* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Scanning System, CT
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
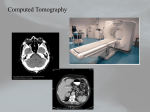
Scanning System, CT Core medical equipment - Information UMDNS 13469 Scanning Systems, Computed Tomography GMDN 37618 Full-body CT system Other common names: Computed Tomography Scanners; Computed Tomography Scanning Systems; Computed X-Ray Tomography Scanners; Computer-Assisted Tomography Scanners; Computerized Tomographs; CT Scanners; CT Scanners, Mobile; CT Scanning Systems; CT Slice Scanners; Multislice Scanners, Computer Tomography; Scanners, Computed Axial Tomography; Scanners, Computed Tomography; Scanners; Computer Tomography, Mobile; Scanners, Computed Tomography, X-Ray; Scanner, computed tomography, full-body; Whole body x-ray CT scanner Health problem addressed These scanners are used for a wide procedures, including spine and head abdominal and pelvic malignancies; to ventricles, the chest wall, and the large assess musculoskeletal degeneration. variety of diagnostic injuries, lesions, and examine the cerebral blood vessels; and to Product description Devices that consist of an x-ray subsystem, a gantry, a patient table, and a controlling computer. A high-voltage x-ray generator supplies electric power to the x-ray tube, which usually has a rotating anode and is capable of withstanding the high heat loads generated during rapid multiple-slice acquisition. The gantry houses the x-ray tube, x-ray generator, detector system, collimators, and rotational frame. Principles of operation Use and maintenance CT scanners use slip-ring technology, which was introduced in 1989. Slip-ring scanners can perform helical CT scanning, in which the x-ray tube and detector rotate around the patient’s body, continuously acquiring data while the patient moves through the gantry. The acquired volume of data can be reconstructed at any point during the scan. All modern CT scanners are multislice. Inside the gantry, an x-ray tube projects a fan-shaped x-ray beam through the patient to the detector array. As the x-ray tube and detector rotate, x-rays are detected continuously through the patient. The computer mathematically reconstructs data from each full rotation to produce an image of one slice. User(s): Computed tomography scanning technician Operating steps Requirements: Stable power source; shielded room and control room During a CT scan, the table moves the patient into the gantry and the x-ray tube rotates around the patient. As x-rays pass through the patient to the detectors, the computer acquires and processes data to form an image. Maintenance: Medical staff; technician; biomedical or clinical engineer Training: Initial training by manufacturer and manuals Environment of use Settings of use: Hospitals; private practices; clinics; stand-alone imaging centers Product specifications Approx. dimensions (mm): 1882 x 2225 x 1006 Approx. weight (kg): 1906 Reported problems Controlling the radiation dose is the most significant concern facing all CT users. Also, unnecessary testing could cause an overexposure to radiation. System problems and communication breakdowns can result in repeat CT scans, and so, facilities need to provide extensive training for these systems to eradicate confusion when using the equipment. Consumables: NA Price range (USD): 329,900-3,200,000 Typical product life time (years): 8 to 10 Shelf life (consumables): NA Types and variations Multislice; 3-D CTA; 4-D imaging http://www.who.int/medical_devices/en/index.html © Copyright ECRI Institute 2011 (not including the GMDN code and device name). Reproduced with Permission from ECRI Institute’s Healthcare Product Comparison System. © Copyright GMDN Agency 2011. GMDN codes and device names are reproduced with permission from the GMDN Agency.