* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War I - GoldLanguage
United States home front during World War I wikipedia , lookup
American entry into World War I wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War I wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the causes of World War I wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War I wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War I wikipedia , lookup
Economic history of World War I wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War I wikipedia , lookup
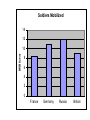
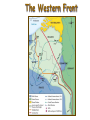
World War I Sara Olds Introduction • Austria-Hungary’s declaration of war against Serbia set off a chain reaction within the alliance system. The countries of Europe followed through on their pledges to support one another. As a result, nearly all of Europe soon joined what would be the largest, most destructive war the world had yet seen. Before It Ends 4 Empires Crumble • • • • 1. British 2. Austria-Hungarian 3. Ottoman 4. Russian 1. The Alliance System Triple Entente: Triple Alliance: Two Armed Camps! Allied Powers: Central Powers: EVENTS AND CAUSES OF WORLD WAR ONE MILITARY ‘ARMS RACE’ BEGINS BETWEEN FRANCE AND GERMANY. ARMIES INCREASE IN SIZE. 1888 - WILHELM II BECOMES KAISER. HIS AMBITIONS FOR GERMANY RAISE TENSIONS BETWEEN THE GREAT POWERS. FRENCH DESIRE FOR REVENGE – RECOVER ALSACE AND LORRAINE 1879-1907: FORMATION OF THE ALLIANCE SYSTEMS: TRIPLE ALLIANCE: Germany, Austria-Hungary, Italy. TRIPLE ENTENTE: France, Russia, Great Britain. 1871 - UNIFICATION OF GERMANY . DEFEAT OF FRANCE. JULY 1914 ASSASSINATION AT SARAJEVO NAVAL RACE 1906-1914; WILHELM’S AMBITIONS FOR EMPIRE THREATENS BRITAIN’S SECURITY 1908-1914 - RIVALRY IN THE BALKANS BETWEEN SERBIA AND AUSTRIA-HUNGARY The Great War Begins • July 31, 1914: Russia announces full mobilization of its armed forces. • August 1, 1914: Germany, taking Russia’s mobilization as a defacto declaration of war, declares war on Russia. • August 3, 1914: Germany declares war on France. • August 4, 1914: Germany declares war on neutral Belgium and invades in a right flanking move designed to defeat France quickly. As a result of this invasion, Britain declares war on Germany. The Great War Begins • Nations Take Sides – By mid-August 1914, there are two sides at war throughout Europe: • Central Powers—Germany, Austria-Hungary; later joined by Bulgaria and the Ottoman Empire • Allies—Great Britain, France, Russia; later joined by Japan, Italy (once a member of the Triple Alliance, but switched sides because Italians believed the war was unjustly started) Who’s To Blame? Soldiers Mobilized 14 12 Millions 10 8 6 4 2 0 France Germany Russia Britain A Bloody Stalemate • As the summer of 1914 turned to fall, the war turned into a long and bloody stalemate, or deadlock, along the battlefields of France. This deadlocked region in northern France became known as the Western Front. The Conflict Grinds Along • The Schlieffen Plan – Called for attacking and defeating France in the west and then rushing east to fight Russia. – Counted on the slow mobilization of Russian forces due to lack of railways. – Called for 39 days for the fall of Paris, and 42 days for the defeat of France. General Alfred Graf von Schlieffen The Conflict Grinds Along (continued) • By early September Germany had swept into France and reached the outskirts of Paris • September 5, 1914—At the First Battle of the Marne, Germany is forced to retreat. • With this defeat the Schlieffen Plan failed because Germany was then forced to fight a two front war. War in the Trenches • Conflict descends into trench warfare—armies fighting from trenches. • Battles result in many deaths and very small land gains. • Life in trenches is miserable, difficult, unsanitary. • New weapons only lead to more deaths. • The slaughter reached a peak in 