* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Specific expert systems
Wizard of Oz experiment wikipedia , lookup
Existential risk from artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Clinical decision support system wikipedia , lookup
Ethics of artificial intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Computer Go wikipedia , lookup
Incomplete Nature wikipedia , lookup
Human–computer interaction wikipedia , lookup
Ecological interface design wikipedia , lookup
Personal knowledge base wikipedia , lookup
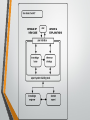
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Lecture # 3 Expert system • • • • Expert system is an artificial intelligence program that has expert-level knowledge about a particular domain and knows how to use its knowledge to respond properly. Domain refers to the area within which the task is being performed. Ideally the expert systems should substitute a human expert. Edward Feigenbaum of Stanford University has defined expert system as “an intelligent computer program that uses knowledge and inference procedures to solve problems that are difficult enough to require significant human expertise for their solutions.” It is a branch of artificial intelligence introduced by researchers in the Stanford Heuristic Programming Project. • • • • • Expert system The expert systems is a branch of AI designed to work within a particular domain. As an expert is a person who can solve a problem with the domain knowledge in hands it should be able to solve problems at the level of a human expert. The source of knowledge may come from a human expert and/or from books, magazines and internet. As knowledge play a key role in the functioning of expert systems they are also known as knowledge-based systems and knowledge-based expert systems. The expert’s knowledge about solving the given specific problems is called knowledge domain of the expert. • • • So, ES is a computer application that performs a task that would otherwise be performed by a human expert. For example, there are expert systems that can diagnose human illnesses, make financial forecasts, and schedule routes for delivery vehicles. Some expert systems are designed to take the place of human experts, while others are designed to aid them. To design an expert system, one needs a knowledge engineer, an individual who studies how human experts make decisions and translates the rules into terms that a computer can understand. PERFORMANCE Performance of the expert system is based on following methods:- ►Knowledge engineering:►Building an expert ENGINEERING. system is known as KNOWLEDGE ►In this knowledge gathers from subject matter experts codifying this knowledge according to the formalism. ►Persons doing this are called KNOWLEDGE ENGINEER. and then COMPONENTS OF EXPERT SYSTEMS COMPONENTS OF EXPERT SYSTEMS An expert system is divided into two sub-systems: knowledge base , reasoning/inference engine and rules. • • • The knowledge base represents facts and rules. The inference engine applies the rules to the known facts to deduce new facts. And rule is a conditional statement that links given conditions to actions or outcomes Knowledge Representation • • • • Knowledge is represented in a computer in the form of rules (Production rule). Consists of an IF part and THEN part. IF part lists a set of conditions in some logical combination. If the IF part of the rule is satisfied; consequently, the THEN part can be concluded. Knowledge Representation • • If flammable liquid was leaked then call the fire department. If the material is acid and smells like vinegar then the leak material is acetic acid. Basic Concept of an Expert System Function • • • • • The expert system consists of two major components: knowledge base and inference engine. Knowledge base contains the domain knowledge which is used by the inference engine to draw conclusions. The inference engine is the generic control mechanism that applies the obvious knowledge to the task-specific data to arrive at some conclusion. When a user supplies facts or relevant information of query to the expert system he receives advice or expertise in response. That is given the facts it uses the inference engine which in turn uses the knowledge base to infer the solution. Knowledge base • • • It is expert systems contain both factual and heuristic knowledge. Factual knowledge is that knowledge of task domain that is widely shared, typically found in textbooks or journals. Heuristic knowledge is less exhaustive, more experiential, more judgmental knowledge of performance. Reasoning • Two methods of reasoning when using inference rules: (i) Backward chaining: it starts with list of goals and works backward if there is data which will allow it to conclude these goals. (ii) Forward chaining: it starts with data available and then concludes a desired goal. CHARACTERISTICS OF EXPERT SYSTEMS • • • • High performance: They should perform at the level of a human expert. Adequate response time: They should have the ability to respond in a reasonable amount of time. Time is crucial especially for real time systems. Reliability: They must be reliable and should not crash. Understandable: They should not be a black box instead it should be able explain the steps of the reasoning process. It should justify its conclusions in the same way a human expert explains why he arrived at particular conclusion. 