* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Carbohydrates
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
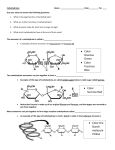
Photosynthesis 2n CO2 Carbohydrates + 2n H O + photons → 2(CH O) 2 2 n + 2n O2 Carb-o-hydrates Sugars, = sugars Starches, The Carbohydrates: and Fibers © 2008 Thomson - Wadsworth Carbohydrates • Carbohydrates are made of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms. • These atoms form chemical bonds that follow the laws of nature. © 2008 Thomson - Wadsworth Simple Carbohydrates • Monosaccharrides are single sugars (most are hexoses). • Glucose serves as the essential energy source, and is commonly known as blood sugar or dextrose. • Fructose is the sweetest, occurs naturally in honey and fruits, and is added to many foods in the form of high-fructose corn syrup. • Galactose rarely occurs naturally as a single sugar. © 2008 Thomson - Wadsworth © 2008 Thomson - Wadsworth Simple Carbohydrates • Disaccharides are pairs of monosaccharides, one of which is always glucose • Condensation reactions link monosaccharides together. • Hydrolysis reactions split molecules and commonly occur during digestion. • Maltose consists of two glucose units. It is produced during the germination of seeds and fermentation. • Sucrose is fructose and glucose combined. It is refined from sugarcane and sugar beets, tastes sweet, and is readily available. • Lactose is galactose and glucose combined. It is found in milk and milk products. © 2008 Thomson - Wadsworth Condensation Hydration © 2008 Thomson - Wadsworth Complex Carbohydrates • Oligosaccharides = few glucose units • Polysaccharides = many glucose units bound/linked together in straight or branched chains. Amylose (Starch) © 2008 Thomson - Wadsworth pentasaccharide verbascose Carbohydrate Class Source Monosaccharide obtained by hydrolysis Glucose (dextrose) Mono- Honey n/a Fructose (levulose) Mono- Honey n/a Galactose Mono- n/a Mannose Mono- n/a Xylose Mono- n/a Maltose Di- Corn Syrup Glucose Sucrose Di- Sugarcane,beets, maple sap Fructose, Glucose Lactose Di- Milk Glucose, Galactose Starch (amylose and amylopectin) Poly- Seeds, Tubers Glucose Glycogen Poly- Liver, Muscle Glucose Cellulose Poly- Plant cells, cotton, wood Glucose Inulin Poly- Artichokes, Dahlias Fructose Xylans Poly- Wood, straw, corn cobs Xylose © 2008 Thomson - Wadsworth The Complex Carbohydrates • Glycogen – Storage form of glucose in the body – Provides a rapid release of energy when needed • Starches – Storage form of glucose in plants – Found in grains, tubers, and legumes © 2008 Thomson - Wadsworth © 2008 Thomson - Wadsworth © 2008 Thomson - Wadsworth Physical Properties Carbohydrates are poly alcohols – they form hydrogen bonds in water Therefore all monosaccharides and disaccharides are soluble in water Some polysaccharides are soluble in water and insoluble in organic solvents Many carbohydrates are sweet to taste Sweetness is a function of their structure sucrose Saccharin (artificial sweetener) Reducing Sugars Alcohols can be oxidized Primary alcohols can oxidize to carboxylic acids Secondary alcohols can be oxidized to ketones Sugars are polyalcohols Glucose which is in equilibrium between a ring compound and an open chain form can oxidize to the acid in the open-chain form with Fehling’s solution Cu2O(s) Cu2+(aq) Hydrolysis: Disaccharides and Polysaccharides Hydrolysis of acetal bonds in disaccharides give monosaccharides H+,H2O or Hydrolysis: Disaccharides and Polysaccharides For polysaccharides hydrolysis proceeds in stages and may yield several products including dextrins (shortened starch molecules), maltose (a disaccharide) Corn syrup, a mixture obtained from partial hydrolysis of corn starch, contains considerable amounts of maltose Dehydration of Carbohydrates: Molisch Test Carbohydrates, like most alcohols undergo dehydration reactions in the presence of sulfuric acid to make alkenes Pentoses (5-Carbon sugars) give furfural When napthol is added a colored compound is made Starch-Iodine Complex: Starch Test Starches are a mixture of amylose and amylopectin Potato starch 90% amylopectin and 10% amylose Amylose reacts with iodine to give an intense blue/black complex Amylopectin reacts with iodine to form a red-purple complex Only large starches give a positive test with I2 not say dextrins Amylose Amlyopectin The Experiment Substance Observations Glucose Fructose Lactose Sucrose Starch Unknown • • • • • Fehling’s test (oxidation) Barfoed’s test (mild oxidation) Seliwanoff’s test (dehydration) Iodine test (starch) Hydrolysis of sucrose and starch Reaction?