* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download EU is an intergovernmental and supranational
Global financial system wikipedia , lookup
Withdrawal from the European Union wikipedia , lookup
European integration wikipedia , lookup
Protectionism wikipedia , lookup
North American Union wikipedia , lookup
World government wikipedia , lookup
Developmental state wikipedia , lookup
Development theory wikipedia , lookup
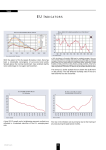
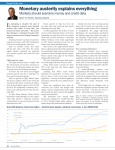
International Economic Organizations Professor Moon Hiwhoa European Union (EU) Siyuan Chen Rie Domon Martina Olund Joe Phillips Kensie Kim Sul Woojung 2006. 05. 24 Overview of European Union • EU is an intergovernmental and supranational institution with 25 democratic member states on the European continent. • Since 1952, EU has grown from 6 to 25 members. Founding members: Belgium, Germany, France, Italy, Luxembourg, and the Netherlands. -1981: -1986: -1995: -2004: Greece Spain and Portugal Austria, Finland, and Sweden Czech Republic, Estonia, Cyprus, Latvia, Lithuania, Hungary, Malta, Poland, Slovakia, and Slovenia -2007: Romania and Bulgaria ??? Overview Cont. • Europe day : 9th May • Europe motto : United in Diversity • Europe flag : EU Objective • The overall objective is economic integration that generates jobs and sustainable growth. Customs Union, 1968 Single market, 19861992 Economic Integration Economic and Monetary Union, 1990-99 The Euro • The currency for 12 EU countries. • Maastricht criteria. • Efficient and convenient trade and travel. • Reserve currency. Governing Institutions Council of Ministers • EU laws and budget • Presidency shifts between members every six month • Secretary General – Javier Solana, Spain The European Parliament • The world’s only international elected assembly, 732 representatives • Monitors the Commission and decides on EU laws and budget • President – Josep Borrell Fontelies, Spain European Commission • Largest EU institution, 25 commissioners • Propose and implement new law • President – José Manuel Barroso, Portugal Economic Institutions The European Central Bank (ECB) • EU’s monetary policy including the Euro • Primary role pruchasing power of the Euro and price stability (2%) • Set interest rates • President – Jean-Claude Trichet, France The European Investment Bank (EIB) • Financing capital investments for Europe’s economic integration • EU states provide the capital • President – Philippe Maystadt, Belgium The European Investment Fund (EIF) • Provides capital and guarantees for the development of SME’s within the EU and candidate countries Priority Issues EU Objectives As outlined in Article 2 of Treaty on European Union High level of employment. Sustainable and non-inflationary growth. Lisbon Strategy Refocused agenda March 2004 “Growth and Jobs” • Targets: • overall employment rate of 70% by 2010 • employment rate for women of over 60% • employment rate of 50% among older workers • annual economic growth of around 3% Growth & Jobs Methodology • an effective internal market • free & fair trade • better regulation • improvement in European infrastructure • investment in R&D • more innovation • a strong industrial base • more and better jobs • an adaptable workforce • better education and skills Sustainable Development Overarching concept of EU. In tandem with Lisbon Strategy and all EU policies. Key challenges (2005) • • • • • • • climate change and clean energy public health threats social exclusion demography and migration management of natural resources sustainable transport global poverty and development ECB objectives Primary objective: to maintain price stability. Other objectives: • • • Setting benchmark interest rate Managing the Euro area’s foreign exchange reserves Ensuring smooth movement of payments across all EU border (as opposed to only within the Euro area) • Managing TARGET (the real-time network for large payments transactions, to help the financial markets work efficiently) Single Euro Payment Area 2010 SEPA: system where all forms of cross-border Euro payments charged only as much as domestic payments cross-border payments and transfers become faster, cheaper, more efficient. ie. previous limit for credit transfers treated like domestic payments €12,500 expanded to €50,000 on January 1, 2006. Evaluation of the Euro From its first stage, the euro has been criticized that the unified currency would bring the structural problem. Because the EU has composed of nation states which have different economic, social and political systems. The current concerns The unitary financial policies are determined by the European Central Bank. 1. each country can not introduce the active economic policies which meet its domestic economic or social systems. 2. High social standards has prevented those nations from developing c.f. the backward nations have got more benefits rather than the advanced nations. 3. Inflation and deflation are occurred at the same time. The EU’s Common Agricultural policies The initial objectives of the CAP : 1. Providing farmers with a reasonable standard of living. 