* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War II and it`s Aftermath
Collaboration with the Axis Powers wikipedia , lookup
German military administration in occupied France during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Pursuit of Nazi collaborators wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II casualties wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II
1939-1945
Hitler’s Lightning War
Germany used “Blitzkrieg” – or lightening war
Planes
bombed airfields, factories, towns, etc.
Then tanks and troops roared into the country
Poland was conquered within a month
Soviet forces took control of
Estonia,
Latvia, Lithuania and part of Finland
April 1940 – Germans in Norway, Denmark,
Netherlands and Belgium
France Falls to Axis Powers
Germany heads toward Paris – Italy
declares war on France
22, 1940 – French surrender
Southern part left as a puppet government
headed by Marshal Philippe Petain.
June
Headquarters in the city of Vichy
France (cont.)
Charles de Gaulle – French general, set
up a government in exile in London.
Committed
to re-conquering France.
Organized Free French military who battled
the Nazis until France was liberated in 1944.
Hitler and the Nazis in Paris
WWII Technology
Air power takes prominent role
Luftwaffe-
German air force
Parachute troops role increases
Tanks were much improved from WWI
Deadlier bombs
Radar – to detect planes
Sonar – to detect submarines
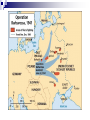
Operation Sea Lion
The Battle of Britain
Known
as the “London Blitz”
8/12/1940 – air attacks on southern England
Germans bombed London for 57 nights
Considered a failure because British did not quit
Continued until May 10,1941
Damages from the London Blitz
Damages from the London Blitz
Damages from the London Blitz
The Mediterranean and the Eastern
Front
Mussolini takes North Africa in September
of 1940 while the Battle of Britain was
going on.
Attacked British controlled Egypt.
Britain strikes back in December and by
February 1941 Italy needs help.
The Mediterranean and the Eastern
Front (Cont.)
Germans come in with the Afrika Korps
and win victories over the British in
northern Africa
Led
by General Erwin Rommel “Desert Fox”
Italy takes Greece and Yugoslavia
The Desert Fox – Erwin
Rommel
Operation Barbarossa
1941 attempted conquest of the USSR
Why invade USSR?
Plentiful
Soviet resources
3 million Germans caught Stalin unprepared
USSR lost 2.5 million troops
Germans were halted by Russian weather
Many Russian people suffered starvation
American Involvement Grows
Lend-Lease Act (1941)
Selling
or lending of war
materials to countries
“Vital to US defense”
Atlantic Charter (Aug.
1941)
FDR
and Churchill agree
on the “Final destruction
of Nazi tyranny”
Pearl Harbor – Day of Infamy
12/7/1941–Japan surprise attacks
American fleet @ Pearl Harbor (Hawaii)
2,400 American
deaths
US declares war on Japan (12/8/1941)
Germany,
later
Italy declare war on US four days
Total War
Factories stopped making cars & refrigerators &
made planes & tanks
Shoes and sugar were rationed
Use of propaganda
War ended unemployment of the depression
Japanese people in US and Canada
Lost their jobs and property
Forced into camps
Seen as a security risk
US Propaganda
Anti - German
US Propaganda – Anti - Japanese
US Propaganda
Anti - Japanese
War Bond Advertisements
“Do your part” Campaign
No room for debate
Japanese Internment Camps 19421945
US government forced over 100,000
Japanese-Americans to relocate
Mostly
Many lost their homes and businesses
Could
from the western states
only keep what they could carry
Conditions in camps
Barbed-wire-surrounded
Un-partitioned
Cots
for beds
Armed guards
toilets
Japanese Internment Camps
Operation Torch
The North African Campaign (1942)
Allied
invasion of North Africa
Led by British and US Forces
British
led by Gen. Bernard Montgomery
US led by Gen. Douglas MacArthur
Turning point in North Africa
El Alamein,
Egypt
British forces finally stop Gen. Irwin Rommel
The Red Army Resists
Turning Point in the Soviet Union
Battle
of Stalingrad
Street by street and house by house battles
Over one million Soviet soldiers died
1943 Germans surrender – 300,000 killed or
injured
Soviets
USSR
then drive Germans back through
Mission to Take Back France
Turning Point in Europe
D-Day
June 6th 1944
Allied paratroopers and ferried troops (176,000)
Fought against heavy gunfire @ the Battle of
Normandy
By
September France was free
Now Allies push towards Germany
Allies advance into Germany
Allies advance into Italy
Allied forced landed in Sicily in 1943
Controlled
Sicily in one month
Italy surrendered within two months
Fighting
continued until the end of the war
Guerillas capture and execute Mussolini
Created another front for the Germans to
worry about
Battle of the Bulge
Germany fought on three fronts
US
to the west (in France)
Soviet Union to the east
US and UK to the south (in Italy)
Germany on the offensive for the last time
75-mile
front in the Ardennes Forest
Germans able to push into Allied lines
Ultimately unsuccessful push
The End in Europe
Germany surrounded by Allied Forces
Hitler commits suicide (4/30/1945) in his
underground bunker
7th Germany surrenders
May 8th = VE Day or Victory in Europe Day
May
Surrender in
France
Surrender in USSR
The Pacific Campaign
Major Battles
Battle
of the Coral Sea
New style of fighting – ships used airplanes
instead of mounted guns
US stopped the Japanese southward advance
Battle
of Guadalcanal
Six month battle
US Marines captured a huge Japanese Air Force
base
Japanese lost 24,000 troops
Toward Victory
Turning Point in the
Pacific Campaign
Battle
of Midway Island
Japanese Navy would
reach no further
US now started to push
closer to Japan
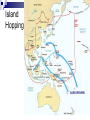
Marked the beginning of
“Island Hopping”
The recapture some
islands while bypassing
others
Island
Hopping
Island Hopping
Defeat of Japan: Invasion vs.
