* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Implantation
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Somatic cell nuclear transfer wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Drosophila embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
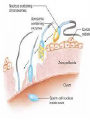
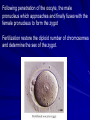
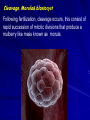
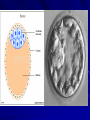
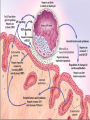
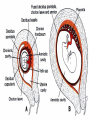
Conception, Implantation & Embryology Dr. Dina Nawfal Conception: Is the union of male and female pronuclear elements Conception normally takes place in the fallopian tube after which the fertilized ovum continues to the uterus and implantation will takes place Spermatogenesis takes about 74 days together with transportation, a total of about 3 months elapses before sperm are ejaculated The sperm achieve motility during their passage through the epididymis sperm capacitation which render them capable of fertilization in vivo does not occur until they are removed from the seminal plasma after ejaculation. Those sperm that do penetrate the cervical os are directed along channels of lower viscosity mucus into the cervical crypts where they are stored for later ascent Uterine contractions probably facilitated by PG in the seminal plasma propel the sperm to the tubes within 5 minutes. Capacitation is the physiological change that sperm must undergo in the female reproductive tract before fertilization The acrosome reaction is the principal components of capacitation, the acrosome is a modified lysosome lies over the sperm head( as a kind of chemical drill-bit) It is designed to enable the sperm to burrow its way into the oocyte Following penetration of the oocyte, the male pronucleus which approaches and finally fuses with the female pronucleus to form the zygot Fertilization restore the diploid number of chromosomes and determine the sex of the zygot. Cleavage, Morula& blastocyst Following fertilization, cleavage occurs, this consist of rapid succession of mitotic divisions that produce a mulberry like mass known as morula. Fluid is secreted by the outer cells of the morula & a single fluid filled cavity develops, known as the blastocyst cavity. An inner cell mass can be identified attached eccentrically to the outer layer of flattened cells; the latter become the trophoblast . The embryo at this stage of development is called the blastocyst. Implantation: The fertilized ovum reaches the endometrial cavity about 3 days after ovulation this occurs under the hormonal (estrogen and progesterone) and the ciliary motility of the fallopian tube. Initial embryonic development primarily occurs in the ampullary portion of the fallopian tube, with subsequent rapid transit through the isthmus this process takes about 3 days On reaching the uterine cavity, the embryo undergo further development for 2-3 days before implanting The blastocyst adheres to the endometrium & a variety of proteolytic enzymes may play a role in separating the endometrial cells and digesting the intercellular matrix. The wall of the blastocyst facing the uterine lumen consist of a single layer of flattened cells. The thicker opposite wall has two zones; The trophoblast & inner cell mass (embryonic disk) the latter then differentiate into a thick plate of primitive (dorsal) ectoderm and the underlying layer of (ventral) endoderm. A small cells appear between the embryonic disk and trophoblast and the space develop within them, which become the amniotic cavity Under the effect of progesterone decidual changes occu in the endometrium of the pregnant uterus. Which is thickened to a depth of 5 to 10 mm The decidua basalis directly beneath the site of implantation The decidua capsularis overlying the developing ovum The decidua vera (parietalis) the remaining lining of the uterine cavity The space between the decidua capsularis and decidua vera is obliterated by 4th month with fusion of capsularis and vera The decidua basalis is invaded extensively by trophoblastic giant cells which appears as early as the time of implantation At about 9th days, lacunae, irregular fluid filled spaces appears within a thickened trophoblastic syncytium this is soon followed by the appearance of the maternal blood within the lacunae as maternal tissue is destroyed and the wall of the maternal capillaries are eroded