1. Dendral 2. Mycin Some Prominent Expert Systems 3. PXDES 4. R1/Xcon Two early expert systems broke ground in the healthcare space for medical diagnoses: Dendral, which helped chemists identify organic molecules, and MYCIN, which helped to identify bacteria to recommend antibiotics and dosages. Expert system-MYCIN • An early expert system developed in early 1970s at Stanford University • <<Rule-Based Expert Systems: The MYCIN Experiments of the Stanford Heuristic Programming Project >> • This expert system was designed to identify bacteria causing severe infections REASONING & PROBLEM SOLVING STRATEGY • MYCIN could use backward chaining to find out whether a possible bacteria was to blame. • “Certainty factor” is used for an assessment of the likelihood of one bacteria. • MYCIN’s problem solving strategy was simple: • For each possible bacteria: Using backward chaining, try to prove that it is the case, finding the certainty. • Find a treatment which ” covers” all the bacteria above some level of certainty. Problem Solving • When trying to proveMYCIN: a goal through backward chaining, system • • could ask user certain questions. Certain facts are marked as “askable”, so if they couldn’t be proved, ask the user. The ask procedure is carried out in following style of dialogue: • MYCIN: Has the patient had neurosurgery? • USER: No. • MYCIN: IS the patient a burn patient? • USER: No. •… • MYCIN: It could be Diplococcus.. Modeling Human Diagnostic Strategies • Problem Solving Strategy used in MYCIN only works when small number of hypotheses (e.g., bacteria). • For hundreds of possible diseases, need a better strategy. • Later medical diagnostic systems used an approach based on human expert reasoning. EXAMPLES OF ES IN MEDICAL -PXDES • It is example of medical expert system. • It is a lung disease, X-ray diagnosis. • It takes our lungs picture from upper side of body which looks like a shadow. • The shadow is used to determine the type and degree of harmness. • These systems include three modes: 1.The knowledge base 2.The explanation interface 3.The knowledge acquisition Contd.. (1) KNOWLEDGE BASE:- • It contains the data of X-ray representations of various stages of the disease. (2) EXPLANATION INTERFACE:- • It details the conclusion. (3) KNOWLEDGE ACQUISITION:- • It allow medical experts to add or change information in the system. Medical Expert Systems Today • Medical expert systems were quite effective in evaluations comparing their performance with human experts. • Support the physicians decisions, rather than doing the whole diagnosis. • Include many useful support materials, such as report generating tools, reference material etc. • Availability: Expert systems are available easily due to mass production software. OF EXPERT SYSTEMS • Cheaper:ADVANTAGES The cost of providing expertise is not expensive. • Reduced danger: They can be used in any risky environments where humans cannot work with. • Permanence: The knowledge will last long indefinitely. • Multiple expertise: It can be designed to have knowledge of many experts. • Explanation: They are capable of explaining in detail the reasoning that led to a conclusion. • Fast response: They can respond at great speed due to the inherent advantages of computers over humans. • Unemotional and response at all times: Unlike humans, they do not get tense, fatigue or panic and work steadily during emergency Expert System Technology There are several levels of ES technologies available. Two important things to keep in mind when selecting ES tools include: 1. The tool selected for the project has to match the capability and sophistication of the projected ES, in particular, the need to integrate it with other subsystems such as databases and other components of a larger information system. 2. The tool also has to match the qualifications of the project team. Expert System Technology Expert systems technologies include: 1. Specific expert systems - These expert systems actually provide recommendations in a specific task domain. 2. Expert system shells - Collection of software packages & tools to design, develop, implement, and maintain expert systems. - are the most common vehicle for the development of specific ESs. A shell is an expert system without a knowledge base. - A shell furnishes the ES developer with the inference engine, user interface, and the explanation and knowledge acquisition facilities. Expert System Technology - Expert system shells are the software containing an interface, an inference engine, and the formatted skeleton of a knowledge base. In essence, an expert system shell is an empty bowl to be filled with the expert knowledge elements that the inference engine may process for users. - Domain-specific shells are actually incomplete specific expert systems, which require much less effort in order to field an actual system. Contd.. 3. Expert system development environments - these systems expand the capabilities of shells in various directions. They run on engineering workstations, minicomputers, or mainframes; offer tight integration with large databases; and support the building of large expert systems. 4. High-level programming languages Several ES development environments have been rewritten from LISP into a procedural language more commonly found in the commercial environment, such as C or C++. ESs are now rarely developed in a programming language.