* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
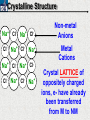
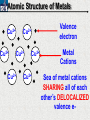
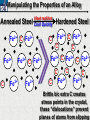
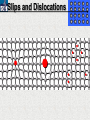
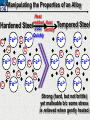
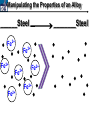
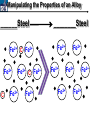
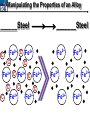
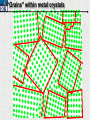
10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 1/5 Making Steel Alloy * * * SIT WITH YOUR DURABILITY GROUPS and/or 3 or 4’s 1. Take out your Video HW notes #26 Alloys 2. You should have already submitted the Durability Lab, Paint Lab, Paint CER, &Electroplating CER before break Essential Questions for this Unit How are chemistry and art connected? Describe how the chemical behavior of metals is related to their atomic structure. Which materials are resistant to acid rain damage and therefore durable for artwork? Why and how do you electroplate one metal with another? How can two soluble solutions react in a double replacement reaction? How can you use precipitates to make pigment for creating different color paint? Describe how the physical behavior of metals is related to their atomic structure. How can you make alloys that have improved properties compared to pure metals. How do you design a reliable scientific experiment? Review of Ionic Bonding Ionic Bonding Metals _______ lose e- to become ________ positively charged ions called _______________ . cations Non-metals gain ____ e- to become __________ negatively charged ions called _______________ . anions The _________________ charged ions oppositely __________ and form _________ ionic bonds. attract Crystalline Structure Na+ Cl- Na+ ClCl- Na+ Cl- Na+ Non-metal Anions Metal Cations Na+ Cl- Na+ ClCl- Na+ Cl- Na+ Crystal LATTICE of oppositely charged ions, e- have already been transferred from M to NM Ionic Solids NOT Good Conductors 1) Why can’t solid ionic compounds conduct electricity until they are dissolved into ions? • Dissolved ions have a charge and thus act like a flow of e- which is electricity! • Ionic solids exist as a lattice of oppositely charged ions where the e- are LOCALIZED Na+ Cl- Na+ Cl- localized means set in specific area, can not move far from their original atom Na+ Cl- Na+ Cl- Cl- Na+ Cl- Na+ Cl- Na+ Cl- Na+ Hard, yet so brittle 2) Why are ionic solids so brittle? Na+ •ClWhen Cl- the Na+struck IONS in the crystal + Cl+ Cl- Nalattice Na SHIFT. Na+ •ClSimilarly Na+ Clcharged ions REPEL and the + ClCl- Nacompound Na+breaks. Metallic Bonding Metallic Bonding When a substance is made up of only share metal atoms, the metal cations ______ valence electrons. all of the ___________ ______ The metal cations are surrounded by a “ ____________ sea of electrons delocalized ______ Atomic Structure of Metals Cu2+ Cu2+ Cu2+ Cu2+ Cu2+ Cu2+ Cu2+ Valence electron Metal Cations Sea of metal cations SHARING all of each other’s DELOCALIZED valence e- Ionic Solids NOT Good Conductors 1) Why are most metals very lustrous and good conductors of heat and electricity? • Valence e- in a metal are shared by all the metal atoms and can move freely, thus good conductors • e- absorb light and are excited easily. They relax and emit nearly all the light they absorb, thus most metals are shiny Cu2+ Cu2+ Cu2+ Cu2+ Cu2+ Cu2+ Cu2+ Metals Are NOT Brittle 2) Why are most metals malleable? • When a metal is struck the atoms SHIFT pass each other WITHOUT REPULSION. • Delocalized e- REARRANGE instantaneously around the cations to keep charge balance Cu2+ Cu2+ Cu2+ Cu2+ Cu2+ Cu2+ Cu2+ Cu2+ Cu2+ Cu2+ Cu2+ Cu2+ Cu2+ Cu2+ Examples of Alloys An _________ is a ________________________ homogeneous solution of different solids (usually metals). These pure metals are combined in order to improve the _______________________________________________________________ Luster, malleability, hardness, durability, resist rusting or corrosion, etc. alloy BRASS ALLOY BRONZE ALLOY Copper & Zinc Copper & Tin GOLD ALLOY Gold & Silver & Copper STEEL ALLOY Iron & Carbon Visualizing the e- Sea Model of Metallic Bonding Manipulating the Properties of an Alloy Spring Steel Fe2+ C Fe2+ Annealed Steel Fe2+ C Fe2+ Fe2+ Fe2+ C 2+ Fe C Heat red-hot Cool Slowly Fe2+ Fe2+ Fe2+ “snaps back” C Fe2+ Fe2+ C Fe2+ Fe2+ Malleable b/c atoms can shift when heated and the crystal reorganizes while cooling slowly Manipulating the Properties of an Alloy Annealed Steel Fe2+ C Heat red-hot Cool Quickly Fe2+ C Hardened Steel Fe2+ C Fe2+ C Fe2+ Fe2+ C Fe2+ Fe2+ C Fe2+ C Fe2+ C C Fe2+ Fe2+ C C C Fe2+ C Fe2+ Brittle b/c extra C creates stress points in the crystal, these “dislocations” prevent planes of atoms from slipping Slips and Dislocations Manipulating the Properties of an Alloy Hardened C Heat red-hot Heat Steel Cool Gently Quickly Fe2+ C Fe2+ C C Fe2+ Fe2+ C C C Fe2+ C Fe2+ C Fe2+ C Tempered Steel C Fe2+ C Fe2+ Fe2+ Fe2+ Fe2+ C C Fe2+ Fe2+ Strong (hard, but not brittle) yet malleable b/c some stress is relieved when gently heated Manipulating the Properties of an Alloy 1) Ratio of different elements 2) How it is heated 3) How it is cooled Manipulating the Properties of an Alloy ________Steel ______Steel Fe2+ Fe2+ Fe2+ Fe2+ Fe2+ Fe2+ Fe2+ Manipulating the Properties of an Alloy ________Steel ______Steel Fe2+ Fe2+ C Fe2+ C Fe2+ Fe2+ Fe2+ C Fe2+ Fe2+ Fe2+ Fe2+ Fe2+ Fe2+ Fe2+ Fe2+ Manipulating the Properties of an Alloy _______Steel ______Steel C Fe2+ Fe2+ C Fe2+ C C Fe2+ C Fe2+ C Fe2+ C C Fe2+ C Fe2+ Fe2+ Fe2+ C Fe2+ Fe2+ Fe2+ Fe2+ Manipulating the Properties of an Alloy “Grains” within metal crystals