* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download future_yuan
Survey
Document related concepts
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Feynman diagram wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Technicolor (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
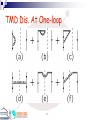
Semi-inclusive DIS: factorization Feng Yuan Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory RBRC, Brookhaven National Laboratory 7/7/2017 1 Outline Introduction Low PT region: TMD parton distributions and QCD factorization High PT region: quark-gluon-quark correlation (ETQS mechanism) Summary 2 Inclusive and Semi-inclusive DIS Inclusive DIS: Partonic Distribution depending on the longitudinal momentum fraction Semi-inclusive DIS: Probe additional information for parto transverse distribution in nucleon 3 Different PT Region Integrate out PT -- similar to inclusive DIS, probe int. PDF Large PT (~QCD) -- hard gluon radiation, can be calculated from perturbative QCD, Polarized ->q-g-q correlations Low PT (~QCD) -- nonperturbative information (TMD): new factorization formula 4 TMD Physics A way to measure Transversity Distribution, the last unkown leading twist distribution Collins 1993 The Novel Single Spin Asymmetries Connections with GPDs, and Quantum Phase Space Wigner distributions Quark Orbital Angular Momentum and Many others … 5 TMD Distribution: the definition Gauge Invariance requires the Gauge Link Brodsky,Hwang,Schmidt 02’ Collins 02’ 6 Belitsky,Ji,Yuan 02’ This definition is also consistent with the QCD factorization 7 Illustrate the Factorization (one-loop order) Take an on-shell quark target Calculate the TMD Dis. and F.F. Separate the cross section into different pieces Show the soft divergence is cancelled out 8 TMD Dis. At One-loop 9 No soft divergence Collinear divergence : ln(m2) Double Logarithms: ln2(2 b2) --- Collins-Soper equation 10 One-loop Factorization: virtual •Vertex corrections (single quark target) p′ p k Four possible regions for the gluon momentum k: 1) k is collinear to p (parton distribution) 2) k is collinear to p′ (fragmentation) 3) k is soft (Soft factor) 4) k is hard (pQCD correction) 11 One-Loop Factorization: real Gluon Radiation (single quark target) p′ k p Three reagions for the gluon momentum k: 1) k is collinear to p (parton distribution) 2) k is collinear to p′ (fragmentation) 3) k is soft (Soft factor) 12 All Orders in Perturbation Theory Consider an arbitrary Feynman diagram Find the singular contributions from different regions of the momentum integrations Power counting to determine the leading regions Factorize the soft (Grammer-Yennie) and collinear gluons (Ward Identity) Factorization theorem. (Collins, Soper, Sterman, Perturbative QCD, Mueller ed.) 13 Factorization Soft Factor SIR05 JLab 14 The Factorization Applies to Semi-inclusive DIS (polarized and unpolarized) Drell-Yan at Low transverse momentum Di-hadron production in e+e- annihilation (extract the Collins function) Many others, … Except for dijet-correlation at hadron colliders because of mixture of ISI and FSI effects Collins-Qiu, 07; Vogelsang-Yuan, 07; Mulders et al, 04-07 Heavy quarkonium production in pp collision, Yuan, 08 15 Power Counting at Large PT kt-even distributions have the same dependence on kt kt-odd distributions are suppressed at large kt Power Counting Rule kt-even: 1/kt2 kt-odd: 1/kt3 16 SIDIS: at Large PT Large PT SIDIS can be calculated from perturbative QCD (same for TMDs) Polarized scattering depends on the quark-gluon correlations in the nucleon Single Spin Asymmetry (Sivers and Collins) at large PT is not suppressed by 1/Q, but by 1/PT 17 A unified picture for SSA In DIS and Drell-Yan processes, SSA depends on Q and transverse-momentum P At large P, SSA is dominated by twist-3 correlation effects At moderate P, SSA is dominated by the transverse-momentum-dependent parton distribution/fragmentation functions The two mechanisms at intermediate P generate the same physics! Ji-Qiu-Vogelsang-Yuan,Phys.Rev.Lett.97:082002,2006 18 A difficulty at next-leadingpower (1/Q) Mismatch at low and high transverse momentum SIDIS at 1/Q Bacchetta-Boer-Diehl-Mulders, 0803.0227 The factorization needs to be carefully examined at this order Earlier works indicates possible problems Afanasev-Carlson, PRD, 2006 Gamberg-Hwang-Metz-Schlegel, PLB, 2006 7/7/2017 19 Transition from Perturbative region to Nonperturbative region? Nonperturbative TMD Perturbative region 20 Summary Semi-inclusive DIS provides important information on nucleon structure and opportunity to study the associated QCD dynamics QCD factorization and universality of the parton distributions are important aspects in these studies The PT dependence will provide us information for the perturbative to nonperturbative transition of QCD 21