* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Islam and Politics - Georgetown University
Salafi jihadism wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Twelver Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
International reactions to Fitna wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Islamofascism wikipedia , lookup
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Afghanistan wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic missionary activity wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Sudan wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic–Jewish relations wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Somalia wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Historicity of Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Origin of Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
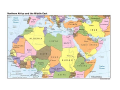
Islam and Politics Comparative Political Systems Georgetown University November 24, 2003 Important Terms Islam = Abrahamic, monotheistic religion characterized by the acceptance of the doctrine of “submission to God” and to Muhammad as the chief and last prophet of God Allah = “God,” as in the God of Judaism and Christianity; non-Muslim Arabs also use this word Muslim = follower of Islam Sunni Islam = accepts the first four caliphs as rightful successors of Muhammad Shi`i Islam = regards `Ali and his descendants as the legitimate successors to Muhammad and rejects the first three caliphs Sheikh = head of an Arab family, or of a clan or a tribe; the chief magistrate of an Arab village; a scholar learned in Islamic traditions Umma = supranational community of Muslims Dawla = Arabic, “state” Majlis = Arabic, “chamber,” “house,” “parliament” Jihad = internal struggle; often (mis)translated as “holy war against infidels” Qur’an = sacred text of Islam, to Muslims the revelations of God to Muhammad Hadith = report of the sayings or actions of Muhammad or his companions, together with the tradition of its chain of transmission Sunna = way of life prescribed as normative in Islam, based on the teachings and practices of Muhammad and on Qur’anic exegesis `Ulama’ = religious scholars Shari`a = Islamic law (4 Sunni schools, 1 Shi`i school) Shura = Islamic principle of consultation Sufism = Islamic mysticism Five Pillars of Islam 1. Prayer (five times daily facing Mecca) 2. Pilgrimage (to Mecca, once in one’s lifetime if able) 3. Faith (“There is no God but God, and Muhammad is his messenger”) 4. Fasting (during the month of Ramadan) 5. Zakat (alms to the poor) Organization of the Islamic Conference - Member States Islam is not confined to the Arab states in the Middle East. In fact, most Muslims are not Arabs. The largest predominantly Muslim state is Indonesia, where 87 percent of the country's 206 million people are Muslims. The people of Pakistan and Bangladesh, the second and third most populous, predominantly Muslim countries, are also not Arabs. Arab League Algeria (Algiers) Bahrain (Manama) Comoros (Moroni) Djibouti (Djibouti) Egypt (Cairo) Iraq (Baghdad) Jordan (Amman) Kuwait (Kuwait) Lebanon (Beirut) Libya (Tripoli) Mauritania (Nouakchott) Morocco (Rabat) Oman (Muscat) Palestine (Arab East Jerusalem, Al-Quds Al-Sharif, as future capital) Qatar (Doha) Saudi Arabia (Riyadh) Somalia (Mogadishu) Sudan (Khartoum) Syria (Damascus) Tunisia (Tunis) United Arab Emirates (Abu Dhabi) Yemen (San’a) Key Topics in Arab Politics Today Understanding Political Economy of Development Religion and Politics Role of Military in Politics Economic and Political Reform Political Succession (a fad topic?) The Persistence of Authoritarianism