* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to Forensics
Forensic accountant wikipedia , lookup
Forensic anthropology wikipedia , lookup
Forensic epidemiology wikipedia , lookup
Criminology wikipedia , lookup
Forensic firearm examination wikipedia , lookup
Digital forensics wikipedia , lookup
Forensic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Forensic linguistics wikipedia , lookup
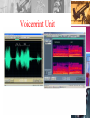
September 2013 Introduction to Forensics The Science Behind Catching Criminals Mrs. Chanin-Bermudez SUPA Forensics Overview • Definition of Forensic Science Scope • History and Development of Forensics • Organization of a Crime Laboratory • Functions of the Forensic Scientist Analysis of Physical Evidence Provision of Expert Testimony Furnishing Training • Scientific Admissibility Definition and Scope of Forensic Science Forensic science is the application of science to those criminal and civil laws that are enforced by police agencies in a criminal justice system. Forensic Science: A Definition • Application of science to law • Applies the knowledge and technology of science for the definition and enforcement of such laws. Forensic science is the application of science to those criminal and civil laws that are enforced by police agencies in a criminal justice system. History • Alphonse Bertillon (1853-1914) First scientific system of personal identification Developed the science of anthropometry, a systematic procedure of taking a series of body measurements as a means of distinguishing one individual from another History and Development 1813 Mathieu Orfila: Father of Forensic toxicology 1892 Francis Galton: first study of fingerprints (Nephew of Darwin) 1879 Alphonse Bertillon: developed the science of anthropometry 1929 Calvin Goddard: developed the comparison microscope for bullet comparisons . …more History 1910 Albert Osborne: Principles of document examination 1893 1950’s Microscope as a tool for the forensic scientist 1910 Hans Gross: Developed the application of scientific principles to criminal investigations Locard’s Exchange Principle Bertillon Measurements History, Con’t • Edmond Locard (1877 -1966) Locard’s Exchange Principle –the exchange of materials between two objects that occurs whenever two objects come in contact with one another. A cross-transfer of evidence occurs. Organization of the Crime Lab • Over 320 public crime labs in the U.S…a tripling of the number since 1966. • Supreme Court decision Miranda v. Arizona (1966) • Increase in drug abuse • Advent of DNA profiling • Most State Governments maintain crime labs plus satellite labs. Organization of Crime Labs • General Organization No nationally organized system— crime labs mirror the fragmented law enforcement structure that that exists on national, state, and local levels • National Level four major federal crime labs, FBI, DEA, ATF, US Postal Organization, Con’t • FBI (Department of Justice) Largest crime lab in the world Broad investigative powers • DEA (Drug Enforcement Agency) Responsible for the analysis of drugs seized in violation of laws regulating the production, sale, and transportation of drugs Organization, Con’t • ATF (Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms, and Explosives) Responsible for the analysis of alcoholic beverages, weapons, and explosives in conjunction with the Gun Control Act and Organized Crime Control Organization, Con’t • State Level Most state governments maintain a lab to service state and local law enforcement Some larger cities maintain their own crime lab, usually under the direction of local police dept. Organization Con’t • Local Level Local labs provide services to county and municipal agencies. Generally, they operate independently of state labs and are financed by local government. Services of the Crime Lab • Physical Science Unit • Biology Unit • Firearms Unit • Document Examination Unit • Photography Unit • Toxicology Unit • Latent Fingerprint Unit • Polygraph Unit • Voiceprint Analysis unit • Evidence Collection Unit Physical Science Unit Physical Science Unit • Investigators: • Chemists • Physicists • Geologists • Items Identified: • drugs, glass, paint, explosives and soil • Job: • Analytical and chemical analysis Biology Unit Biology Unit • Investigators: • Biologists • Biochemists • Identify and Compare: • botanical materials such as wood and plants. • Job: • Identification and DNA profiling of dried blood stains, other body fluids, comparison of hairs and fibers Firearms Unit Firearms Unit • Identify and examine: • • • • Firearms Discharged bullets Cartridge cases Shotgun shells • Responsibility: • Examination of garments to detect firearm discharge residue • Determine approximate distance from target when weapon was fired. Document Analysis Unit Document Analysis Unit • Identify and Examine: • Handwriting and typewriting to determine authenticity and/or source • Job: • Analysis of paper and ink and indented writings (impressions) • Recreate: • Obliterations, erasures • Burned or charred documents Photography Unit Photography Unit • Examine and Record: • Physical evidence at the scene • Specialize in: • Digital imaging, IR, UV, and X ray photography to make invisible information visible to the naked eye • Beyond the Scene: • Preparation of photographic exhibits for courtroom presentation. Can you find the Relationship? Toxicology Unit • Investigators: • Chemists • Biologists • Examine: • Body fluids and organs for the presence or absence of drugs and poisons. • Determines Blood alcohol content • Job: • Works with the coroner or medical Latent Fingerprint Unit Latent Fingerprint Unit • Process and examine: • Fingerprints to determine possible matches with victims and suspects Polygraph Unit Polygraph Unit • Job: • Analyze respiration, perspiration, blood pressure and pulse rate to