2. Consumers with safe and quality food at fair prices. 3 Making a unified-stable market. 4. Increasing productivities in the member countries. The CAP’s three principle mechanisms Import tariffs towards non-member’s countries. Internal intervention price. Agricultural subsidies. Criticism of the CAP’s policies Artificially high food prices Disproportionate benefits among EU nations New members with large agricultural sectors These results are against the initial aims. European Central Bank Conservative Monetary Policy Article 2 Mandate (Treaty of European Union) - Price stability highest priority Inflation rate = below, but near 2% European Central Bank Conservative Monetary Policy Criticism: “Excessive” focus on price stability -Exclusion of growth and employment considerations. Economic growth = approximately 2% a year - Relatively high unemployment = above 8% European Central Bank Conservative Monetary Policy Single central bank = appropriate monetary policy for increasingly varied region? • More developed members need monetary stimulus. • Others have property “bubbles”. • Less developed members combating inflation. • Expansion increasing economic variance. European Central Bank Independence • No direction from EU governing bodies or member governments. • Governors five year terms. • Executive board members 8-year terms (non-renewable). • Capital from the euro area banks. European Central Bank Independence Accountability to a democratic society? - Connected to human rights/environment? ECB secretive? - Internal meetings not public. - Comments on proposed decisions not invited, not published. - No direct citizen comments after decisions and actions. Service Directive Movement of Labor Service = 60%-70% of EU’s economy - 60% of jobs EU commission proposed the service directive - Open trade in service economy. - “Country of origin” rule = Service providers temporarily operate in other markets under laws of provider’s home country. - Must justify all regulations: necessary, proportional and nondiscriminatory. Service Directive Movement of Labor Opposition - Weaken individual state protections. - “Race to the bottom”. -Companies relocate to lower cost, less regulated eastern European members. Service Directive Movement of Labor Final version = some liberalism -“Economic needs” tests eliminated. • Foreign providers not required to prove would not destabilize local economy. - Business: no particular legal form. - Business: no particular language. -Complete formalities for cross-border business on- line/single contact point. - Authorization schemes = transparent and clear. Service Directive Movement of Labor Final version = some liberalism removed - “Country of origin” principle removed. • Host countries can impose requirements on foreign firms to protect public policy, security, health, environment and to enforce rules for employment conditions. • European Court of Justice will develop the field. -Excludes temporary work agencies, healthcare, taxation, security and social services relating to housing, childcare and support for families. Service Directive Movement of Labor Portent of future? Britain: may not open its labor market to Bulgarian/Romanian worker. - Poll: 76% of British = must be annual limit on immigrants. Czech Republic: might restrict access by Bulgarian and Romanian workers. Service Directive Movement of Labor • Barriers fully maintained: Austria, Germany. • Subject to restrictions: Czech Republic, Estonia, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Slovakia and Slovenia. • Barriers lifted: Finland, Greece, Ireland, Portugal, Spain, Sweden and UK “Economic Patriotism” Movement of Capital EU’s goal = few or no barriers to investment. Utility industries - Direct competition difficult. - So, competition through takeovers. - But, “Patriotic investment” inhibiting capital’s flow? “Economic Patriotism” Movement of Capital French government - Right to veto cross-border deals in “strategic sectors”. - Permitted merger between two French utilities = Discouraged takeover by Italian company. - Allowed French companies to repel takeovers by diluting capital. - Opposed Netherlands-based Mittal Steel’s takeover of Luxembourg’s Arcelor. “Economic Patriotism” Movement of Capital Spain - Laws protect national electricity champion, Endesa Britain - Considering changing merger law. - Prevent takeover of major gas supplier, Centrica, by the Russian state gas monopoly, Gazprom • Gazprom threatened to shift gas supplies. “Economic Patriotism” Movement of Capital Austria -Austrian region prevented takeover of regional bank by Ukrainian consortium. Poland - Blocked takeover of local bank by Italy’s UniCredit. “Economic Patriotism” Movement of Capital Finance minister Kari-Heinz Grasser of Austria: - “Continuing protectionism is one of the reasons for the current levels of unemployment in our countries” Conclusion EU: Path & Obstacles to Integration Unprecedented – Unequaled economic integration. Bore peace and prosperity. Integration reaching limits? Union fracturing? Thank you !