* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Understanding Drug Labels
Survey
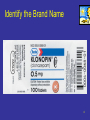
Document related concepts
Transcript
Understanding Drug Labels Chapter 8 MAT 119 Drug Names • Brand, trade, proprietary – Manufacturer’s name for a drug – Brand name is usually most prominent –® - means registered –™ - means Trade Mark • Generic – Established, nonproprietary name – Generic name must be on all drug labels 2 Brand and Generic Names 3 Identify the Brand Name 4 Identify the Generic Name 5 Identify Drug Name: Generic or Brand? Note: Generic Name only 6 Dosage Strength • Dosage weight or amount of drug provided in a specific unit of measurement 7 Form (more in Chapter 10) • Structure and composition of drug – Solid forms for oral use – Injectable – Suppositories – Creams – Patches 8 Identify Form Note apothecary & is incorrect Should be gr 1/150 9 Identify Form 10 Supply Dosage • Both dosage and form – Dosage per tablet – Dosage per milliliter 11 Total Volume • Full quantity contained in bottle or vial – Total number of tablets or other solids – Total fluid volume for liquids 12 Administration Route • Site of body or method of drug delivery – Oral • Tablets, capsusles, caplets – Enteral (into the GI tract via tube) – Sublingual – Injection (IV, IM, subcut) – Topical 13 Identify the Administration Route 14 Directions for Reconstituting Some drugs are dispensed in powder form and must be reconstituted for use (more in chapter 12) 15 Continued Directions for reconstitution 16 Continued 17 Continued 18 Label Alerts • Warnings or special alerts – Examples • Refrigerate at all times • Keep in a dry place Alert 19 Name of Manufacturer 20 Expiration Date • The medication should be used, discarded or returned to the pharmacy by the expiration date. Exp in powder form Exp when reconstituted 21 Lot or Control Numbers • Important if drug is recalled – required by Federal Law • Quickly identifies a particular group of medication packages Control No. 22 National Drug Code (NDC) • Every drugs has an NDC – similar to SS# 23 Controlled Substance Schedule • Classifies drugs according to potential for use and abuse – Schedule I – highest potential for abuse – Schedule V – lowest potential for abuse Has the letter C with Roman Numerals 24 Bar Code Symbols • Used in retail sales; document drug dosing, even at the patient’s bedside. Bar Code 25 United States Pharmacopeia (USP) National Formulary (NF) • The USP and NF are the two official national lists of approved drugs. • These initials are placed after the generic drug name – be careful not to confuse a drug form like SR – sustained release 26 Unit or Single-Dose Labels • Most oral and some IV medications given in the hospital setting are available in single (unit) doses. • The total volume is usually omitted on these containers because they only hold a single dose. 27 Combination Drugs • Some medications are a combination of two or more drugs in one form. • Combination drugs are sometimes prescribed by the number of caplets, capsules or milliliters to be given rather than by dosage strength (ex. Percocet). 28 Supply Dosage expressed as a Percent • Percentage (%) solutions express the number of grams of the drug per 100 milliliters of solution. • Betoptic Opthalmic Solution 0.5% – contains 0.5 g of drug per 100 mL 0.5g : 100 mL = 500 mg : 100 mL = 5 mg/mL 29 Supply Dosage expressed as a Ratio • Ratio solutions express the number of grams of the drug per total milliliters of solution. • Epinephrine 1:10,000 – contains 1 g of the drug per 10,000 mL solution 1 g: 10,000 mL = 1,000 mg: 10,000 mL = 1 mg/10 mL 30 Check Labels Before administering a medication to a patient, check the drug label three times: 1. On first contact - against the medication order or MAR 2. When preparing the medication 3. Before administering it. 31 Six Rights of Medication Administration – Right patient – Right drug – Right amount – Right route – Right time – Right documentation • The right patient must receive the right drug in the right amount by the right route at the right time, followed by the right documentation. 32 Identify parts of the drug label Brand name? Route? Label alerts? Manufacturer? 33 Identify parts of the drug label •NDC #? •Generic name? •Route? 34 Identify parts of the drug label oSupply dosage? oVolume? oBrand name? 35