determine credibility • Used in conjunction with interrogation to determine credibility of suspects and witnesses. Voiceprint Unit Voiceprint Unit • Interpret: • Telephone threats • Analyze: • Tape recorded messages • Compare: • Suspect voice recording to evidence to match source Evidence Collection Unit Evidence Collection Unit • CSI: • Crime Scene Investigation • Consists of: • trained personnel who are dispatched to the crime scene to collect and preserve physical evidence. • They simply collect the evidence, Locard’s Principle Revisited • Attempt the Hypothetical Case with a partner. • Answers: – Victim was inside the car means fibers from its interior have been transferred onto the victim’s clothing. – Blood from the victim has been transferred onto the velour interior. – Fiber, blood, hair, and skin cells may also have been transferred between the criminal and victim. – Tire tracks from the car may have been left in the woods. – This would probably lead to the make of car, since the tires are special. – If the vehicle was located, small driving imperfections in the tread could link it to the crime. – The type of soil at the crime scene may still be on the car’s tires, too. – Interior of suspect’s car could be tested for the fibers, hair, skin cells and blood of the victim. Functions of the Forensic Scientist • Frye v. United States: 1923 Rejection of Lie Detector (Polygraph) results necessitated guidelines for determining judicial admissibility of scientific examinations. • The Frye Standard: The court must decide if the questioned procedure, technique or principles are “generally accepted” by a meaningful segment of the scientific community. Daubert v. Merrel • Whether the scientific technique or theory can be tested. • Whether the technique or theory has been subject to peer review and publication. • The technique’s potential for error. • Existence and maintenance of standards controlling the technique’s operation. • Whether the scientific theory or method has attracted widespread acceptance within a relevant scientific community. Coppolino v. State • M.E. testified that victim died of an overdose of a drug called succinylcholine chloride based on his toxicology report. • Succinylcholine chloride breaks down into succinic acid in the body. • This drug had never before been detected in a human body. • Defense argued that this test was new and absence of corroborative experimental data by other scientists. • The court rejected the defense’s argument on the grounds that although the tests may be new and unique, they are admissible only if they are based on scientifically valid principles and techniques. Expert Testimony • Must be competent: education degrees, member of applicable societies, published papers or books, etc. • Defense may cross-examine the potential expert witness. • The individual trial judge is the ultimate decision maker regarding expert witnesses. Training in Recognition, Collection, and Preservation of Evidence • Specially trained evidence collectors: CSI • On 24-hour call to aid criminal investigators in retrieving evidence • Specially equipped with all the proper evidence collection equipment • Unfortunately, some police forces still don’t use them or the police themselves have contaminated the crime scene before the CSI team gets there! Forensic Pathology • Investigation of sudden, unnatural, unexplained, or violent death. • Medical Examiner vs Coroner = M.D. vs political appointee. • Autopsy: http://www.pathguy.com/autopsy.htm • Causes of death: natural, homicide, suicide, accident, undetermined. • Rigor mortis: starts within the first 24 hours and disappears after 72 hours. Helpful in estimating time of death. See “Algor mortis” • Livor mortis: settling of blood after the heart stops. Skin appears dark blue. Used to determine position of body at time of death. Other Areas involving Forensics • Anthropology: Examination of human skeletal remains • Entomology: insect life span can be used to determine the time of death. • Psychiatry: competency of suspect; serial killed profiles • Odontology: body identification based on dental records; evidence using bite marks left on victims • Engineering: accident reconstruction to determine causes Services of the Crime Lab Functions of the Forensic Scientist • Analysis of Physical Evidence Applies the principles and techniques of the physical and natural sciences to the analysis of evidence Must be aware of the demands and constraints of the judicial system Scientific procedures and techniques must satisfy the criteria of admissibility established by the courts Functions Con’t • Provision of Expert Testimony May be required to testify with respect to methods and conclusions at a trial or hearing. • Furnish Training Train law enforcement in the proper recognition, collection, and preservation of physical evidence Scientific Admissibility • Frye Standard Court must decide if a questioned procedure, technique, or principles are “generally accepted” by a meaningful segment of the scientific community In practice, this has meant providing experts to testify that the procedure is generally accepted Courts have also taken note of books, papers, and past judicial decisions in this regard Admissibility, Con’t • Daubert Standard Court decides on the admissibility of science in the courtroom “General Acceptance” is not an absolute prerequisite for admissibility To ascertain the veracity of scientific evidence presented the judge should use the following areas of inquiry Daubert Criteria • Technique or theory can be (and has been) tested • Technique or theory has been subject to peer review and publication • Technique’s potential rate of error • Existence and maintenance of standards controlling the technique’s operation • Method or theory has attracted widespread acceptance within a relevant scientific community