the Bomb
FDR dies--Harry Truman takes office
US estimated that an invasion would cost
millions or more in casualties
Why did Truman drop the A-Bomb?
An
invasion would be too costly
To impress the Soviet Union with US power
The Atomic Bomb
Hiroshima (8/6/45)
Plane was the “Enola Gay”
Atomic Bomb named “Little Boy”
Killed more than 70,000
Nagasaki (8/9/45)
Plane was “Bockscar”
Atomic bomb named “Fat Man”
Killed more than 40,000 people
September 2nd 1945
Peace treaty is signed
Hiroshima
Hiroshima
Hiroshima
Nagasaki
Nagasaki
Atomic Bomb Survivors
Atomic Bomb Survivors
The Holocaust:
Nazi Genocide of the Jews
Kill all people who were racially inferior
Jews, Slavs, gypsies and mentally ill
Forced Jews to live in ghettos and
concentration camps and wear yellow
stars
“Final Solution” of the Jewish problem =
Genocide
The Death Camps
Auschwitz, Sobidor, Treblinka & Lodz
Gassed in showers and used in medical
experiments
By 1945, over 6 million Jews were killed
5
million other people were killed as well
The Infamous Yellow Stars
THE WARSAW GHETTO
Auschwitz
Location: Poland: 37 miles west of Krakow
Operational May 1940 – Jan. 1945
Estimated 1.1 million killed here
Largest of the German concentration camps.
The SS authorities established three main camps near
the Polish city of Oswiecim
Auschwitz I in May 1940;
Auschwitz II (also called Auschwitz-Birkenau) in early 1942
Auschwitz III (also called Auschwitz-Monowitz) in October 1942.
Wall where prisoners were shot after
trials.
Auschwitz I
Block 11, also
known as the
death block,
since it was
known no
prisoners who
went in here
came back alive.
Gallow, where the SS officer in charge
of the camp was hung at the end of the
war.
Auschwitz- Birkenau
Death's Gate
What is left of the wood camp.
The brick camp, currently undergoing
preservation
Tracks leading
into Birkenau
Track platform, where selection took
place. Before liberation there had
been two gas chambers at the end of
the tracks on each side.
Auschwitz (cont.)
On January 27, 1945, Auschwitz was liberated
by Soviet troops, a day commemorated around
the world as International Holocaust
Remembrance Day.
In 1947, Poland founded a museum on the site
of Auschwitz I and II, which
By 1994 had seen 22 million visitors—700,000
annually—pass through the iron gates crowned
with the infamous motto, Arbeit macht frei ("work
makes you free").
Results of World War II
Casualties
Estimated
Genocide
Due
60 million people died from the war
to the “Final Solution”
Occupation
Control
of Germany and Japan
Aftermath of World War II
War Crimes Trials
The Split of Germany
The Creation of the United Nations
The Beginning of the Cold War
War Crimes Trials
The Holocaust
Death
camp evidence discovered after the
war
Nuremberg Trials
“Crimes
against humanity”
Trials showed that political & military leaders
could be accountable for wartime actions
Postwar Japan
Defeat left
country in ruins.
Was stripped of
its colonial
empire.
Occupied by the
US
US General Douglas MacArthur and Emperor
Hirohito
Occupation by US
General Douglas MacArthur in charge of US
occupation
Began process of demilitarization
Disbanded
Japanese army.
Left with a small by police force.
Democratization of Japan
up new constitution for Japan – Feb. 1946
Accepted and went into affect May 3, 1947.
Drew
Occupation Brings Deep Changes
Japan now a constitutional monarchy.
Emperor no longer considered divine
Became just a figurehead
New constitution guaranteed that the political
power
rest the people
Two House Parliament elected by the people called
the Diet
All citizens over the age of 20, including women had
the right to vote
Article 9 stated the Japanese could no longer make
war, only fight if they were attacked.
Occupation (cont.)
Sept. 1951 the US and 47 other national
sign of formal treaty with Japan.
This
officially ended the war.
Six months later US occupation was over.
Japan agreed to a continuing US presence to
protect their country.
The Creation of the United Nations
Allies set up international organization to
ensure peace
General Assembly – all nations belong
Security Council
5
Permanent members: US, Russia, Britain,
France and China
The United Nations