* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Display the Test Result of the Digital Circuit with Graph
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
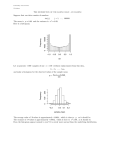
Display the Test Result of the Digital Circuit with Graph Introduction: The digital multimeter, or DMM, has become a necessary instrument for electronic test benches of all types. In developed countries, the digital multimeter is used in roughly 70-80% of applications while the older analog meter is used much less often. But the typical DMM has had some of its own shortcomings: For example, the analog meters allowed the user to “peak” their test devices by watching for a positive or negative “dip” in the meter’s movement. In addition, there are often cases where it would be advantageous to make readings of two different parameters at the same time; for example, Voltage and Current. It is also handy to have quick access to statistics on our measurements or a trending graph, similar to a strip chart recorder display. With computer interface ports such as LAN, GPIB or USB we can send our data readings to a PC for storage and further calculations. This can take some time. However, with SIGLENT’S SDM3055 Digital Multimeter further data calculations can be performed in the DMM without having to send the data to a PC. With the benefit of its 4.3 inch color TFT-LCD display and a resolution of 480 * 272, the user can display two separate parameters, statistics, histograms, trend charts, Pass/Fail, etc. Four different display modes provide the user with fast and important data. histogram 1/ 8 bar graph Trend data Simple and intuitive user interface allows for quick and easy data interpretation. By clicking a button or two on the SDM3055’s front panel the user can easily access structured interfacing and arithmetic menus. And by using the 6 soft-keys located below the display, navigation is made even easier. Figure 1. Display: offers four different displays. Large multi-function Display The horizontal bar-graph function allows the user a quick view - if and how much the measured value is changing. This is often more handy than trying to interpret the direction and magnitude changes in a numerical read-out. This bar-graph can also be used with the Limit function or when using the Math features. Figure2. bar graph can help you to see the measurement results rapidly Powerful Trend Graph If one expects the data to remain relatively constant then a measurement can be made only one time. More typically, however, the measured value will drift over time, be effected by other parameters or change due to some external disturbance. With the SDM3055(A) trending graph the user can see if and how the data has been changing over the last minute or since the last Clear. As an example, this function could be used to monitor the output of a power supply as load conditions change. Or multiple DMMs could be used to simultaneously graph Voltage, Current, and Temperature changes over time. Figure 3.the trend shows the measurement result change over time. Histogram Function Provides Quick Statistical Information If the lowest measured values are constantly changing, for example, we want to know what the nature of this change is. With the Histogram function we now see the statistical variation of our measured values. Calculated values such as mean, standard deviation, and distribution shape are all critical information used in understanding these changes. The Histogram scale can be set to Automatic or to a Manual value of 10, 20, 40, 100, 200 or 400 depending on our requirements. We can also capture values outside the range of our display such as the occasional power glitch or other external interference. 3/ 8 Figure 4 .histogram displays the distribution of the of measured values. User interface display adds arithmetic and statistical functionality. Statistical functions can be used both with displayed values but also with trend graphs, histograms, and bar charts. Figure 5 shows the DC Voltage reading plus the statistical values to help in determining measurement point stability. 4/ 8 Figure 6: Showing statistics and histogram functions on single display. Figure 7: Displaying statistics and trend graph simultaneously. 5/ 8 Figure 8.Using statistical display and bar graph display. Limit Test The Limit function provides a visual and audio indication that alerts the user when a specific preset condition has been exceeded. For example, if one was monitoring the temperature of a circuit prototype in a hot dip tank, the Limit function would alert you before an expensive prototype might be damaged. The Limit function can be used in all four test modes. Figure 9: The Limit function in the normal digital mode. Figure 10: Showing the Limit function when in the Trending display mode. 6/ 8 Figure 11. This example shows the Limit function used in the Histogram function display. Figure 12. Using the Limit function in the Histogram function display mode. The following illustrates the powerful graphics capabilities of the SIGLENT SDM3000 multimeters: A manufacturer of battery charging systems needs to run a test to determine the minimum use of battery power in order for their system to smoothly shut down or restart the charging circuit. Because the battery charger does not utilize a buffer circuit the charger should not respond instantaneously to voltage changes. In order to simulate the charging circuit the design team uses a triangle waveform provided by the SDG5000 arbitrary / function generator. Engineers use the SIGLENT SDM3055 to measure the on / off output voltage of the detector circuit as well as the Histogram mode to display the results. Looking at the frequencies of 1 Hz or less, the display shows the histogram distribution with the appropriate results. However, when 7/ 8 interference occurs the circuit reacts abnormally, displaying an intermediate output value. From the display we can see at what frequencies this occurs and design a simple cut-off frequency filter in the circuit to solve the problem. Ramp standard histogram histogram with noise In conclusion: The SDM3055 multi-meter with its data analysis features has shown us the unique advantages of this meter. Ordinary multimeters can display simple values only and using a an external PC can slow down the process and requires additional programming. However, by using the SIGLENT SDM3055 digital multimeter, a few keystrokes will access powerful built-in arithmetic and statistical functionality. The user need not plot readings and calculate statistical data as this is performed within the unit itself. SIGENT’s core business is test & measurement instrumentation, adhering to our core competencies and using strict quality control and technological innovation, the SIGENT Technologies brand of products will continue to grow as your best choice and trusted partner! 8/ 8