* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Water Introduction PPT
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
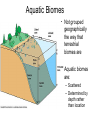
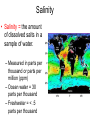
Water Earth’s Hydrosphere • Hydrosphere = all the parts of the earth that are made up of water – Oceans, Lakes, Rivers – Underground water, clouds The Hydrosphere • More than 70% of Earth’s surface is covered by water. • > 97% of the hydrosphere is salt water – Oceans – Salt Lakes (Great Salt Lake in Utah) • Salt water = Water that contains dissolved salts – 35 g of salt/liter of ocean water Fresh Water • Less dissolved salt than salt water • Lakes, ponds, streams & underground water • <3% of the hydrosphere – >2/3 = frozen glaciers and ice caps Fresh Water • Surface water = water in lakes, streams, and rain runoff • Ground water = found beneath the surface of the earth – Moves more easily through rock layers that are porous – Aquifer = an underground layer of porous rock that contains water Aquifers • Sometimes flow between two layers of rock that water cannot seep through • Pressure accumulates – Water pressure – Weight of rock layer above water • Artesian Wells = wells in which water flows to the surface due to high pressure • Water contained in aquifers is replenished very slowly Aquatic Biomes Aquatic Biomes • Water covers more than 70% of earth. • Aquatic Habitat = a habitat in which organisms live in or on water. Aquatic Biomes • Not grouped geographically the way that terrestrial biomes are • Aquatic biomes are: – Scattered – Determined by depth rather than location Abiotic Factors • Abiotic factors which determine aquatic biomes and terrestrial biomes are not the same • Abiotic factors in terrestrial biomes: – Temperature – Rainfall Abiotic Factors: Aquatic Biomes • • • • Amount of dissolved salts in the water Depth of the water Rate of water flow Amount of dissolved oxygen in the water Salinity • Aquatic biomes can be divided into two main groups based on the amount of dissolved minerals in the water. – Saltwater – Freshwater • All water contains some dissolved salts and other minerals. – Saltwater contains more than freshwater. Salinity • Salinity = the amount of dissolved salts in a sample of water. – Measured in parts per thousand or parts per million (ppm) – Ocean water = 30 parts per thousand – Freshwater = < .5 parts per thousand Salinity • Brackish Water = water that is more saline than freshwater but less saline than ocean water. Ex: Where the Mississippi River meets the Gulf of Mexico – Common in river deltas and coastal marshes – Where fresh water meets the ocean Freshwater Salinity • Lakes, Ponds, Rivers • Exceptions = hypersaline (more saline than the ocean!) lakes – Great Salt Lake in Utah, Mono Lake in California – 40 parts per thousand Salinity vs. Density • Saltwater is denser than fresh water: – Salinity is tested using a hydrometer – Measures buoyancy (how much mass can float on the water) Temperature vs. Density • Warm water is less dense than cooler water – Water temperatures decrease & density increases at lower water depth zones Depth • Ecosystem is greatly influenced by the amount of sunlight that penetrates to the bottom. – Determines the type of plants that grow – Remember: producers (includes plants) form the base of the food web! Depth Zones • Photic Zone = the top layer of water, which receives enough sunlight for photosynthesis to occur – Depth of the photic zone depends upon the turbidity of the water – Open ocean - photic zone = up to 200 m deep Depth Zones • Aphotic Zone = below the photic zone, sunlight never reaches the aphotic zone – Only found in the ocean and deep lakes Depth Zones • Benthic Zone = The floor of a body of water – Ocean = supports microscopic decomposers & scavengers – Shallow freshwater = sunlight allows insect larvae, snails, catfish and turtles to survive