* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Excretory System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
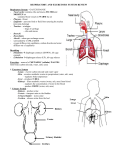
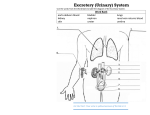
Do Now 1 1. What is one major waste product produced by every cell in the body? 2. Where does the waste product go in order to be excreted? 3. How does the waste product get to the excretory organ? 4. What are some other excretory organs? Do Now #2 1. Which human excretory structure aids in the maintenance of normal body temperature? a) b) c) d) Sweat gland Nephron Liver Urinary bladder 2. An individual running a marathon may experience periods of oxygen deprivation that can lead to a) b) c) d) Anaerobic respiration in muscle cells, forming lactic acid Aerobic respiration in muscle cells, generating glycogen Anaerobic respiration in liver cells, producing glucose Aerobic respiration in liver cells, synthesizing alcohol 3. What is the name of the process that builds up large molecules such as starch? Do Now 3 - Skin 1. What would happen if sweat glands become blocked? 2. Why do people pour water on themselves on a hot day after running? 3. Why do you urinate less when you run and sweat? Excretory System How does the Excretory System help maintain homeostasis? Excretory System Helps the body maintain homeostasis by excreting metabolic wastes through sweat, urine, and exhalation. Where does the waste come from? Cells carrying out their life functions Carbon dioxide comes from – Aerobic Cellular Respiration Water comes from – Aerobic Cellular Respiration Urea comes from – Breakdown of proteins and amino acids Organs of the Excretory System • • • • Liver Lungs Skin Urinary System Label 1 - Liver Functions: 1. Waste removal removes worn out red blood cells (120 days) Removes alcohol and other poisons from blood 2. Detoxification – converts harmful substances into inactive or less toxic substances Converts harmful ammonia into safer urea 2 - Lungs Function: 1. Waste removal – lungs remove CO2 and some H2O vapor Carbon Dioxide & Water Vapor are waste products of: Cellular Respiration Equation: Equation: 3 - Skin Functions: 1. Protection – keeps harmful pathogens from entering the body 2. Excretion – removes water, salts, and urea from the blood as sweat 3. Regulation – helps control your body temperature Skin “Excretion” How does the skin remove metabolic waste in sweat? The circulatory system transports waste around the blood Capillaries, containing blood, are next to sweat glands so waste (urea, salts and water) diffuse into sweat glands and excreted as sweat Skin “Regulation” How does the skin regulate or control body temperature? Sweat glands excrete sweat (water, urea, salts) Sweat evaporates off skin taking heat away with it! (evaporation is a cooling process) So, your body sweats to cool down! Negative Feedback Mechanism 1. If your body gets hot, what does your body do to stop itself from being too hot or getting even hotter? 2. If your body gets cold, what does your body do to preserve or conserve heat? 4 – Urinary System Urinary system includes 4 major organs: 1. Kidney 2. Ureter 3. Bladder 4. Urethra Kidney Function: Kidneys filter metabolic wastes from the blood to produce urine Kidneys control the concentration of substances in the body fluids Made up of millions of nephrons that are the actual filters of the kidney Nephrons: About 1.25 million nephrons found in each kidney Filters and cleans blood Create Urine Urine - concentrated waste (salts, urea, amino acids, glucose, water) How Do Nephrons Create Urine? http://ww 1. Filtration Where does the Urine go? After urine formation, it goes to: 1. Ureter – two tubes from each kidney that carry urine to the bladder 2. Bladder – temporary storage site of urine until it is time to be released 3. Urethra – one tube that carries the urine from the bladder to the outside of the body Final Stop for Urine Excretory Review