* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download thin film waveguides and sol-gel processing
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
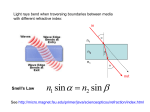
NTSE - Nano Technology Science Education Project No: 511787-LLP-1-2010-1-TR-KA3-KA3MP THIN FILM WAVEGUIDES AND SOL-GEL PROCESSING READING BEFORE EXPERIMENT Have you ever thought why internet is faster when you use fiber optic connections? Or, “What is the relation between the Internet and fiber optics?” It is said that Internet resembles the human brain. Can you think about why it is so? • Fiber Optics is a data-delivery system transmitting light and sound through glass fibers. In telecommunications, the fibre optic technology has replaced the copper-wire technology by delivering information 1000 times faster and 100 times farther. • An optical fiber typically includes a core surrounded by a cladding material with a low index of refraction (Fig. 1). Light is kept in the core by total internal reflection, and the fiber acts as a waveguide. Figure 1: Optical Fibre(1) • The index of refraction is a way of measuring the speed of light in a material. Light travels fastest in a vacuum, like in outer space. The speed of light in a vacuum is about 300,000 kilometers (186,000 miles) per second. Index of refraction is calculated by dividing the speed of light in a vacuum by the speed of light in the other medium. The refraction of a vacuum is therefore 1, by definition. The typical value for the cladding of an optical fiber is 1.52. (The index of refraction of the cladding is less than that of the core, causing rays of light leaving the core to be refracted back into the core) • The total internal reflection is a phenomenon that happens when a propagating wave strikes a medium boundary at an angle larger than a particular critical angle with respect to the normal to the surface. 1 • If the refractive index is lower on the other side of the boundary and the incident angle is greater than the critical angle, the wave cannot pass through, and is entirely reflected. • Internet fibers optics resembles the brain, because the functions depend on the ability of transmitting electrochemical signals to other cells, and responding appropriately to the signals received from other cells. Moreover, the myelin sheats covering the axons in the brain cells (neurons) resemble the claddings. • Fibers are widely used in other areas as in light guides in medical applications or for decorative applications, including signs, art, fashion, and toys. Some jewelry boutiques use optical fibers to illuminate their crystal showcases from many different angles. Figure 2: Propogation of light through.(2) Figure 3: The brain cell.(3) Figure 4: Fiber optics used in desing and fashion.(4) So, what can be the relation between “thin films” and “sol-gel processing”? The term “sol-gel” refers to a process in which solid nanoparticles dissolved in a liquid (a sol), and brought back together in a controlled manner, to form a continuous three-dimensional network extending throughout the liquid (a gel).(5) The starting materials in the preparation of "sol" are usually inorganic metal salts or metal organic compounds, like metal alkoxides. Sol-gel is a chemical solution process used to make ceramic and glass materials in a wide variety forms of thin films, fibers, or powders. These include ultra-fine or 2 spherical shaped powders, thin film coatings, ceramic fibers, microporous inorganic membranes, monolithic ceramics and glasses, and extremely porous aerogel materials. In a typical sol-gel process, the precursor is subjected to a series of hydrolysis and polymeration reactions to form a colloidal suspension, or a "sol". Further processing of the "sol" enables one to make ceramic materials in different forms: Thin films can be produced on a piece of substrate by spin-coating or dipcoating. Wet gels can be produced if the "sol" is cast into a mold. With further drying and heat-treatment, the gel is converted into dense ceramic or glass articles. Aerogel, a highly porous and extremely low density material, can be obtained if the liquid in a wet gel is removed under a supercritical condition. Ultra-fine and uniform ceramic powders are formed by precipitation, spray pyrolysis, or emulsion techniques. Ceramic fibers can be drawn from the sol by adjusting the sol’s viscosity. An overview of the sol-gel process is presented in the figure 5. Figure 5: The sol-gel processes.(6) The invention: When glass fibers of core/cladding design were introduced in the early 1950s, they were only used in short lengths because of the presence of impurities. In 1966, electrical engineers Charles Kao and George Hockham proposed using fibers in telecommunication and within two decades silica glass fibers were being produced with sufficient purity that infrared light signals could travel through them for 100 km or more. In 2009 Kao was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics for his work. Subsequently, plastic fibers were introduced, which are cheaper to produce and more flexible than glass fibers, but their greater reduction of light limits their use to shorter links within buildings or automobiles.