* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is management?
Business simulation wikipedia , lookup
Operations research wikipedia , lookup
Strategic management wikipedia , lookup
Project management wikipedia , lookup
Operations management wikipedia , lookup
High-commitment management wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable management wikipedia , lookup
Management consulting wikipedia , lookup
International Council of Management Consulting Institutes wikipedia , lookup
Student’s Name (R. No.) : Ajay Datta (130770111014)
Class : E.C.
Semester : 3
Subject : Engineering Economics & Management (E. E. M.)
Topic : Definition, nature & scope of management &
administration & Skills, types & roles of a manager.
Submitted to : Shruta Ma’am
DEFINITIONS
Management (noun):
The responsibility for and
control of a company or similar
organization. Successful
management could be described
as the act of joining people
together to accomplish desired
goals and objectives using
available resources efficiently
and effectively.
Administration (noun):
1. A group of people working to
manage and control the
operations of a business or
organization;
2. The act or process of
administering, especially
regarding management.
What is management?
• A leadership role
• Title and position of power
• Task management
• Disciplined/responsibility
What is administration?
• Academic
• Government
• A group of managers
How is leadership a part of management and
administration?
• Not necessarily about being “in charge” – instead, being inspirational
•
•
•
•
•
•
Motivational
Innovative
Open/inviting
Lifelong learner
Flexible/willing to change
Risk taker
Nature and Characteristics of Management :
The salient features which highlight the nature of management are as follows:
(i)
Management is goal-oriented: Management is not an end in itself. It is a means to
achieve certain goals. Management has no justification to exist without goals. Management
goals are called group goals or organisational goals. The basic goal of management is to
ensure efficiency and economy in the utilisation of human, physical and financial resources.
The success of management is measured by the extent to which the established goals one
achieved. Thus, management is purposeful.
(ii)
Management is universal: Management is an essential element of every organised
activity irrespective of the size or type of activity. Wherever two or more persons are
engaged in working for a common goal, management is necessary. All types of organisations,
e.g., family, club, university, government, army, cricket team or business, require
management. Thus, management is a pervasive activity. The fundamental principles of
management are applicable in all areas of organised effort. Managers at all levels perform
the same basic functions.
(iii) Management is an Integrative Force: The essence of management lies in the
coordination of individual efforts in to a team. Management reconciles the individual
goals with organisational goals. As unifying force, management creates a whole that is
more than the sum of individual parts. It integrates human and other resources.
(iv) Management is a Social Process: Management is done by people, through people and
for people. It is a social process because it is concerned with interpersonal relations.
Human factor is the most important element in management. According to Appley,
“Management is the development of people not the direction of things. A good manager is
a leader not a boss. It is the pervasiveness of human element which gives management its
special character as a social process”.
(v) Management is multidisciplinary: Management has to deal with human behaviour under
dynamic conditions. Therefore, it depends upon wide knowledge derived from several
disciplines like engineering, sociology, psychology, economics, anthropology, etc. The vast
body of knowledge in management draws heavily upon other fields of study.
(vi)
Management is a continuous Process: Management is a dynamic and an
on-going process. The cycle of management continues to operate so long as there
is organised action for the achievement of group goals.
(vii) Management is Intangible: Management is an unseen or invisible force. It
cannot be seen but its presence can be felt everywhere in the form of results.
However, the managers who perform the functions of management are very much
tangible and visible.
(viii)
Management is an Art as well as Science: It contains a systematic body of
theoretical knowledge and it also involves the practical application of such
knowledge. Management is also a discipline involving specialised training and an
ethical code arising out of its social obligations.
SCOPE OF MANAGEMENT:
The field of management is very wide. The operational areas of
business management may be classified into the following categories:
(i) Production Management:
Production management implies planning, organising, directing and
controlling the production function so as to produce the right goods, in right
quantity, at the right time and at the right cost. It includes the following activities:
(a) designing the product (b) location and layout of plant and building (c) planning
and control of factory operations (d) operation of purchase and storage of
materials (e) repairs and maintenance (f) inventory cost and quality control
(g) research and development etc.