1916. – February 1916: Battle of Verdun—Each side lost more than 300,000. – July-November 1916: The Somme—Each side suffered more than 500,000 casualties. – Only 5 miles were gained in each of these battles. The Western Front Trench Warfare Trench Warfare “No Man’s Land” The Somme – July, 1916 e 60,000 British soldiers killed in one hour. e Over 1,000,000 killed in 5 months. War New Weapons of the War • poison Gas – chlorine and phosgene—both toxic substances that caused suffocation – mustard gas—a blistering agent that caused severe burns and blisters on the skin and severely damaged the lungs. It sometimes took five weeks to die from mustard gas exposure. • • • • machine gun tank submarine airplanes Australian troops in the trenches equipped with gas masks, Battle of Ypres, 1917 • Mustard gas burns from World War I The British Vickers machine gun required a six man team to operate. One to fire, one to feed the ammunition, and the rest to help carry the weapon and supplies. British Mark I tank on September 26, 1916 Submarines: German U-Boat U-14 Flame Throwers Grenade Launchers Flying Aces • Manfred Albrecht Freiherr von Richthofen (2 May 1892 – 21 April 1918) was a German fighter pilot known as the "Red Baron". He was the most successful flying ace of World War I, being officially credited with 80 confirmed air combat victories. He was killed in combat with Canadian pilots near the Somme River. The Airplane “Squadron Over the Brenta” Max Edler von Poosch, 1917 The Flying Aces of World War I Eddie Rickenbacher, US Francesco Barraco, It. Eddie “Mick” Mannoch, Br. Willy Coppens de Holthust, Belg. Rene Pauk Fonck, Fr. Manfred von Richtoffen, Ger. [The “Red Baron”] The Zeppelin Trench Foot (too disgusting to be pictured) • Affected feet become numb and then turn red or blue. As the condition worsens, they may swell. Advanced immersion foot often involves blisters and open sores, which lead to fungal infections; this is sometimes called tropical ulcer (jungle rot). • If left untreated, immersion foot usually results in gangrene, which can require amputation. If immersion foot is treated properly, complete recovery is normal, though it is marked by severe short-term pain when feeling returns. Like other cold injuries, immersion foot leaves sufferers more susceptible to it in the future. The Battle on the Eastern Front • Early Fighting – Eastern Front—site of main fighting along the German-Russian border. – Russians push into Austria and Germany, but soon forced to retreat. • Russia Struggles – Russia’s war effort was suffering by 1916; many casualties and few supplies. – The huge size of Russian army keeps it a formidable force and prevents Germany from sending more troops to the Western Front. T. E. Lawrence & the “Arab Revolt”, 1916-18 So How’d the US Get In? The Sinking of the Lusitania The Zimmerman Telegram The Yanks Are Coming! Americans in the Trenches • What America Brought to Help End the War • • • • 1. Foodstuffs 2. Munitions 3. Oil 4. Manpower • • • • End of War: 1. Americans advancing in France 2. British Blockade – Starving Germany 3. Propaganda leaflets • Kaiser forced to leave Holland 11 a.m., November 11, 1918 The Armistice is Signed! 9,000,000 Dead World War I Casualties Russia 10,000,000 9,000,000 8,000,000 7,000,000 6,000,000 5,000,000 4,000,000 3,000,000 2,000,000 1,000,000 0 Germany AustriaHungary France Great Britain I taly Turkey US • Paris Conference – League of Nations (forerunner of United Nations) Wilson’s 14 Points: End secret diplomacy Reduce arms Evacuate Belgium Create independent Poland etc. The Treaty of Versailles is a Set Up for Things to Come What’s in it? •Reparations •NO Re-arming the Rhineland •Alsace-Lorraine given to France The Soldiers Brought Back a Present • Spanish Influenza • Will globally kill between 20 and 40 MILLION people. • 500,000 Americans die – More than WWI, WWII, Korean War and Vietnam War combined 48