* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Population Ecology - Madeira City Schools
Source–sink dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Two-child policy wikipedia , lookup
Human overpopulation wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
The Population Bomb wikipedia , lookup
World population wikipedia , lookup
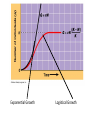
Population Ecology Chapter 36 I. Population Structure and Dynamics A. Population ecology is the study of how and why populations change 1. Population – group of individuals of a single species that occupy the same general area. B. Population density – number of individuals of a species per unit area or volume 1. Dispersion pattern – the way individuals are spaced within their area a. Clumped b. Uniform c. Random C. Models can predict patterns of population growth 1. Exponential growth a. the larger the population gets, the faster it grows b. this growth cannot continue for a long time….why? c. idealized picture of unregulated growth d. G= rN (G = growth rate, N = population size, r = per person (capita) rate of increase) e. how do you get r? net increase total population 2. Logistical Growth – idealized picture of population growth that is slowed by limiting factors as the population increases a. G = rN (K-N) K b. K = carrying capacity Exponential Growth Logistical Growth C. Carrying Capacity = the number of organisms of a certain species that an environment can support 1. “Limiting Factors” are things that keep a population from growing (keep it at carrying capacity) a. Density Dependent Limiting Factors = things that affect a population only when the population is dense examples: competition, predation, hunting, parasitism, crowding and stress (rodents), disease. b. Density Independent Limiting Factors = things that affect a population no matter how dense the population is examples: mostly abiotic factors, temperature, storms, habitat disruption, natural disasters floods, drought, any D. Boom and bust cycles E. Life history patterns 1. Life history – schedule of reproductions and death a. age of first reproduction b. frequency of reproduction c. number of offspring d. amount of parental care 2. Life histories have been shaped by natural selection 3. r-selection a. r is maximized b. usually small, short lived animals or plants c. these species may experience unpredictable disturbances 4. K-selection a. population size is near K b. usually large, long-lived animals or plants c. stable environments II. Human Population Growth A. Demography = study of population growth characteristics B. Age of organisms affect population growth a. pre-reproductive years b. reproductive years c. post-reproductive years C. Immigration = movement of individuals into a population D. Emigration = movement of individuals from a population Why are these graphs shaped the way they are?