* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ulcerative Colitis and Colectomy
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
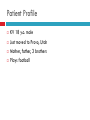
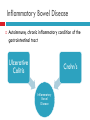
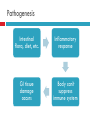
ULCERATIVE COLITIS Brittney Hudson Patient Profile KV 18 y.o. male Just moved to Provo, Utah Mother, father, 3 brothers Plays football Medical History Ear tubes Disease Progression Bloody diarrhea x 3 months June 2011 – 12-14 times/day Fatigue Decreased appetite Lost 10-15 pounds Diagnosis Colonoscopy – July 2011 Ulcerative Colitis Inflammatory Bowel Disease Autoimmune, chronic inflammatory condition of the gastrointestinal tract Ulcerative Colitis Crohn’s Inflammatory Bowel Disease Etiology Immune System GI System Genetics Environmental Factors Pathogenesis Intestinal flora, diet, etc. Inflammatory response GI tissue damage occurs Body can’t suppress immune system Signs and Symptoms Abdominal pain Diarrhea Nausea Vomiting Osteopenia Dermatitis Hepatobiliary complications Disease effect on Nutrition Weight loss Electrolyte imbalances Anemia Malabsorption Food allergies or aversions Fear of eating Self-imposed dietary restrictions General Treatment Recommendations Induce and maintain remission of disease Corticosteroids Anti-inflammatory agents Immunosuppressive agents Colectomy Ileostomy Beginning Treatments Prednisone Constantly changing doses Unresolving symptoms Drugs/Medications Medication Purpose Prenidsone Anti-inflammatory and Immunosuppressive Methotrexate Immunosuppressive Remicade Anti-inflammatory and Immunosuppressive Zofran Nausea Side Effects of Prednisone Weight gain Acne Hyperlipidemia Hypertension Osteopenia Joint pain Procedures Colectomy with ileostomy placement on September 25, 2012 Diet before Colectomy Poor Didn’t feel like eating Elemental formula – Neocate Jr Diet after Colectomy TPN and clear liquids – small bowel obstruction Lost 25 pounds Taken off TPN due to hepatitis – October 18, 2012 ALT - 482 U/L (10-40 U/L is normal) AST - 200 U/L (15-45 U/L is normal). UVRMC Admitted on October 25, 2012 Dehydration Weight Loss and Malnutrition Intractable nausea Malnutrition When nutritional reserves are depleted or nutrient intake is inadequate to meet the body’s daily metabolic needs. Signs and Symptoms Weight loss Protein wasting Fatigue Refeeding Syndrome When patients are moderately or severely malnourished Tissue growth Not enough electrolytes Fluid overload KV’s Treatments NJ tube feeding was started Ate sparingly Ileostomy takedown NJ tube feeding started again KV pulled it out TF replaced KV vomited it out TPN started Psychiatric Counseling Drugs/Medications Medication Purpose Prenidsone Anti-inflammatory and Immunosuppressive Cyproheptatdine (Periactin) Appetite stimulator Zofran Nausea Calcium Supplementation Magnesium “ Potassium “ Sodium “ Zinc “ Multivitamin “ Nutrition Assessment Food/Nutrition Related History Unremarkable before diagnosis After diagnosis: poor appetite, anxiety Diet Clear Liquid Regular Full Liquid Clear Liquid NPO Regular NPO Regular Clear Liquid NPO Regular NPO Regular Start 11/5 11/4 11/3 11/1 10/31 10/29 10/29 10/28 10/27 10/27 10/26 10/26 10/25 Food/Nutrition Related History Diet Start 3 L standard TPN with 20% lipids 2 times per week 11/6 Peptamen AF 10 mL/hr 11/3 Peptamen AF 50 mL/hr 10/28 Peptamen AF 35 mL/hr 10/27 Anthropometrics Height: 5’8” Weight 190 180 Pounds 170 160 150 140 130 120 Weight Biochemical Data Magnesium 2.5 2 m 1.5 E q / L 1 0.5 0 Magnesium Biochemical Data Phosphorus 6 5 4 m g / 3 d L 2 1 0 Phosphorus Biochemical Data Potassium 5 4.5 4 m 3.5 E q 3 / L 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 Potassium Biochemical Data Albumin 6 5 4 g / 3 d L 2 1 0 Albumin Nutrition Focused Physical Findings Attentive and cooperative Respiratory and cardiovascular systems normal Abdomen was soft, non-tender, active bowel sounds No rashes or legions OK muscle tone Comparative Standards Calories Kcals 1775 – 2130 Protein kcals/ kg gm gm/kg 25-30 85 - 107 1.2 – 1.5 Fluid mL mL/kg Based On 2840 40 Actual Body Weight (71 kg) Nutrition Diagnosis Inadequate oral intake related to nausea/vomiting/dehydration as evidenced by weight loss of 30 pounds the past two months. Nutrition Intervention Problem Long-Term Goal Inadequate oral intake related to nausea/vomiting/dehydration as evidenced by weight loss of 30 pounds the past two