* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mesopotamia: the rise of civilization
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
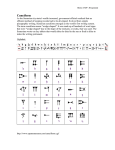
Everyone is gifted….but some people never open the package. Neanderthal Man: 250,000-30,000 years • Cooperated through language • Advanced stone tools • Used fire for cooking and protection • Wore clothing • Buried dead • Lived in caves [cave art ? 2012] CroMagnon / modern Man: 35,000- present time • Sewing needles, buttons • Snug boots; hooded parkas, pants w/ leggings • Fish hooks & harpoons • Bows and arrows • Flint tools and weapons • Lamps / animal fat • Why are the discoveries of Jarmo, Jericho and Catal Huyuk of interest to historians? Ancient Jericho What makes “a way of life” a civilization? • • • • • • • • • Writing system Organized economy Specialization of labor Social classes Legal code Advanced art Central government Several cities with monumental architecture ***Religion – the central force in primary civilizations Marshland and swamps… Mesopotamia: the rise of civilization The Assyrian capital at Nineveh Ashurbanipal King of Assyria (669-631 BCE) Cuneiform tablet – symbol writing on clay tablets with a reed stylus Sir Henry Rawlinson The Behistun Rock Cuneiform tablets • How did Mesopotamia get its name How was Mesopotamia transformed around 3000 BC? • Each city was the property of a specific deity. • Temple priests interpreted the will of the gods and acted as stewards of a city's deity. • The ruler of the city – a priestking often was visited and instructed by the community's god. Religion was the central force: • • • • • • Explained the workings of nature Eased the fear of death Justified rules and morality United people in a common view Bolstered the authority of rulers Promoted creativity in art, literature and science How did Mesopotamians define the purpose of man’s existence? Why did a mood of uncertainty and anxiety pervade the Mesopotamian psyche? • • • • Frequent floods and droughts Windstorms Invasions The gods were unpredictable The Standard of Ur • King Gudea of Lagash C. 2150 bc • The inscription describes a temple dedicated to the goddess Geshtinanna • How did King Sargon earn a place in our history books? Third Dynasty of Ur…Ur-Nammu, 2113-2096 BC The ancient Sumerians were very smart people: • • • • • • • • • Cuneiform Law codes Literature Schools Numbering system Kiln-dried bricks & pottery Lunar calendar Potter’s wheel The wheel • • • • • • • • • The wheelbarrow Sailboats Bronze tools and weapons The plow Frying pans Razors Cosmetic sets Shepherd’s pipes harps Why were King Hammurabi’s law codes obeyed?