* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Presentation
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
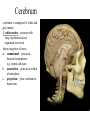
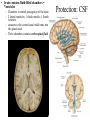
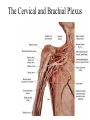
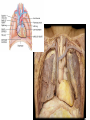
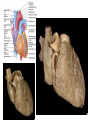
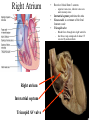
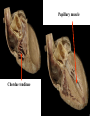
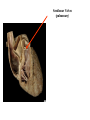
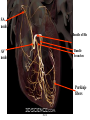
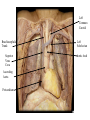
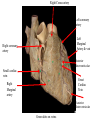
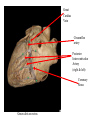
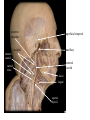
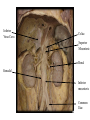
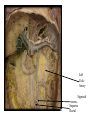
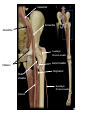
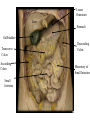
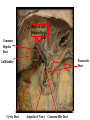
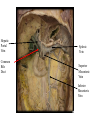
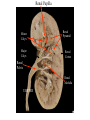
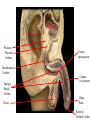
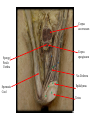
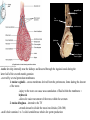
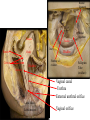
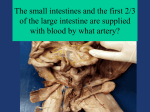
Cerebrum • Cerebrum = largest portion -left and right cerebral hemispheres divided by the longitudinal fissure -connected by the corpus callosum -folded into ridges and grooves: grooves = sulci -sulci divide the cerebrum into lobes -ridges = gyri (gyrus) – many gyri and sulci have specific names e.g. Central sulcus •Frontal and parietal lobes Cerebrum -cerebrum is comprised of white and gray matter: 1. white matter - neurons with long, myelinated axons -organized into tracts -three categories of tracts a. commisural – join areas between hemispheres e.g. corpus callosum b. association – joins areas within a hemisphere c. projection – joins cerebrum to brain stem • brain contains fluid-filled chambers = Ventricles – Chambers in central passageway of the brain – 2 lateral ventricles, 1 third ventricle, 1 fourth ventricle – connects to the central canal which runs into the spinal canal – These chambers contain cerebrospinal fluid Protection: CSF I III II V VI VII IX X VIII •Cervical •and lumbar enlargements Dorsal Ramus Ventral Ramus Dorsal Root ganglion Dorsal Root Spinal nerve Ventral Root Dorsal Ramus Dorsal Root Ventral Ramus Ventral Root Rami Communicantes The Cervical and Brachial Plexus The Lumbar and Sacral Plexuses, Right Atrium • Receives blood from 3 sources – • • • Interatrial septum partitions the atria Fossa ovalis is a remnant of the fetal foramen ovale Tricuspid valve – – Right atrium Interatrial septum Tricuspid AV valve superior vena cava, inferior vena cava and coronary sinus Blood flows through into right ventricle has three cusps composed of dense CT covered by endocardium Papillary muscle Chordae tendinae Semilunar Valves (pulmonary) SA node Bundle of His Bundle branches AV node Purkinje fibers 20-16 Left Common Carotid Brachiocephalic Trunk Left Subclavian Superior Vena Cava Aortic Arch Ascending Aorta Pericardium Left Common Carotid Left Subclavian Aortic Arch Parietal Pricardium Diaphragm Right Conus artery Left coronary artery Left Marginal Artery & vein Right coronary artery Anterior Interventricular Small cardiac vein Great Cardiac Vein Right Marginal artery Anterior Interventricular Green dots on veins Great Cardiac Vein Circumflex artery Posterior Interventricular Artery (right & left) Coronary Sinus Green dots on veins vertebral thyrocervical suprascapular thoracoacromial Common Carotid subscapular circumflex humeral deep radial brachial radial collateral ulnar collateral brachial ulnar radial Ulnar collateral Radial collateral brachial Common interosseous ulnar radial interosseous Deep palmar arch Superficial palmar arch Digital arteries posterior auricular superficial temporal maxillary occipital internal carotid external carotid carotid sinus facial lingual superior thyroid Inferior Vena Cava Celiac Superior Mesenteric Renal Gonadal Inferior mesenteric Common Iliac Left Gastric Hepatic Proper Common Hepatic Splenic Splenic Vein Celiac trunk Inferior Mesenteric Left Colic Artery Sigmoid Superior Rectal Common iliac External iliac Internal iliac Ascending br Of Lateral circumflex Lateral circumflex Obturator Deep femoral Medial circumflex Descending br Of Lateral circumflex Femoral Femoral Deep Femoral Genicular Descending br Of Lateral circumflex Genicular Arteries of the Knee Anterior Tibial Eustacian tube With tubal tonsil Parotid Sublingual Submandibular Thoracic Aorta Esophagus Diaphragm Liver FUNDUS BODY PYLORIC REGION PANCREAS DUODENUM Lesser Omentum Liver Stomach Gallbladder Transverse Colon Ascending Colon Small Intestine Descending Colon Mesentery of Small Intestine Right & Left Hepatic Ducts Common Hepatic Duct Pancreatic Duct Gallbladder Cystic Duct Ampulla of Vater Common Bile Duct Hepatic Portal Vein Common Bile Duct Splenic Vein Superior Mesenteric Vein Inferior Mesenteric Vein kidney URETER URETER BLADDER Renal Papilla Minor Calyx Major Calyx Renal Pyramid Renal Cortex Renal Pelvis Renal Medulla URETER Bladder Rectum Prostate Prostatic Urethra Corpus spongiosum Membranous Urethra Spongy/ Penile Urethra Testes Corpus cavernosum Glans Penis External Urethral Orifice Corpus cavernosum Spongy/ Penile Urethra Corpus spongiosum Vas Deferens Spermatic Cord Epididymus Testes pampiniform plexus Vas deferens testicular artery Epididymus Seminiferous Tubules Tunica Albuginea Tunica Vaginalis -testis: develop internally near the kidneys and descend through the inguinal canal during the latter half of the seventh month gestation -covered by several protection membranes 1. tunica vaginalis – serous membrane derived from the peritoneum, forms during the descent of the testes -injury to the testes can cause an accumulation of fluid within the membrane = hydrocele -allows for easier movement of the testes within the scrotum 2. tunica albuginea – internal to the TV -extends inward to divide the testes into lobules (200-300) -each lobule contains 1 to 3 coiled seminiferous tubules for sperm production Round ligament Broad ligament Fundus Fornix Body Cervix Bladder Fundus Ovary Bladder Fimbrae of oviduct Rectum Fallopian Tube (oviduct) Vaginal canal Urethra External urethral orifice Labia minora Labia majora Vaginal orifice