* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 28 Color
Thomas Young (scientist) wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Dispersion staining wikipedia , lookup
Anti-reflective coating wikipedia , lookup
Retroreflector wikipedia , lookup
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Transparency and translucency wikipedia , lookup
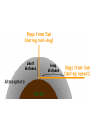
Chapter 28 Color Spectrum: The spread of colors seen when light is passed through a prism or diffraction gradient. That is, when light of that particular wavelength strikes the retina of our eye, we perceive that specific color sensation. Each individual wavelength within the spectrum of visible light wavelengths is representative of a particular color. When all the wavelengths of the visible light spectrum strike your eye at the same time, white is perceived. White light: Light that is a combination of all colors. Like sun light. White is not a color but a combination of all colors. Black is also not a color but the absence of the wavelengths of the visible light spectrum. So when you are in a room with no lights and everything around you appears black, it means that there are no wavelengths of visible light striking your eye as you sight at the surroundings. The way we see color is by the reflection of color off of a surface. The colors that we see are reflected off a surface while the other colors are absorbed by the surface. You look at a flower and see a green stem. The stem absorbs all other colors and reflects green. Pigment: material that selectively absorbs colored light. A red piece of class appears red because it absorbs all the colors that compose white light, except red, which it transmits. If an object absorbs all of the frequencies of visible light except for the frequency associated with green light, then the object will appear green Additive Primary Colors: Any three colors (or frequencies) of light which produce white light Red, Green and Blue are the three primary colors of white light. Color television is based on the ability of the human eye to see combinations of the three colors as a variety of different colors. Pixels in the screen are set to be red, green or blue. Depending on how you adjust their brightness you will get different colors. Complementary Colors: When 2 colors are added together to produce white. Red and cyan = white green and magenta = white yellow and blue = white Mixing colored paints is different than mixing light. If you mix red and green paint you get brown. Paints do not reflect a single color of light. They reflect several colors. Color subtraction is on page 429 – 431. Read these pages. Why is the Sky Blue? The atmosphere is a gaseous sea which contains a variety of types of particles. The two most common are gaseous oxygen and nitrogen. These particles are very effective in scattering the higher frequency, lower wavelength portions of white light. Which means that Blue, Indigo, and violet are scattered. The lower frequency, longer wavelength waves are more likely to get through. This scattering of the higher frequencies of light illuminates the skies with light on the BIV end of the visible spectrum. Compared to blue light, violet light is most easily scattered by atmospheric particles; however, our eyes are more sensitive to light with blue frequencies. Thus, we view the skies as being blue in color. As you leave our atmosphere the particles in the air get fewer and fewer so less of the light is scattered so it will appear black. Like on the moon. Why are sunsets Red? Because when the sun is low in the sky it has more of our atmosphere to travel through allowing the lower frequency colors to be scattered also. During sunset hours, the light passing through our atmosphere to our eyes tends to be most concentrated with red and orange frequencies of light. For this reason, the sunsets have a reddish-orange hue Why is water greenish – blue? Read pages 435 - 436