(7) 3 Figure 6: Picture of Charles Kao in his lab.(7) Activity-1: MAKE YOUR OWN FIBER OPTIC You will need: An large and empty plastic bottle Laser pointer Drill Access to a sink How to do the experiment: 1. Drill a hole into the middle of the plastic bottle. 2. Cover the hole with your finger and fill the bottle with water. Do not put the lid back on the bottle. Keep the bottle near a sink. 3. Shine a laser pointer through the back of the bottle so it shines straight out through the drilled hole. 4. Take your finger away from the hole and watch where the light shines. Why did this happen? What you see is a spot of light at the bottom of the curved stream of water. But as we all know that light travels in straight lines - how did this happen? If you sit under water in a swimming pool and look straight up, you can usually see a wavy image of the ceiling and other swimmers above the surface. However, if you try looking at the surface from a shallow angle, you will notice that you can no longer see the ceiling but the surface behaving a bit like a mirror. This phenomenon is called total internal reflection and occurs when the angle between the surface of the water and the direction of the travelling light is quite small. 4 Activity-2: MAKE YOUR OWN THIN FILM You will need: Shallow pan Narrow piece of black paper Clear nail polish How to do the experiment: 1. Holding onto one end, slide the paper into the pan. Make sure it’s completely under water (except for the end you’re holding). 2. Use the brush to drip one drop of nail polish onto the surface of the water. 3. Watch what happens—the polish instantly spreads out into a thin film! 4. Lift the paper up and out of the water. 5.The film of nail polish will stick to the paper. Does the nail polish still look clear? Why did this happen? The nail polish spreads out into a thin film, which creates iridescent colors on the paper. The film is only a few hundred nanometers thick. The film is slightly thicker in some places and thinner in others. The film reflects light differently depending on how thick it is, so you see different colors. Thin films can reflect light in special ways, because they’re only a few hundred nanometers thick. That’s in the same size range as the wavelength of visible light. Soap bubbles and oil slicks are some other examples of thin films that create beautiful, iridescent colors. Activity-3: Watch the video of “Fiber optic thin film fabrication by sol-gel processing”. Activity-4: Watch the video about fiber optics at “http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0MwMkBET_5I” 5 EVALUATION A. Fill in the blanks with an appropriate expression. (5 minutes) 1- A …………….. is a stable dispersion of colloidal particles or polymers in a solvent. 2- …………….. is a chemical solution process used to make ceramic and glass materials in the form of thin films, fibers , or powders. 3- A ……….. consists of a three dimensional continuous network, which encloses a liquid phase. 4- An ………… is essentially a waveguide for light. B. Select True (T) or False (F) for each of the following statements. (5 minutes) ( ) 1- There is a connection between the Internet and fiber optics. ( ) 2- Optical fibers have a core and cladding that surrounds the core. ( ) 3- Fiber Optics is a data-delivery system transmits light through glass fibers connects the developed world delivers information 100.000 times faster than copper-wire technology. ( ) 4. The index of refraction of the cladding is higher than that of the core. REFERENCES (1) http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/205837/fibre-optics (2) http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Optical_fiber (3) http://webspace.ship.edu/cgboer/neuron.gif (4)lhttp://www.lumigram.com/catalog/images/luminous%20fiber%20optic%20dress%20(Lu miT(op%20Sophia)%201.jpg (4) lhttp://www.luxurylaunches.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/tablecloth2.jpg (5) http://www.aerogel.org/?p=992 (6) http://www.lswn.it/files/img_1_sol_gel_process.jpg (7) http://www.goforich.co.uk/cafescientifique/images/kao_1219.jpg http://www.aflglobal.com/Products/Fiber-Optic-Cable/OPGW.aspx (Fiber optic cable) http://sewreview.com/img/gallery/913.jpg (Fiber optic fashion) http://www.bbc.co.uk/norfolk/features/ba_festival/ks_fibreoptics.pdf http://www.doctormadscience.com/video/fiber-optic-water/ http://www.nisenet.org/sites/default/files/catalog/uploads/9881/diy_nano_print_rainbow film 03 21.pdf http://www.uio.no/studier/emner/matnat/kjemi/KJM5100/h06/undervisningsmateriale/10 KJM5100_2006 sol gel_d.pdf http://eltexamprep.com/files/Chapter%207%20The%20Internet%20and%20Fiber%20Optic s.ppt 6