* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PPTX
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Management of multiple sclerosis wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Common cold wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis signs and symptoms wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
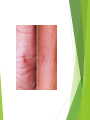
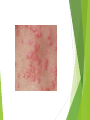
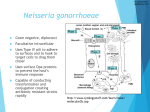
Gonorrhea Mario Nastasi What is it? Sexually Transmitted Infection. Caused by Neisseria Gonorrhoeae, a bacterium that can grow and multiply easily in mucus membranes of the body. Can grow in the warm, moist areas of the reproductive tract, including the cervix, uterus, and fallopian tubes in women, and in the urethra in women and men. Can also grow in the mouth, throat, and anus. A.K.A the “clap” or “drip” How is it Spread? Most often through sexual contact with an infected person. May also be spread by contact with infected bodily fluids, so that a mother could pass on the infection to her newborn during childbirth. The infection is easily spread and occurs most often in people who have many sex partners. How Common is Gonorrhea? Very common in the U.S. According to the CDC, there are as many as 700,000 new cases, with less than half of them reported. There were 334,826 reported cases of gonorrhea in the U.S. in 2012. Sexually active teenagers have one of the highest rates of reported infections. Symptoms Not all people infected have symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they are often within two to 10 days after exposure, but they can take up to 30 days to develop. • Symptoms for women: Greenish yellow or whitish discharge from the vagina. Burning when urinating. Bleeding between periods. Lower abdominal or pelvic pain. • Symptoms for men: Greenish yellow or whitish discharge from the penis. Burning when urinating. Painful or swollen testicle. Treatments Either an oral or injectable antibiotic. Partner should also be treated at the same time. Patients infected with gonorrhoeae frequently are coinfected with trachomatis. Dual therapy is recommended. Always take all of your antibiotics, even if you’re feeling better. It is becoming harder to treat some gonorrhea, as drug-resistant strains of gonorrhea are increasing. If Untreated Can cause serious and permanent health problems in both women and men. Spread to your blood or joints (life-threatening) Increased risk of HIV. Men: Can cause a painful condition in the tubes attached to the testicles. In rare cases, can cause men to be sterile. Women: Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) Formation of scar tissue that blocks fallopian tubes. Infertility Long-term pelvic/abdominal pain. Prevention Condoms/Safe sex. Limit number of sex partners. Abstinence