* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 20 (Electricity) Practice Test
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Lumped element model wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
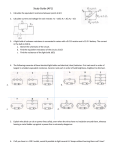
Name: ________________________ Class: ___________________ Date: __________ ID: A Chapter 20 (Electricity) Practice Test Modified True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the sentence or statement true. ____ 1. Electric charges that are different attract each other. _________________________ ____ 2. Conduction is the transfer of electrons from a charged object to another object by rubbing. _________________________ ____ 3. The unit of measure of voltage is the ohm. _________________________ ____ 4. As the temperature of most conductors increases, the resistance decreases. _________________________ ____ 5. For a constant voltage, increasing the resistance will cause the current to decrease. _________________________ ____ 6. In a parallel circuit, there is only one path for current to take. _________________________ ____ 7. If one light bulb is removed from a parallel circuit with three bulbs, the brightness of the other bulbs will decrease. _________________________ 8. Like charges ____________________ and opposite charges ____________________. 9. When a pathway through which charges can move forms suddenly, _________________________ occurs. 10. The SI unit of electric current is the ____________________. 11. Scientists usually define the direction of current as the direction in which ____________________ charges would flow. 12. Wood, plastic, and rubber are good electrical ____________________, and copper is a good electrical ____________________. 13. The SI unit of resistance is the ____________________. 14. Potential difference is measured in _________________________. 15. A complete path through which charge can flow is an electric ____________________. 16. To calculate power, multiply voltage measured in ____________________ by ____________________ measured in amps. 17. The transfer of excess charge through a conductor to Earth is called ____________________. 1 18. Electric force is ____________________ proportional to the amount of charge and ____________________ proportional to the square of the distance between the charges. 19. A material that has almost zero resistance when it is cooled to low temperatures is a(an) _________________________. Figure 20-1 20. In Figure 20-1, where is the field of each charge the strongest? 21. What is a charge’s electric field? 22. What are three ways that a charge can be transferred? 23. What is the law of conservation of charge? 24. What is the difference between direct current and alternating current? 25. Explain why metal wire coated with plastic or rubber is used in electric circuits. 2 26. What is the voltage in a circuit if the current is 3 amps and the resistance is 3 ohms? Explain your answer. 27. If the voltage is 90 volts and the resistance is 30 ohms, what is the current? Explain your answer. 28. How much energy does a 50-watt light bulb use compared to a 100-watt light bulb if both are shining for the same length of time? Explain your answer. 29. What is a circuit breaker? 3 Use the diagram to answer each question. 30. Which circuit—A or B—represents a series circuit? Explain your answer. 31. Which circuit—A or B—is a parallel circuit? Explain your answer. 32. Which circuit diagram represents circuit B? 33. What will happen to bulb 1 in circuit A if the switch is opened? 34. Will removing bulb 1 in circuit B cause bulb 3 to go out? Explain. 4 35. What will happen to bulb 2 in circuit diagram D if bulb 1 burns out? 36. Suppose you have one light bulb in a simple circuit. If you add a second identical light bulb in series, what would happen to the brightness of the first bulb? If instead you add the second bulb in parallel, what would happen to the brightness of the first bulb? Explain your answers. 37. Why does plugging too many appliances into the same circuit cause too much current to flow through the circuit? What can happen as a result? 38. How are friction, induction, and static discharge involved in lightning? 5 39. How are conduction and induction alike and how are they different? 40. Explain why you may produce a static discharge if you touch a metal doorknob after walking on a wool carpet. 41. How is current related to resistance? 42. What is the resistance of a lamp operating at 115 volts and using 0.25 amp of current? What relationship did you use to find the answer? 6 Figure 20-2 43. Are both circuits in Figure 20-2 series circuits? Explain your answer. 44. In which direction do the electrons move in Figure 20-2? How does this compare to the direction of the current? 45. Based on the circuit diagrams in Figure 20-2, what would happen if one of the bulbs in Circuit A burned out? What would happen if one of the bulbs in Circuit B burned out? Explain your answers. 46. In Figure 20-2, what device could be added to the circuits to open the circuits? Explain how this device works. Compare this device to safety devices that stop the current in a home. 7 Figure 20-3 47. Compare the resistance in the three circuits shown in Figure 20-3 when the switches are closed. Explain the cause of any differences. 48. In Figure 20-3, how will the current compare in Circuits A, B, and C when the switches are closed? Explain your answer. 49. When the switches are closed in Figure 20-3, which bulbs will be the brightest and which will be the dimmest? Assume that all of the light bulbs and batteries are identical. Explain your answer. 50. Using the same materials, how could you change the circuits in Figure 20-3 so that all the bulbs would have the same brightness? Explain your answer. 8