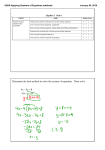
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Little Penguin - Wildlife Land Trust
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Conservation biology wikipedia , lookup
Conservation psychology wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Source–sink dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Bermuda petrel wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Conservation movement wikipedia , lookup
Habitat destruction wikipedia , lookup
Mission blue butterfly habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Little Penguin Little penguins - (c) iStockphoto/Julie Wax At a glance The fairy penguin ( Eudyptula minor ) is the smallest speciesSphenisciformes of its order ( ), typica Lacking any seasonal variation in appearance, the head, fins and upperparts are generally blue, with sla Little penguins (also known as fairy penguins) are generally inshore, opportunistic feeders with a diet of mainly small schooling fish such as anchovies (Engraulis australis) and pilchards (Sard inops neopilchardus ), as well as squid and other small ocean dwelling creatures. Their nesting behaviour is also 1/3 Little Penguin opportunistic, using anything that provides relative shelter where burrowing conditions are poor, including pipes or under vegetation. Typically however, they burrow in sand dunes, rock piles, sea caves and occasionally under buildings. There's usually a tunnel 60 to 80 cm long with a nest bowl at one end large enough for a penguin to stand in. Like many seabirds, they have a fairly long lifespan (six to seven years) and reach sexual maturity at about three years for males and two years for females. They are monogamous only within a breeding season and share incubation and chick rearing duties for the first three months. Nest building is usually in September, producing a clutch of one or two white or lightly mottled brown eggs. Although both eggs normally hatch, competition for food usually leads to just one chick fledging successfully. Found in Australia and New Zealand, their northern distribution is likely restricted by food availabilit Humane Society International (HSI) has long been involved with the species, successfully nominating the 'Little penguin population, Manly Point area' as an Endangered Population under the NSW Threatened Species Conservation Act, 1995, in 1997. While considering HSI's nomination, the NSW Scientific Committee found that the decline of Sydney's little penguin population is due to habitat destruction from development and predation from domestic and introduced animals, particularly dogs. Other threats included reduced food sources, toxic effects of oil spills, jet skis and powerboats, chronic lead poisoning (by ingestion of lead fishing sinkers) and entanglement in fishing tackle and plastic debris. 2/3 Little Penguin Despite being in generally good health (estimated world population is around 350,000 to 600,000 individuals) the Manly penguins are of significant conservation value given their disjunction from other populations, their occurrence in Sydney Harbour, and being the only known breeding colony on mainland NSW. Little penguins living so close to a major urban centre highlights the importance of habitat conservation and the integral role of community participation in the conservation of biodiversity, both factors integral to the Wildlife Land Trust. Following HSI's nomination and the eventual listing of the species, a Recovery Planwas developed by the NSW Government, outlining several recovery actions to maintain and enhance the endangered population, including: monitoring the population to identify potential habitat; educating the community; including the colony in marine pollution management; and protecting habitat through the environmental planning and assessment process. A 2007 progress report noted that these actions appear to have arrested the declining numbers of the population, with promising signs such as increased chick fledging apparent. 3/3