* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Characteristics of Stars
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Fermi paradox wikipedia , lookup
Gamma-ray burst wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Space Interferometry Mission wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Star catalogue wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
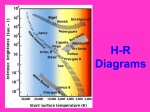
Characteristics of Stars What is a galaxy? It is a cluster of stars (hundreds of billions of stars) Our solar system is located in the Milky Way Galaxy * Our galaxy is named the Milky Way because of it’s white milky color. Not because of the candy bar!!!! What is the Universe? All of space and everything in it!!!! Consists of billions of galaxies. Most of the Universe is empty space, due to everything being soooooo far apart! Distances to Stars Instead of using kilometers, astronomers use a unit called light-year. A light year is the distance light travels in one year or 9.5 million million kilometers. * If we wanted to travel to the center of the Milky Way it would take 25,000 years traveling at the speed of light. That is a distance of 250 million billion kilometers. Measuring Distances to Stars Parallax- apparent change in position of an object when you look at it from different places. (Thumb example) Astronomers use the parallax shift to measure distance to stars: First they observe a star & then observe it again 6 months later. The less the star moved the further away it is The more the star moved the closer it is Classifying Stars Three main characteristics: Size Temperature Brightness Size Color & Temperature A star’s color reveals its temperature: Stars that are red are the coolest (3,200 degrees Celsius) Betelgeuse Stars that glow blue-white are the hottest (15,000 degrees Celsius) Rigel Brightness Brightness of a star depends on its temperature and size. How bright a star is also depends on its distance from Earth. Brightness is described in two different ways: Apparent magnitude Absolute magnitude Brightness Apparent Magnitude Brightness as seen from Earth. Ex. Sun looks very bright but this does not mean the sun gives off more light than other stars. It just means it is closer to Earth. Absolute Magnitude Brightness a star would have if it were at a standard distance from Earth Astronomers determine the apparent magnitude and distance from Earth in order to calculate the absolute magnitude Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram