* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 24.2 The Sun and the Seasons
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy on Mars wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
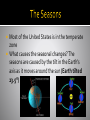
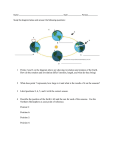
Earth moves in 2 ways: Rotation (spinning of the Earth’s axis) and Revolution (Movement of one body in space around another) Earth’s rotation causes day/night, as Earth rotates from west-east, the sun appears to move from east-west As Earth continues to spin toward the east, the sun sets in the west and night falls As Earth rotates on its axis, it also travels around the sun It takes about 365 ¼ days to complete a full revolution around the sun (Called an Earth year) Different parts of the Earth receive different amounts of sunlight depending on their latitude (measures distance in degrees north or south of the equator) Regions near the equator receive more sunlight than the poles Scientists use lines of latitude to mark out 3 different types of regions within which temperature are generally similar (tropic, temperate, polar zones) 23.5° south-23.5° north =tropic zone 23.5° north-66.5°north and from 23.5° south66.5° south=temperate zones 66.5° north-North Pole and from 66.5° southSouth Pole=polar zones Most of the United States is in the temperate zone What causes the seasonal changes? The seasons are caused by the tilt in the Earth’s axis as it moves around the sun (Earth tilted 23.5°) Because the tilt in the Earth’s axis, the latitude at which the noon sun appears directly overhead changes each day A solstice occurs on 2 days each year when the sun is directly overhead at latitude 23.5° north or 23.5° south In the northern hemisphere the summer solstice begins around June 21st (start of summer, tilted towards sun, daylight hours longer) In the northern hemisphere 6 months later on about December 21st the winter solstice marks the beginning of winter (tilted away from sun, daylight hours shorter) Seasons affected by the tilt of the Earth not where it is in its orbit Marks the beginning or spring and autumn (halfway between the solstices) At an equinox neither hemisphere is tilted toward the sun, and the lengths of the days/nights are equal The vernal equinox which occurs about March 21st in the northern hemisphere marks the start of spring The autumnal equinox which occurs about September 22nd in the northern hemisphere marks the star of autumn (Noon sun is directly overhead at the equator)