* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Types of Economies
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
Transition economy wikipedia , lookup
Participatory economics wikipedia , lookup
Nouriel Roubini wikipedia , lookup
Workers' self-management wikipedia , lookup
Economic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Sharing economy wikipedia , lookup
Criticisms of socialism wikipedia , lookup
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Economics of fascism wikipedia , lookup
Market socialism wikipedia , lookup
Uneven and combined development wikipedia , lookup
Post–World War II economic expansion wikipedia , lookup
Economic planning wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Italy under fascism wikipedia , lookup
Social market economy wikipedia , lookup
Production for use wikipedia , lookup
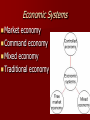
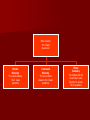
7.3 Types of Economies Economic Systems Market economy Command economy Mixed economy Traditional economy Market Economy An economic system in which businesses and consumers, not the government, decide what is produced. It is also known as Free Enterprise or Capitalism. The economy is influenced by Competition, Supply, and Demand. No pure market economy exists, thus most economies in the world are Mixed. Most market economies exist in the western countries. Many criticize the current “bailouts” going on in our current economy. Free Enterprise or Capitalism Capitalism generally refers to an economic system in which the means of production are all or mostly privately owned. Profit is the main motive. In a capitalist economy, “Greed is Good” because a person’s want to make profit will drive the economy. If a producer of a product creates and sells something the public does not want, the consumer will simply not buy it. The producer will go out of business. Gordon Gekko says Greed is Good Many argue that corporation executives have taken this concept too far! Consumer sovereignty - the idea that consumers control the market with their wants. If consumers do not like an item, they will simply not buy it and it will go out of business. Competition - more than one type of a product for consumers to choose between. Competition lowers the price for consumers and increases the product’s quality. Private Property - consumers in a market economy have a choice what they buy and own. Profit Motive - the want to make money drives the American economy. Adam Smith – “Father of Capitalism” Wealth Adam Smith of Nations - 1st modern economic book based on free market, profit motive, and laissez-faire economics. Laissez-faire - “to let alone”. Laissez-faire was an idea that promoted free trade of the individual and as little government involvement as possible. Invisible Hand - Smith argued that the pursuit for your own financial success will guide the economy like an invisible hand. An individual’s self-interest will benefit society’s economy as a whole. Command Economy An economic system in which the Government controls everything in the economy. It is also known as a planned economy because the government plans every aspect in the economy. There is no private property or ownership. It is all shared by everyone. Many Communist countries have changed their economic beliefs. Karl Marx – “Father of Communism” Karl Marx Communist Manifesto Wrote about a classless utopian society where government owned all of the means of production. VI Lenin used his ideas to set up the USSR. A dictator is needed to control this economy. Marx is often called the father of communism. The Cold War (1945-1991) developed from the tension between the United States and the Soviet Union. It was a clash of different ideas about economic systems and government control. It led to wars in Korea and Vietnam for the USA. Many feared Communism would spread world-wide. A Mixed Economy mixed economy is an economic system that incorporates the characteristics of several different economic systems. Usually combines a mixture of market (free) and command (government) economies. The individual will have the economic freedom of choice intertwined with government planning (like Social Security or free healthcare). Does this sound like the USA? John Maynard Keynes The Keynesian Theory – Economic system that promotes mixed economies. – He stressed the importance of government involvement for a successful economy. – During the Great Depression, he felt it was the government’s duty to help. FDR eventually used many of Keynes’s ideas. Fiscal Policy – the strategy of how the government is going to spend its revenue. Deficit Spending – The government spending more money than it takes in. John Maynard Keynes Traditional Economy A traditional economy is the least developed type of economy because it makes economic decisions the way it has always been. It is based on tradition, custom, and the way things have always been done. They have not changed very much over time. Most traditional economies are agricultural only. Often they exchange goods by bartering (trade). Traditional economies are not efficient. They offer few goods and it is very much based on labor. They are often called “Third World Countries” Found in agricultural parts of Asia, Africa, and South America. Most Successful Economic Systems combine individual freedom and some government planning. • Communism • China • North Korea • Cuba Command Economy Mixed Economy • Socialism • Canada • Western Europe • Mixed Market • USA • Mostly market with some government planning Mixed Market Economy Market Economy • Capitalism • Free Enterprise • NO PURE MARKET ECONOMY EXISTS! Who answers the 3 basic questions? Market Economy The people answer the 3 basic questions Command Economy The Government Answers the 3 basic questions Mixed Economy The market and the Government work Together to answer the 3 questions