* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Writing Curriculum Overview
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Distributed morphology wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Junction Grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Ojibwe grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Untranslatability wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Transformational grammar wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
Abbreviation wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Comparison (grammar) wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Classical compound wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
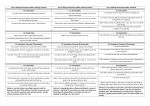
Writing Curriculum Overview Year 1 Form capital letters. Form digits 0-9. Understand which letters belong to which handwriting 'families' (i.e. Letters that are formed in similar ways) and to practise these. Composition Composing a sentence orally before writing it. Sequencing sentences to form short narratives Rereading what they have written to check that it makes sense Vocabulary Grammar Punctuation Leaving spaces between words. Joining words and joining clauses using an 'and'. Beginning to punctuate sentences using a capital letter and a full stop, question mark or exclamation mark. Understanding how words can combine to make sentences Writing Curriculum Overview Year 2 Transcription segmenting spoken words into phonemes and representing, spelling many correctly. learning to spell common exception words. learning to spell more words with contraction forms. Add suffixes to spell longer words, including -ment, -ness, -less, -ly Handwriting Form lower -case letters of the correct size relative to one another. Start using some of the diagonal and horizontal strokes needed to join letters and understand which letters, when adjacent to one another, are best left un-joined. Write capital letters and digits of the correct size, orientation and relationship to one another and to lower case letters Use spacing between words that reflects the size of the letters. Composition Writing narratives about personal experiences and those of others (real and fiction). Encapsulating what they want to say, sentence by sentence Re-reading to check that their writing makes sense and that verbs to indicate time are used correctly and consistently, including verbs in the continuous form. Proof-reading to check for errors in spelling, grammar and punctuation [for example, ends of sentences punctuated correctly] Vocabulary Grammar Punctuation learning how to use both familiar and new punctuation correctly, including full stops, capital letters, exclamation marks, question marks and commas in lists. Learning how to use apostrophes for contracted forms Sentences with different forms: statement, question, exclamation, command. Expanded some nouns phrases to describe and specify [for example, the blue butterfly]. The present and past tenses correctly and consistently including the progressive form. Subordination (using when, if, that or because) and co-ordination (using or, and, or but) Understanding the use of the suffixes -er, -est in adjectives and the use of -ly in standard English to turn adjectives into adverbs. Beginning to use inverted commas to punctuate direct speech. Writing Curriculum Overview Year 3 Transcription Use some prefixes and suffixes and understand how to add them in context (English appendix 1). Spell some homophones. Learning the possessive apostrophe (singular). Write from memory simple sentences, dictated by the teacher, that includes words and punctuation taught so far. Handwriting Beginning to increase the legibility, consistency and quality of their handwriting (for example, by ensuring that the down strokes of letters are parallel and equidistant; that the lines of writing are spaced sufficiently so that the ascenders and descenders of letters do not touch). Composition Composing and rehearsing simple sentence structures orally (including dialogue), progressively building a varied and rich vocabulary and an increasing range of sentence structures (English Appendix 2). Begin to organise simple paragraphs around a theme. Beginning to assess the effectiveness of their own 'and others' writing and suggesting improvements. Beginning to propose changes to grammar and vocabulary to improve consistency, including the accurate use of pronouns in sentences. Proof-read for some spelling and punctuation errors. Begin to use the correct tense throughout a piece of writing. Vocabulary Grammar Punctuation Using conjunctions, adverbs and prepositions to express time and cause. Choosing nouns and pronouns appropriately for clarity and cohesion and to avoid repetition. Writing Curriculum Overview Year 4 Transcription Use further prefixes and suffixes and understand how to add them (English Appendix 1). Spell further homophones. Place the possessive apostrophe accurately in words with regular plurals (for examples, girls', boys') and in words with irregular plurals. Beginning to place the possessive apostrophe accurately in words with regular plurals (for example, girls', boys') and in words with irregular plurals (for example, children's). Handwriting Increase the legibility, consistency and quality of their handwriting (for example, by ensuring that the down strokes of letters are parallel and equidistant; that lines of writing are spaced sufficiently so that the ascenders and descenders of letters do not touch). Composition Composing and rehearsing sentences orally (including dialogue), progressively building a varied and rich vocabulary and an increasing range of sentence structure (English Appendix 2). Organising paragraphs around a theme. Assessing the effectiveness of their own and others' writing and suggesting improvements. Proposing changes to grammar and vocabulary to improve consistency, including the accurate use of pronouns in sentences. Proof-read for spelling and punctuation errors. Vocabulary Grammar Punctuation Using commas after fronted adverbials. Using and punctuating speech. Using expanded noun phrases to convey complicated information concisely. Writing Curriculum Overview Year 5 Transcription Beginning to distinguish between homophones and other words which are often confused Handwriting Beginning to choose which shape of a letter to use when given choices and deciding whether or not to join specific letters. Composition Beginning to identify the audience for and purpose of the writing, often selecting the appropriate form and using other similar writing as models for their own. Beginning to select appropriate grammar and vocabulary, understanding how such choices can change and enhance meaning Beginning to describe settings, characters and atmosphere and integrating dialogue to convey character and advance the action in narratives Beginning to use a range of devices to build cohesion within and across paragraphs Beginning to use some organisational and presentational devices to structure text and to guide the reader [for example, headings, and bullet points]. Beginning to assess the effectiveness of their own and others' writing. Beginning to propose changes to vocabulary, grammar and punctuation to enhance writing Use the correct tense throughout a piece of writing. Beginning to ensure the correct subject verb agreement when using singular and plural, distinguishing between the language of speech and writing and choosing the appropriate register. Proof-read for spelling and punctuation errors. Vocabulary Grammar Punctuation Using brackets, dashes or commas to indicate parenthesis. Understanding devices to build cohesion within a paragraph [for example, then, after that, this, firstly]. Understanding linking ideas across paragraphs using adverbials of time [for example, later], place [for example, nearby] and number [for example, secondly] or tense choices [for example, he had seen her before] Using commas to clarify meaning or avoid ambiguity in writing. Writing Curriculum Overview Year 6 Transcription Use further prefixes and suffixes and understand the guidance for adding them. Spell some words with 'silent' letters [for example, knight, psalm, solemn]. Continue to distinguish between homophones and other words which are often confused. Handwriting Choosing which shape of a letter to use when giving choices and deciding whether or not to join specific letters. Composition Identifying the audience for and purpose of the writing, selecting the appropriate form and using other similar writing as models for their own. Selecting appropriate grammar and vocabulary, understanding how such choices can change and enhance meaning. Describing settings, characters and atmosphere and integrating dialogue to convey character and advance the actions in narratives. Using a wide range of devices to build cohesion within and across paragraphs. Proposing changes to vocabulary, grammar and punctuation to enhance effects and clarify meaning Ensuring correct subject and verb agreement when using singular and plural, distinguishing between the language of speech and writing and choosing the appropriate register. Proof-read for spelling and punctuation errors. Vocabulary Grammar Punctuation Using hyphens to avoid ambiguity. Using passive verbs to affect the presentation of information in a sentence. Linking ideas across paragraphs using a wider range of cohesive devices: repetition of a word or phrase, grammatical connections [for example, the use of adverbials such as on the other hand, in contrast, or as a consequence], and ellipsis. Using semi-colons, colons or dashes to mark boundaries between independent clauses. Using a colon to introduce a list. Punctuating bullet points consistently.