* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pop Quiz! - AP Biology with Ms. Costigan
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Fertilisation wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
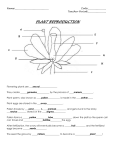
Pop Quiz! 4. Which of the following statements concerning fertilization in ferns is true? • a. It occurs within the female structure. • b. It requires water. • c. The fertilization product is a seed. • d. It occurs within the female structure; and It requires water. • e. It occurs within the female structure; It requires water; and the fertilization product is a seed. 5. Gametophytes are • a. haploid plants that produce spores. • b. diploid plants that produce spores. • c. haploid plants that produce gametes. • d. diploid plants that produce gametes. • e. diploid or haploid plants that produce gametes. Pop Quiz! 6. Alternation of generations refers to the • a. expression of recessive traits. • b. presence of a diploid and a haploid generation in the life cycle of plants. • c. presence of the different sexes in two different plants. • d. occurrence of a sexually reproducing diploid stage followed by an asexually reproducing haploid stage during the life cycle of higher plants. PLANTS! Reproduction Part 2 (lecture 16) (Gymnosperms & Angiosperms) First Seed Plants • Gymnosperm: conifers – vascular – heterospory • male vs. female gametophytes – seeds • naked seeds (no fruit) – pollen • contain male gametophyte – life cycle dominated by sporophyte stage • coniferous trees you are familiar with are diploid • reduced (microscopic) gametophyte • reduction of gametophyte protects delicate egg & embryo in protective sporophyte – protected from drought & UV radiation Pollen • Pollen eliminated the water requirement for fertilization – spread through wind & animal Ragweed pollen…oh my itchy eyes! sporangium & pollen male male (pollen) cones female female cones pine embryo Gymnosperm Life Cycle First Flowering Plants • Angiosperm: flowering plants – vascular – heterospory • male vs. female gametophytes – flower • specialized structure for sexual reproduction – seeds within fruit – pollen – life cycle dominated by sporophyte stage • trees & bushes you are familiar with are diploid • reduced (microscopic) gametophyte Flower • Modified shoot, modified leaves • Male – sepals – petals – Stamens Stigma Style Ovary Anther Stamen Filament • Filament & anther • Female sepals petals stamens – Carpel • Stigma, style, & ovary Petal carpel Ovule Sepal Carpel Flowering Plant Pollination • Pollination – transfer of pollen from the anther to a stigma – If pollination occurs, a pollen tube forms – The pollen tube transfers sperm to the ovule which will result in a zygote (new plant) and a 3n (triploid) nucleus that will form endosperm • Endosperm is the nutrient storing tissue in a seed Seed & Plant Embryo • Seed offers… – protection for embryo – stored nutrients for growth of embryo cotyledons = “seed” leaves, first leaves of new plant endosperm (3n) cotyledons embryo (2n) seed coat Double Fertilization • Remember: 3 Features of the Angiosperm Cycle – • Flowers, Fruits, & Double Fertilization The Process: – – – – – Pollination (pollen grain lands on stigma) Tube Nucleus (pollen tube produced down the style) Generative Nucleus (2 sperm form by mitosis) Enters ovary through micropyle 1 sperm fertilizes haploid egg to form zygote; other sperm combines with 2 polar nuclei to form 3n endosperm (food-storing tissue) polar nuclei Angiosperm Life Cycle male gametophyte = pollen grain (haploid) dehiscence pollen grains egg cell ovary sac sperm nuclei travel down pollen tube 3n endosperm female gametophyte = ovary sac (haploid) 2n zygote double fertilization 2n embryo new sporophyte in seed (diploid) Monocots & Dicots • Angiosperm are divided into 2 classes – dicots (eudicot) • 2 cotyledons (seed leaves) • leaves with network of veins • woody plants, trees, shrubs, beans – monocots • 1 cotyledon • leaves with parallel veins • grasses, palms, lilies Pop Quiz! 1. The heterosporous condition led to evolution of •a. gymnosperms and angiosperms. •b. pollen grains and seeds. •c. male and female plant parts. •d. pollen grains and seeds in male and female plant parts. •e. gymnosperms and angiosperms which bear pollen grains and seeds in male and female plant parts. Pop Quiz! 2. Which of the following produces no seeds? • a.Cycads • b.Conifers • c.Horsetails • d.Ginkgos • e.Tomato 3. Microspores mature into • a.ovules. • b.seeds. • c.pollen grains. • d.anthers. Pop Quiz! • 4. Gymnosperms – a. were the first plants not to have swimming sperm and were therefore freed from the need for water to reproduce. – b. are divided into two groups, the monocots and dicots. – c. were the first plants to develop vascular tissues. – d. were the first plants to develop flowers to attract insects. Pop Quiz! • 5. Which of the following statements about pine cones is correct? – a. Cones are exclusively female structures. – b. Cones are the result of pollination. – c. One type of cone produces microspores. – d. Seeds are enclosed in cones. – e. One type of cone produces microspores; and seeds are enclosed in cones.