(ii) Marketing Management:
Marketing management refers to the identification of consumers
needs and supplying them the goods and services which can satisfy these wants. It
involves the following activities: (a) marketing research to determine the needs and
expectation
of consumers (b) planning and developing suitable products (c) setting appropriate
prices (d) selecting the right channel of distribution, and (e) promotional activities
like advertising and salesmanship to
communicate with the customers
(iii) Financial Management:
Financial management seeks to ensure the right amount and type of
funds to business at the right time and at reasonable cost. It comprises the following
activities: (a) estimating the volume of funds required for both long-term
and short-term needs of business (b) selecting the appropriate source of funds (c) raising
the required funds at the right time (d) ensuring proper utilisation and allocation of
raised funds so as to maintain safety and liquidity of funds and the creditworthiness and
profitability of business, and (e) administration of earnings Thus, financial management
involves the planning, organising and controlling of the financial resources.
(iv) Personnel Management:
Personnel management involves planning, organising and controlling the
procurement, development, compensation, maintenance and integration of human resources
of an organisation. It consists of the following activities: (a) manpower planning (b)
recruitments, (c) selection, (d) training (e) appraisal, (f) promotions
MANAGERS:
Managers –
The people responsible for supervising the use of an organization’s resources
to meet its goals
ORGANIZATIONAL PERFORMANCE:
A measure of how efficiently and effectively managers use available
resources to satisfy customers and achieve organizational goals
FOUR FUNCTIONS OF MANAGEMENT
LEVELS OF MANAGEMENT:
RELATIVE AMOUNT OF TIME THAT MANAGERS SPEND ON THE FOUR
MANAGERIAL FUNCTIONS :
MANAGERIAL SKILLS
Conceptual skills
Human skills
The ability to analyze and diagnose a situation and distinguish between
cause and effect.
The ability to understand, alter, lead, and control the behavior of other
individuals and groups.
Technical skills
Job-specific skills required to perform a particular type of work or
occupation at a high level.
SKILL TYPES NEEDED
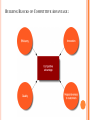
BUILDING BLOCKS OF COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE :
BUILDING COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE
Increasing efficiency
Reduce the quantity of resources used to produce goods or services
Increasing Quality
Improve the skills and abilities of the workforce
Introduce total quality management
Increasing speed, flexibility, and innovation
How fast a firm can bring new products to market
How easily a firm can change or alter the way they perform their activities
RESOURCES {ASSETS}
7 categories of resources:
People
Money
Time
Work Procedures
Energy
Materials
Equipment
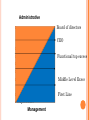
Administrative
Board of directors
CEO
Functional top excess
Middle Level Execs
First_Line Suupervisors
Supervisors
Management
First Line
TRAITS OF A MANAGER
Best Traits
Fair/just in decisions
Trusting/trusted at the same time
Caring & analytical in thought
Empowering & capable/responsible
Always punctual
Worst Traits
Deceitful
Dishonest
Shows favouritism
Lazy
Unorganized
MANAGEMENT LEVELS AND TIME SPENT ON
FUNCTIONS
Plan.
Top
28%
Middle 18%
Lower 15%
Organ. Lead.
36%
22%
33%
36%
24%
51%
Control.
14%
13%
10%
MANAGEMENT SKILLS :
Conceptual Skills : Cognitive ability to see the organization as a
whole and the relationship among its parts
Human Skills : Ability to work with and through other people and to
work effectively as a group member
Technical Skills : Understanding of and proficiency in the
performance of specific tasks.
WHAT IS IT LIKE TO BE A MANAGER?
Managerial Activities
- Long hours
- Most time spent in oral
communication
- Characterized by variety,
fragmentation, and brevity
- Fast paced and require a high
energy level to be successful
Managers give up the
right to:
- Be one of the gang
- Put your self-interest first
- Ask others to do things you
wouldn’t do
- Vent your frustrations
- Resist change