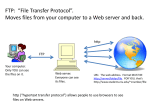
Chapter 5 Preparatory year Alimam Islamic university Chapter 5 Chapter Objectives: • Explain how the Internet works. • Describe methods for access the internet. • Define and differentiate between the internet the World Wide Web. • Explain the concept of hypertext. • Contrast Web browsers and Web servers. • Explain how search operators can improve Web search results. • List the most popular internet services and explain what they do . What is the internet • The internet is a global computer network made up of thousands of privately and publicly networks . • Computers can exchange data • The internet is referred to as cyberspace • Internet backbone are maintained by network service providers(NSPs) How is the Internet Works؟ • Volunteers maintain the Internet networks. • Private and public groups provide the equipment. • Network service providers such as AT&T maintain the Internet backbone, the main high-speed routes. 4 INTEROPERABILITY Interoperability : • Is the ability to work with the computer even if it is a different brand and model. • The reason is the TCP/IP • TCP/IP supply the standard methods of: 1. Packaging information 2. Transmitting information. Accessing the internet: going online • Internet service providers(ISPs) Companies that provide access to the internet. • ISPs have several roles and responsibilities: • Provide and maintaining a connection to the internet . • Support the Hardware and software needed to service that connection . • Protect their site and network from external thearts . • Online service : services that are available only to subscribers. Methods to Access the Internet • Dial-up access : – Run over normal telephone lines – While online, your phone is unavailable for calls – Speed: 14-56 kbs. Disadvantage: – slowest Advantage: – cheapest connection Active modem Methods to Access the Internet • Digital subscriber line(DSL): – Offer faster access speeds than dial-up – Operates over normal telephone lines. – Can be used simultaneously with the telephone. – Average Speed: 1.5 megabits per second. DSL Modem Methods to Access the Internet • Cable Access : – provides a high-speed Internet connection using a cable modem – no phone line is needed ,but a cable modem is required. • Satellite access: - It requires: 1. A satellite dish 2. Phone line and modem for an Internet connection. 9 Methods to access the Internet • Fiber-optic service (FiOS): • Provides fast Internet access . • Fiber-optic lines run directly to users’ homes. •No modems are required. 10 The Internet and the Web: What’s the Difference? • World Wide Web( WWW): - collection of internet resources . FTP, audio, video,……. – Contains billions of documents – Is a portion of the Internet – Uses the Internet as a means to transport information – Is a separate entity from the Internet 11 Features of the Internet • Web page - Document that may include text, graphics, sound, animation, and video. • Web site - collection of Web pages. • Web browser - program that displays Web pages and linked items. • Home page - Web page that displays every time the browser is started. 12 Features of the Internet • Hyperlinks or links: - Bring other documents . • Hypertext - Move to additional related information. • Hypertext Markup Language(HTML) - Create Web pages. • Extensible Markup Language (XML): - Reduce the complexity of HTML. a 13 The Internet and the Web: What’s the Difference? • Internet - Physical connection of network. • Web - Application runs on the top of the Internet architecture. 14 Features of the Internet • Web browser: - Displays a Web document – and the linked documents. • Plug-ins: - Browsers use for extra features such as sound and video. • The most popular browsers – Mozilla Firefox – Google Chrome – Internet Explorer – Opera – Safari 15 Features of the Internet • – – – Windows Internet Explorer: Enables to view the World Wide Web contents. Connects to the Internet. Receives e-mail and assists with downloading and transferring files from the Internet – Displays Web site graphics. – Plays audio and video files associated with a Web site. 16 Exploring Internet Services • Sponsored links: - Displayed as results at a search engine site. – Gain from increasing traffic to their Web site – Placed near the top or on the right side of the search engine results page . • History feature: – History list. – Recently visited Web pages and sites. – Internet Explorer tracks sites visited in the last 20 days. 17 Features of the Internet • Downloading: - Process of transferring a file to the user computer . • Uploading: - Process of transferring a file from the user’s computer. • Internet Protocol (IP) address. - Devices connected to the Internet is given IP . - Four bytes address.(ex:192.168.2.1) 18 Features of the Internet • Uniform Resource Locator (URL) - Identification of an Internet resource’s . - URL is a unique web site address. • URL is made up of: - Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) - Domain name. - Path - Resource name. 19 Features of the Internet • Web servers - Stores web sites. - Process the requests - Send the requested documents. • Ways to access a Web page – Type a URL into the address bar. – Click a tab in the browser window. – Click a hyperlink. 20 Common Top-level Domain Name Top-Level Domain Name Used By Top-Level Domain Name Used By .com Commercial businesses .mil Military .biz Businesses .aero Aviation .edu Educational institutions .net Network organizations .info Information .coop Cooperative .gov Government agencies .org Nonprofit organizations .pro professionals .museum museum 21 Finding Information on the Web • search engines : - Web sites with search capabilities . - Programs that search for keywords. - Index databases of Web pages. - Fast information searches. 22 Finding Information on the Web • Specialized search engines: - Index information • Portals: - Provide organized subject guide links to topics. Example of portal: 23 Exploring Internet Services • Pop-ups: - Windows that display on the screen without being requested. • Pop-Up Blocker: - stops these windows from displaying. 24 Finding Information on the Web • Use Web information for schoolwork. – Access authoritative online sources. – Locate published works. – Provide appropriate online and offline reference citations in your work. • Internet service - Set of standards or protocols. - Identify how computers communicate through the Internet. 25 Exploring Internet Services • Electronic mail (e-mail) : - Sending and receiving messages. • E-mail attachment: - A file included with an e-mail message. E-mail address: - Unique address. - consists of a user name, hosting e-mail service, and the top-level domain. 26 Exploring Internet Services • Spam: - Unsolicited e-mails received by users. - Usually from advertisers. Spam 27 Exploring Internet Services • Instant messaging (IM) systems: – Requires additional software – Real-time communication. – Notifies users . – May be susceptible to—spam 28 Exploring Internet Services • Internet relay chat (IRC): - Ability to join chat groups called channels. • Social networking: - Ability to create large communities online. 2 channels Xaric, a text-based IRC use on Mac OS 29 Exploring Internet Services • Copyright laws: - Protect authors of original works. - Exceptions to this law is the use of small amounts of information for educational purposes. The Copyright Act of 1790 in the Columbian Centinel 30 Summary • The Internet is a global computer network. • The Internet enables computers connected to it to exchange data. • Public or private Internet service providers supply users with access to the Internet. 31 Summary • The World Wide Web, which is made up of billions of hypertext documents, uses the Internet. • Web browsers display Web documents and give users the ability to use linked documents. • A URL is made up of a protocol, a domain, a path, and a resource name. 32 Summary • Search engines permit users to search the databases of the Web. • Information found on the Web should be critically evaluated for being reputable and accurate. 33