* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Middle Colonies
Colonial American bastardy laws wikipedia , lookup
History of the Jews in Colonial America wikipedia , lookup
Plymouth Colony wikipedia , lookup
History of Jamestown, Virginia (1607–99) wikipedia , lookup
Colonial period of South Carolina wikipedia , lookup
Colony of Virginia wikipedia , lookup
Colonial South and the Chesapeake wikipedia , lookup
Province of Maryland wikipedia , lookup
Colonial American military history wikipedia , lookup
New Castle Court House Museum wikipedia , lookup
New Netherland wikipedia , lookup
Roanoke Colony wikipedia , lookup
Dominion of New England wikipedia , lookup
Province of Massachusetts Bay wikipedia , lookup
Jamestown supply missions wikipedia , lookup
Massachusetts Bay Colony wikipedia , lookup
Thirteen Colonies wikipedia , lookup
Province of New York wikipedia , lookup
London Company wikipedia , lookup
List of colonial governors of New Jersey wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church in the Thirteen Colonies wikipedia , lookup
English overseas possessions in the Wars of the Three Kingdoms wikipedia , lookup
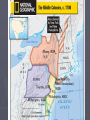
Middle Colonies Chapter 3, Lesson 3 England and the Colonies ► In England, the Puritans in Parliament were having a power struggle with Charles I. ► In 1642, civil war will break out. Oliver Cromwell led the Parliamentary forces and forced the King to surrender. ► In 1649, King Charles I is beheaded after a parliamentary court finds him guilty of treason. A new government is then established with Cromwell as its protector. ► Many from New England returned to England to fight with the Parliamentary forces and eventually returned to Royal Colonies like Virginia. England and the Colonies ► After Cromwell dies in 1658, Parliament reestablishes the monarchy with limits on the ruler. ► Charles II, son Charles I, takes the thrown in 1660. His reign is known as the restoration because the monarchy had been restored. ► At this time England had two clusters of colonies in America. Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Connecticut, and Rhode Island in the north. Maryland and Virginia in the south. England and the Colonies ► The Dutch were settled between these two groups of colonies. A few Dutch merchants created the Dutch West India Company to trade in the Americas in 1621. ► There posts along the Hudson would eventually become the colony of New Netherland. There main settlement was New Amsterdam located on Manhattan Island. The island was purchased from the Manhates for small quantities of beads and other goods. England and the Colonies Having a great seaport it became the center of shipping to and from the Americas. ► In order to populate the colony the Dutch West India Company: Brought over families from the Netherlands, Finland, Germany, and Sweden. Gave out land to those who brought at least 50 settlers to work it. ► Those who owned these riverfront lands were known as patroons. Ruled like kings and had their own courts and laws. Settlers owed their patroons a share of their crops and labor. ► England Takes Over ► The Dutch had thriving river trade as well as had an excellent harbor It’s no surprise the English want this. ► England sends its fleet to attack New Amsterdam. ► Peter Stuyvesant was governor of the colony. Had strict rules and heavy taxes resulting in many of the people in New Netherland to turn on him. ► When the English arrived he surrendered since he was not prepared for a battle against the English. King Charles II would give it to his brother, the Duke of York, who renames the colony New York. England Takes Over ► King Charles II would give it to his brother, the Duke of York, who renames the colony New York. ► New York was a proprietary colony. The owner known as a proprietor, owned all the land and ran the government. ► It was different from the New England colonies who could elect the governor and the assembly. ► Most of the colonists in New York lived in the Hudson River valley. ► The Duke of York promised freedom of religion to the diverse colonists. In 1654, 23 Brazilian Jews settled in New Amersterdam. England Takes Over ► They were the first Jews to settle in North America. ► By 1664, New York had about 8,000 inhabitants. It was a diversified population including Dutch, Germans, Swedes, Native Americans, and Puritans from New England, and 300 enslaved Africans. ► New Amsterdam, later New York, would be one of the fastest growing areas in the colony. By 1683, its population rose to about 12,000. England Takes Over ► The Duke of York appointed a governor and council to deal with colonial affairs. The colonists wanted to have a representative government like the other English colonies. The Duke resisted but the people of New York would not give up. In 1691, the English government finally allowed New York to elect a legislature. Oliver Cromwell King Charles II Peter Stuyvesant New Jersey ► The Duke of York would eventually give the southern part of his colony to Lord John Berkeley and Sir George Carteret. The land was located between the Hudson and Delaware River. They named the colony New Jersey, after the island of Jersey in the English Channel, where Carteret was born. ► To attract settlers to the colony, they offered large tracts (area of land) and generous terms. They were promised freedom of religion, trial by jury, and a representative assembly. The assembly would make local laws and set taxes. New Jersey ► Like New York, New Jersey was diverse ethnically and religiously. A lack of a natural harbor prevented it from developing a port like New York. ► As such, The proprietors did not make as much money as they had hoped. Berkeley sold his share (West Jersey) in 1674. Carteret’s sold his share (East Jersey) in 1682. ► By 1702, the colony belonged to the King, making it a royal colony. However, the colonists continued to make local laws. Pennsylvania ► In 1680, William Penn approached King Charles with a plan. Penn’s father had loaned the King a lot of money and he inherited the King’s promise of payment. Penn didn’t want the money though, and instead asked for land in America. The King was happy to rid himself of debt and gave him land stretching inland from the Delaware River. ► The new colony, Pennsylvania was almost as large as England. Pennsylvania ► William Penn belonged to a group of dissenters known as the Society of Friends, also known as Quakers. Believed individuals had an “inner light” that could guide him or her to salvation. Everyone could experience religious truth directly, so church officials were unnecessary. Everyone was equal before God. Though they had firm beliefs they tolerated others beliefs. Pennsylvania ► Many saw Quakers as a threat to established traditions. They would not bow or take off their hats to lord or ladies because they believed everyone was equal. They were also pacifists (people who refuse to use violence or fight in wars) ► Quakers were fined, jailed, and even executed for their beliefs. Pennsylvania ► William Penn saw Pennsylvania as a “holy experiment.” It was a chance to test out Quaker ideals of toleration and equality into practice. ► In 1682, he came to America to supervise the building of Philadelphia, “the city of brotherly love.” Penn designed the city himself, making him America’s first town planner. Penn also wrote Pennsylvania’s first constitution. ► Penn believed the land belonged the Native American and people should pay for it. Pennsylvania ► In 1682, he would negotiate the first of several treaties with the Native Americans. ► To encourage more settlers to come he had pamphlets passed out in various languages. By 1683 more than 3,000 English, Welsh, Irish, Dutch, and German settlers had arrived. ► In 1701, Penn granted colonists the right to elect representatives to the legislative assembly through the Charter of Liberties. Pennsylvania ► The southern most portion of Pennsylvania was known as the Three Lower Counties. Settled by Swedes in 1638 The area has been taken over by the Dutch and the English before becoming part of Pennsylvania. The Charter of Privileges allowed the lower counties to form their own legislature in 1704. From that point on the counties functioned as a separate colony known as Delaware, supervised by Pennsylvania’s governor.