months. Increase oral intake to the point where the patient will be able to consume enough to meet estimated needs without the use of PN or EN. Short-Term Goal Have patient consume 10-15% of calories through oral intake and gradually increase to keep the gut stimulated. Specific Intervention and Client Objectives 1. Intervention: Food and/or Nutrient Delivery a. Patient switched between a clear liquid, full liquid and regular select diet throughout his hospital stay depending on his tolerance. A select diet means he was able to call down and order food when he felt like it. Objective: Patient will call down and order something from room service everyday. Specific Intervention and Client Objectives 2. Intervention: Nutrition Education a. Review nutrition relationship to his disease Objective: Patient will be able to explain the effect his disease and health status has on his nutritional status. b. Recommended modifications Objective: Patient will be able to explain how to best increase his oral intake (i.e. eat one thing and see how his body reacts so he can figure out if any certain foods cause a bigger problem for him than others). Nutrition Diagnosis Altered GI function related to ulcerative colitis and colectomy as evidenced by need for TPN and/or EN. Nutrition Intervention Problem Long-Term Goal Altered GI function related to ulcerative colitis and colectomy as evidenced by need for TPN and/or EN. Discontinue TPN and/or EN as soon as patient is able to consume most of his estimated calories by mouth. Short-Term Goal Provide enough calories and protein through TPN and/or EN to meet his estimated needs while avoiding refeeding syndrome. Specific Intervention and Client Objectives 1. Intervention: Food and/or Nutrient Delivery a. Patient was started on Peptamen AF after being admitted to UVRMC. Objective: Patient will receive adequate calories and protein to meet his needs and not have any issues with the feeding tube. Objective: Will be infused at 50% (35mL/hr) of needs on Day 1, 75% (50 mL/hr) of needs on Day 2 and 100% (70 mL/hr) of needs on Day 3. Target infusion rate of Peptamen AF at 70 mL/hr will provide 1660 mL, 2015 kcals, 126 g protein and 1344 mL free fluid which meets his needs. Specific Intervention and Client Objectives b. Patient was started on TPN after his feeding tube was dislodged because of vomiting. Objective: Patient will be able to tolerate TPN better than EN. Objective: Standard TPN will be infused 2.5 L/day and 20% lipids 2 times/week providing 2060 kcal and 100 g protein which will meet KV’s estimated needs. Specific Intervention and Client Objectives 2. Intervention: Nutrition Education a. Purpose of the nutrition education Objective: Patient will be able to explain the purpose of enteral nutrition and parenteral nutrition and the role it will play in his recovery. b. Survival Information Objective: Patient will be able to explain how he will be able to wean off of EN and/or TPN (i.e. tolerance to oral intake and adequate oral intake). He will also explain his role in the process (i.e. being willing to try foods and not being anxious about it). Nutrition Monitoring and Evaluation PO intake Refeeding syndrome Tolerance of EN and TPN Appropriateness of Care Pretty appropriate Multiple doctors Back and forth Difference of opinions Dietitian not consulted each time TPN not lowered when LFTs started increasing Discharge To home on TPN References (1) American Dietetic Association. Nutrition Care Manual. http://nutritioncaremanual.org/index.cfm. (2) Mahan LK, Escott-Stump S. Krause’s Food and Nutrition Therapy. 12th ed. St. Louis: Saunders Elsevier; 2008. (3) Mayo Clinic. Prednisone and other corticosteroids. http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/steroids/HQ01431 (4) Medline Plus. Methotrexate. http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/druginfo/meds/a682019.html#side-effects (5) Web MD. Drugs &Medications. http://www.webmd.com/drugs/drug-16554Remicade+IV.aspx?drugid=16554&drugname=Remicade+IV (6) Pagana KD, Pagana TJ. Mosby’s Manual of Diagnostic and Laboratory Tests. 4th ed. St. Louis: Mosby Elsevier; 2010. (7) Periactin Side Effects. http://www.drugs.com/sfx/periactin-side-effects.html (8) Utah Valley Regional Medical Center Standards of Care (9) The American Dietetic Association. International Dietetics & Nutrition Terminology Reference Manual. Chicago: American Dietetic Association; 2011.