* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lactose Intolerance Lesson
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
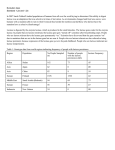
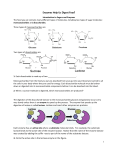
LACTOSE INTOLERANCE Lactose intolerance is the inability to digest lactose, a carbohydrate found in milk and other dairy products. Lactose To properly digest lactose, each lactose molecule must react with one molecule of water. This reaction breaks the polymer into two monomers, which can then be used for energy. Lactose O H H Water Most humans are able to catalyze the breakdown of lactose using an enzyme called lactase. O H H Lactase If lactose does not break apart, it cannot be used for energy. It sits in the intestines and starts to ferment. Fermentation of lactose in the gut, causing gas: Lactose intolerant individuals do not produce the lactase enzyme, or they produce it incorrectly. Identify the reactants in this reaction. Lactose and H2O O H H Lactase Explain why the lactose and water will not react without the help of an enzyme. High A.E. O H H Lactase Explain how the enzyme lactase catalyzes this reaction. Lowers the A.E. O H H Lactase Explain how the enzyme lactase lowers the A.E. of this reaction. Holds the reactants in place Makes the reaction easier O H H Lactase Explain why lactose-intolerant individuals could not use a different enzyme to catalyze the breakdown of lactose. The fit between enzyme and substrate must be precise Lock and key Explain why a person would have trouble digesting lactose when they have a high fever. Enzymes are proteins Change shape at high temperatures