* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Physics Review with Key Ideas #1-19
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Derivations of the Lorentz transformations wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Speeds and feeds wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
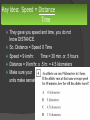
Use your yellow answer document Key Idea: Average speed = Total distance Total Time Total distance = 50 meters Total Time = 25 min. 50/25 = 2 meters/min. Check units and make sure your answer makes sense! Key Idea: The slope of a distance vs. time graph tells you the SPEED of the object. Slope = Rise Run Rise = change in distance Run = Change in time Distance = Speed Time Key Idea: follow the pattern and predict A spring scale measures force in Newtons like the ones we used in class. The pattern for distance pulled is every .5 cm = increase of 2 N So you can predict: 3 cm = 12 N And 3.5 cm = 14 N Key Idea: Speed = Distance Time They gave you speed and time, you do not know DISTANCE. So, Distance = Speed X Time Speed = 9 km/hr. Time = 30 min. or .5 hours Distance = 9 km/hr. x .5 hr. = 4.5 kilometers Make sure your units make sense! Key Idea: Must use Speed = Distance Time To solve for TIME Q: Time = Distance Speed Time = 100 meters = 2 m/s Time = 50 seconds Check units and make sure it makes sense!!! D S T Key Idea: Velocity is SPEED in a given DIRECTION What is the only answer that includes both UNITS for SPEED and DIRECTION? Key Idea: Velocity is SPEED in a given DIRECTION If speed changes, velocity changes If position changes, velocity can still be constant If direction changes, velocity changes If acceleration (change in speed) changes, velocity changes. So only B could be correct. Key Idea: The slope of a distance vs. time graph tells you the SPEED of an object. Slope = Rise Run Rise = change in position (distance) Run = Change in time Distance = Speed Time Rise = 18 – 0 m___ = 18 m Run = 10 s – 4 s 6s Speed = 3 m/s Key Idea: The slope of a speed vs. time graph tells you the acceleration of the object First identify what it is asking. It is asking how FAR did it travel. So it is traveling at 10 m/s for 2 seconds. D= S X T D = 10 m/s X 2 sec. D = 20 m D S T Use your yellow answer document Key Idea: Force is described with both direction (arrows) and magnitude (numbers) The forces have the same magnitude, but different directions, so they are DIFFERENT, so you can eliminate A and B. So D is the only possible answer. Key Idea: When forces act in opposite directions, you find their difference to calculate net force. Difference = 200 N – 150 N Net force = 50 N Key Idea: When forces are balanced, an object does not CHANGE it’s motion. Balanced forces cause no CHANGE in motion, unbalanced forces cause CHANGE in motion. The forces are BALANCED. The ball is falling, so we know it will keep falling due to gravity, but will fall at a CONSTANT speed. Key Idea: The net force causes an object to accelerate in the direction of the force. Find the Net Force on the box by finding the difference between up/down and left/right The net forces acts 30 N DOWN and 10 N to the LEFT. So it will move Down and to the Left Key Idea: Force = Mass X Acceleration This questions wording is CONFUSING!! It is on purpose. Identify what it is asking: When would you need to add MORE force to get the same ACCELERATION? A and B are opposites C and D would both speed up the box by reducing friction So if you increase mass you must increase force Density and Buoyancy Density = Mass/Volume If an object is less dense than the fluid it is in, it will float, if it is more dense it will sink. The volume of an object is equal to the volume of the fluid it displaces. Buoyant force = the weight of the fluid displaced. If buoyant force = weight it will float, if buoyant force is less than the weight, it will sink. Key Idea: Density = _Mass_ Volume Density = 64 g 8 ml = 8 g/ml The formula is given to you on the reference chart. USE IT!! Key Idea: Objects that are less dense than water Keythose Idea: will float, more dense than water will sink. Calculate the density of all 4 samples. Remember the trick of dividing by base 10: move the decimal to the left Which is LESS than 1 g/ml? #3 will float. The rest will sink Key Idea: Objects that are less dense than water will float, those more dense than water will sink. IF it is more dense than 1.14 g/cm3 it will sink, if it is less dense it will float. Only ironwood is more dense than 1.14 g/cm3