* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download This net force causes the bob to slow down.
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
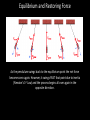
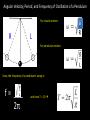
Harmonic Motion in Pendulums NOOOOOO! The period of oscillation is independent of my fear! WHS 2014/2015 Lee Wignall So you pull it back…..then what? Notice how the only time the tension and gravity are equal and opposite is when the bob is straight down. That means there is a NET FORCE in any other position. There are two net forces: 1) Since there is less gravity acting against tension as it rises, there is a net centripetal force (toward the center). This is what causes the bob to turn. 2) There is also a new net force directed backward because of the angle between tension and gravity. This net force causes the bob to slow down. Warm up questions 1. Why does a pendulum follow a curved path? 2. Explain why a pendulum speeds up, slows down, and momentarily stops at various points in its path. So you pull it back…..then what? Notice how the only time the tension and gravity are equal and opposite is when the bob is straight down. That means there is a NET FORCE in any other position. There are two net forces: 1) Since there is less gravity acting against tension as it rises, there is a net centripetal force (toward the center). This is what causes the bob to turn. 2) There is also a new net force directed backward because of the angle between tension and gravity. This net force causes the bob to slow down. Equilibrium and Restoring Force Equilibrium: The position in a system where the net force is zero. The natural “resting” point of a system. The position the system strives to achieve. Restoring force: a force that drives a system back toward equilibrium. equilibrium This component of gravity is the restoring force. Equilibrium and Restoring Force As the pendulum swings back to the equilibrium point the net force becomes zero again. However, it swings PAST that point due to inertia (Newton’s 1st Law) and the process begins all over again in the opposite direction. Angular Velocity, Period, and Frequency of Oscillation of a Pendulum For circular motion: R L For pendulum motion: Sooo, the frequency of a pendulum’s swing is: f = ___ 2π and since T = 1/f a Sample Problems What is the period of a pendulum that is 1.5 meters long? What is its frequency? How many times will it oscillate (make a full cycle) in 10 seconds? Sample Problems (answers) What is the period of a pendulum that is 1.5 meters long? What is its frequency? T = 2.46 s f = 0.41 Hz How many times will it oscillate (make a full cycle) in 10 seconds? It will oscillate 4.1 times Where will the pendulum be in 10 seconds? (predict with 2 different masses)